Large Delta T Thermal Cycling Induced Stress Accelerates Equilibrium and Transformation in Super DSS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
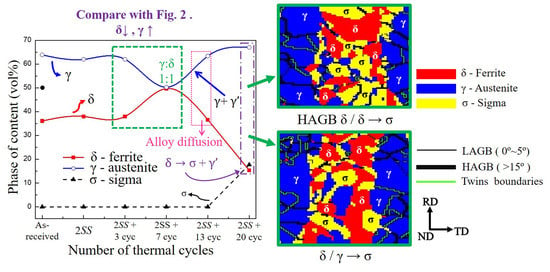
3.1. The Microstructure of XRD and EBSD
3.2. Misorientation Angle and KAM Analysis
3.2.1. Misorientation Angle Analysis
3.2.2. Kernel Average Misorientation (KAM) Analysis
3.3. Grain Orientation Variation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The volumes of the δ phase and the γ phase reached the ideal ratio of 1:1 at 2SS + 7 cycles, following the thermodynamic equilibrium. The grain boundary misorientation angles of most γ grains ranged between 53° and 63° and were not affected by the thermal cycles. In contrast, the misorientation angles of δ grains were widely distributed from 3° to 63°.
- The KAM value was affected by the thermal cycles, and its distribution of γ grain change was always significantly greater than that of the δ grains because of the γ recrystallization and twin formation.
- However, the most frequent orientation of δ varied from as-received <001> and <111> to <001> and <113> → <101> and <111> → <111> with few <112> → <001> → few <111> as the cycle numbers increased. This was attributed to the grain rotation during growth and the recrystallization of δ grains.
- In contrast, the most frequent orientation of the γ phase was stable and stayed at <315> orientation close to <101>.
- The σ formation generated a wider KAM angle distribution than did the γ and δ grains at 2SS + 20 cycles, representing the high local strain produced between σ and γ, or between σ and δ, or between σ and σ.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sahu, J.; Krupp, U.; Ghosh, R.; Christ, H.-J. Effect of 475 °C embrittlement on the mechanical properties of duplex stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 508, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chail, G.; Kangas, P. Super and hyper duplex stainless steels: Structures, properties and applications. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2016, 2, 1755–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varbai, B.; Májlinger, K. Physical and Theoretical Modeling of the Nitrogen Content of Duplex Stainless Steel Weld Metal: Shielding Gas Composition and Heat Input Effects. Metals 2019, 9, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tehovnik, F.; Arzensek, B.; Arh, B.; Skobir, D.; Pirnar, B.; Zuzek, B. Microstructure evolution in SAF 2507 super duplex stainless steel. Mater. Technol. 2011, 45, 339–345. [Google Scholar]
- Siegmund, T.; Werner, E.; Fischer, F. The irreversible deformation of a duplex stainless steel under thermal cycling. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1993, 169, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berecz, T.; Mészáros, I.; Szabó, P.J. Decomposition of the ferritic phase in isothermally aged SAF 2507 duplex stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Forum 2008, 589, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.; Kang, J. Effect of aging treatments on microstructure and impact properties of tungsten substituted 2205 duplex stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2000, 16, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balancin, O.; Hoffmann, W.A.M.; Jonas, J.J. Influence of microstructure on the flow behavior of duplex stainless steels at high temperatures. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2000, 31, 1353–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Nelson, T.; Sterling, C.; Steel, R.; Pettersson, C.O. Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded SAF 2507 super duplex stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 397, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fargas, G.; Mestra, A.; Mateo, A. Effect of sigma phase on the wear behavior of a super duplex stainless steel. Wear 2013, 303, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, N.; Kolts, J.; Flasche, L.H. A Duplex Stainless Steel for Chloride Environments. JOM 1985, 37, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Weng, K.; Yang, J. The effect of high-temperature exposure on the microstructural stability and toughness property in a 2205 duplex stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 338, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, E.; De Benedetti, B.; Rosalbino, F. Microstructural evolution and localized corrosion resistance of an aged superduplex stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2004, 46, 1351–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fargas, G.; Anglada, M.; Mateo, A. Effect of the annealing temperature on the mechanical properties, formability and corrosion resistance of hot-rolled duplex stainless steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 1770–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, J.-O.; Kangas, P.; Wilson, A.; Karlsson, T. Mechanical properties, microstructural stability and kinetics of σ-phase formation in 29Cr-6Ni-2Mo-0.38N superduplex stainless steel. