Enhancing Protein Crystallization under a Magnetic Field
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
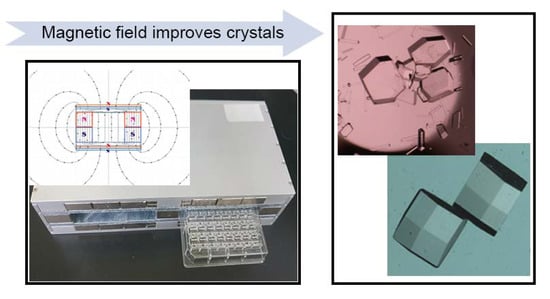
2.1. Magnetic Device Design
2.2. Cloning, Expression, Purification, and Crystallization
2.2.1. Hen Egg-White Lysozyme (HEWL)
2.2.2. Enoyl Acyl Carrier Protein Reductase (ENR)
2.3. X-ray Diffraction and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Hen Egg-White Lysozyme (HEWL)
3.1.1. Crystal Growth and Morphology
3.1.2. Comparison of Diffracting HEWL Crystals
3.2. Enol Acyl Reductase Carrer Protein (ENR))
3.2.1. Crystal Growth and Morphology
3.2.2. Comparison of Diffracting ENRG93V Crystals
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamilton, W.C.; Ibers, J.A. Hydrogen Bonding in solids; Methods of Molecular Structure Determination; W.A. Benjamin: New York, NY, USA, 1968; pp. 1–284. [Google Scholar]
- Chayen, N.E.; Helliwell, J.R.; Snell, E.H. Macromolecular Crystallization and Crystal Perfection; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.H.; Suh, S.W.; Song, H.K. A cytosine modification mechanism revealed by the structure of a ternary complex of deoxycytidylate hydroxymethylase from bacteriophage T4 with its cofactor and substrate. IUCRJ 2019, 6, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, B.; Haddad, M.; Maley, F.; Jensen, J.H.; Kohen, A. Hydride transfer versus hydrogen radical transfer in thymidylate synthase. J. Am. Chem Soc. 2006, 128, 5636–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, R.; Yang, H.; He, J.; Zhu, W. The effects of magnetic fields on water molecular hydrogen bonds. J. Mol. Struct. 2009, 938, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-T.; Weng, C.-I. The effect of an external magnetic field on the structure of liquid water using molecular dynamics simulation. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, P.D.; Afonine, P.V.; Baskaran, K.; Berman, H.M.; Berrisford, J.; Bricogne, G.; Brown, D.G.; Burley, S.K.; Chen, M.; Feng, Z.; et al. Announcing mandatory submission of pdbx/mmcif format files for crystallographic depositions to the protein data bank (PDB). Acta Cryst. D Struct Biol. 2019, 75, 451–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burley, S.K.; Berman, H.M.; Kleywegt, G.J.; Markley, J.L.; Nakamura, H.; Velankar, S. Protein data bank (PDB): The single global macromolecular structure archive. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1607, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeda, M.; Miyanoiri, Y.; Terauchi, T.; Yang, C.J.; Kainosho, M. Use of h/d isotope effects to gather information about hydrogen bonding and hydrogen exchange rates. J. Magn. Reson. 2014, 241, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, E.A.; Benhaim, M.A.; Lee, K.K. Bridging protein structure, dynamics, and function using hydrogen/deuterium-exchange mass spectrometry. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 843–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.C. The evolution of hydrogen atom parameters under changing external conditions by time-of-flight single crystal neutron diffraction. Crystallogr. Rev. 2007, 13, 143–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, Y.; Hosoya, T.; Ohhara, T. Hydrogen migration mechanism in crystalline-state photoisomerization by analyzed neutron diffraction. Crystallogr. Rev. 2006, 12, 83–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebschner, D.; Afonine, P.V.; Moriarty, N.W.; Langan, P.; Adams, P.D. Evaluation of models determined by neutron diffraction and proposed improvements to their validation and deposition. Acta Cryst. D Struct. Biol. 2018, 74, 800–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorrec, F. Protein crystallization screens developed at the mrc laboratory of molecular biology. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carter, C.W., Jr.; Carter, C.W. Protein crystallization using incomplete factorial experiments. J. Biol. Chem. 1979, 254, 12219–12223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cox, M.J.; Weber, P.C. An investigation of protein crystallization parameters using successive automated grid searches (sags). J. Cryst. Growth 1988, 90, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luft, J.R.; Wolfley, J.R.; Said, M.I.; Nagel, R.M.; Lauricella, A.M.; Smith, J.L.; Thayer, M.H.; Veatch, C.K.; Snell, E.H.; Malkowski, M.G.; et al. Efficient optimization of crystallization conditions by manipulation of drop volume ratio and temperature. Protein Sci. 2007, 16, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.-K.; Yin, D.-C.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Lu, Q.-Q.; Guo, Y.-Z.; Guo, W.-H. Effect of temperature programmes on protein crystallisation. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2010, 45, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Sazaki, G.; Tamura, K.; Sawada, T.; Nakajima, K. Effects of high pressure on the solubility and growth kinetics of monoclinic lysozyme crystals. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2004, 50, 329–334. [Google Scholar]
- Hammadi, Z.; Veesler, S. New approaches on crystallization under electric fields. Prog. Biophys Mol. Biol. 2009, 101, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Haq, M.I.; Lebrasseur, E.; Choi, W.K.; Tsuchiya, H.; Torii, T.; Yamazaki, H.; Shinohara, E. An apparatus for electric-field-induced protein crystallization. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Haq, M.I.; Lebrasseur, E.; Tsuchiya, H.; Torii, T. Protein crystallization under an electric filed. Crystallogr. Rev. 2007, 13, 29–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Boggon, T.J.; Chayen, N.E.; Raftery, J.; Bi, R.C.; Helliwell, J.R. Bound-solvent structures for microgravity-, ground control-, gel- and microbatch-grown hen egg-white lysozyme crystals at 1.8 a resolution. Acta Cryst. D Biol. Cryst. 1999, 55, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, H.; Uda, S.; Fujiwara, K.; Nozawa, J. Control of effect on the nucleation rate for hen egg white lysozyme crystals under application of an external ac electric field. Langmuir 2011, 27, 8333–8338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, D.C.; Wakayama, N.I