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2000, 31, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-S.; Cheng, G.-J.; Yen, H.-W.; Yang, Y.-L.; Chang, H.-Y.; Wu, C.-Y.; Wang, S.-H.; Yang, J.-R. Microstrain and boundary misorientation evolution for recrystallized super DSS after deformation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 246, 122815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbadua, S.A.; Nezhad, H.Y.; Mgbemena, C.E.; Chima, L.O. Thermal cycling effects on the fatigue behaviour of low carbon steel. J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 2011, 10, 1345–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, T.; Kumar, B.R.; Singh, V. A Thermal Cycling Route for Processing Nano-grains in AISI 316L Stainless Steel for Improved Tensile Deformation Behaviour. Def. Sci. J. 2016, 66, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.R.; Das, S.; Sharma, S.; Sahu, J. Effect of thermal cycles on heavily cold deformed AISI 304L austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.R.; Mahato, B.; Sharma, S.; Sahu, J. Effect of cyclic thermal process on ultrafine grain formation in AISI 304L austenitic stainless steel. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2009, 40, 3226–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhara, T.; Kikumoto, K.; Saito, H.; Sekine, T.; Ogawa, T.; Morito, S.; Maki, T. Phase transformation from fine-grained austenite. ISIJ Int. 2008, 48, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sellars, C.M.; Whiteman, J.A. Recrystallization and grain growth in hot rolling. Met. Sci. 1979, 13, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokizane, M.; Ameyama, K.; Takao, K. Ultra-fine austenite grain steel produced by thermomechanical processing. Scr. Met. 1988, 22, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.S.; Cheng, G.J.; Yen, H.W.; Wu, L.T.; Yang, Y.L.; Wu, R.T.; Yang, J.R.; Wang, S.H. Thermal cycling induced stress–assisted sigma phase formation in super duplex stainless steel. Mater. Des. 2019, 182, 108003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.R.; Gujral, A. Plastic deformation modes in Mono- and bimodal-type ultrafine-grained austenitic stainless steel. Met. Microstruct. Anal. 2014, 3, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, H.; Najafizadeh, A. Fabrication of the ultrafine grained low carbon steel by cold compression and annealing of martensite. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2015, 69, 1467–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellicia, D.M.; Sutarsis; Kurniawan, B.A.; Wulanari, D.; Purniawan, A.; Wibisono, A.T. Study of sigma phase in duplex SAF 2507. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 202, 12039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghaemifar, S.; Mirzadeh, H. Refinement of banded structure via thermal cycling and its effects on mechanical properties of dual phase steel. Steel Res. Int. 2018, 89, 1700531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trusov, P.V.; Kondratev, N.S. Crystal plasticity modeling of duplex steels at high temperatures. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1040, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, J.; Frommeyer, G.; Carsí, M.; Ruano, O.A. Superplastic properties of a δ/γ stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 307, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, T.; Furuhara, T.; Tsuzaki, K. Microstructure development by thermomechanical processing in duplex stainless steel. ISIJ Int. 2001, 41, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinlong, L.; Tongxiang, L.; Chen, W.; Limin, D. Effect of ultrafine grain on tensile behaviour and corrosion resistance of the duplex stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 62, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eghlimi, A.; Shamanian, M.; Eskandarian, M.; Zabolian, A.; Nezakat, M.; Szpunar, J.A. Evaluation of microstructure and texture across the welded interface of super duplex stainless steel and high strength low alloy steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 264, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhara, T.; Maki, T. Variant selection in heterogeneous nucleation on defects in diffusional phase transformation and precipitation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 312, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, H.H.; Sandim, H.R.Z.; Zilnyk, K.D.; Verlinden, B.; Raabe, D. Microstructural stability of a niobium single crystal deformed by equal channel angular pressing. Mater. Res. 2017, 20, 1238–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saraf, L. Kernel average misorientation confidence index correlation from FIB sliced Ni-Fe-Cr alloy surface. Microsc. Microanal. 2011, 17, 424–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tayon, W.; Crooks, R.; Domack, M.; Wagner, J.; Elmustafa, A.A. EBSD study of delamination fracture in Al–Li alloy 2090. Exp. Mech. 2008, 50, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcagnotto, M.; Ponge, D.; Demir, E.; Raabe, D. Orientation gradients and geometrically necessary dislocations in ultrafine grained dual-phase steels studied by 2D and 3D EBSD. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 2738–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiyama, K.; Mori, K.; Matsunaga, T.; Kimachi, H.; Saito, T.; Hino, T.; Ishii, R. Creep-damage assessment of high chromium heat resistant steels and weldments. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 510, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hsu, E.; Szpunar, J.; Utsunomiya, H.; Sakai, T. Deformation mechanism and texture and microstructure evolution during high-speed rolling of AZ31B Mg sheets. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 7148–7156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Ji, J.H.; Hwang, S.W.; Park, K.-T. TRIP aided deformation of a near-Ni-free, Mn–N bearing duplex stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 535, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.I.; Nowell, M.M.; De Kloe, R.; Chan, L. Orientation precision of electron backscatter diffraction measurements near grain boundaries. Microsc. Microanal. 2014, 20, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, F.V.; Escobar, D.P.; De Oliveira, N.J.L.; Andrade, M.S. Hot deformation behavior of a ferritic stainless steel stabilized with Nb during hot rolling simulation at different temperature ranges. J. Mater. Res. 2016, 31, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.P.; Chen, D.; Kuo, J.C. Grain Boundary Evolution of Cold-Rolled FePd Alloy during Recrystallization at Disordering Temperature. Materials 2015, 8, 3254–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.P.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, D.; Kuo, J.C. Effect of cold deformation on the recrystallization behavior of FePd alloy at the ordering temperature using electron backscatter diffraction. Mater. Charact. 2014, 94, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.S.; Kokawa, H. Preferential precipitation site of sigma phase in duplex stainless steel weld metal. Scr. Mater. 1999, 40, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shockley, J.M.; Horton, D.J.; Wahl, K. Effect of aging of 2507 super duplex stainless steel on sliding tribocorrosion in chloride solution. Wear 2017, 380, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, D.M.E.; Junior, F.C.P.; Plaut, R.L.; Padilha, A.F. Comparative study on sigma phase precipitation of three types of stainless steels: Austenitic, superferritic and duplex. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2006, 22, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maetz, J.Y.; Cazottes, S.; Verdu, C.; Kleber, X. Precipitation and phase transformations in 2101 lean duplex stainless steel during isothermal aging. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 47, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahay, S.S.; Joshi, K.B. Heating rate effects during non-isothermal annealing of AlK steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2003, 12, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nye, J. Some geometrical relations in dislocated crystals. Acta Met. 1953, 1, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, M.F. The deformation of plastically non-homogeneous materials. Philos. Mag. 1970, 21, 399–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| C | Cr | Ni | Mo | Mn | Si | Cu | N | P | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 24.8 | 6.25 | 3.74 | 0.62 | 0.43 | 0.33 | 0.243 | 0.02 | Bal. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, P.-J.; Chen, S.-C.; Yen, H.-W.; Chang, H.-Y.; Yang, J.-R.; Wang, S.-H.; Chiu, P.-K.; Lin, T.-R. Large Delta T Thermal Cycling Induced Stress Accelerates Equilibrium and Transformation in Super DSS. Crystals 2020, 10, 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10110962
Yu P-J, Chen S-C, Yen H-W, Chang H-Y, Yang J-R, Wang S-H, Chiu P-K, Lin T-R. Large Delta T Thermal Cycling Induced Stress Accelerates Equilibrium and Transformation in Super DSS. Crystals. 2020; 10(11):962. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10110962
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Ping-Jui, Shih-Che Chen, Hung-Wei Yen, Horng-Yi Chang, Jer-Ren Yang, Shing-Hoa Wang, Po-Kai Chiu, and Tzy-Rong Lin. 2020. "Large Delta T Thermal Cycling Induced Stress Accelerates Equilibrium and Transformation in Super DSS" Crystals 10, no. 11: 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10110962
APA StyleYu, P. -J., Chen, S. -C., Yen, H. -W., Chang, H. -Y., Yang, J. -R., Wang, S. -H., Chiu, P. -K., & Lin, T. -R. (2020). Large Delta T Thermal Cycling Induced Stress Accelerates Equilibrium and Transformation in Super DSS. Crystals, 10(11), 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10110962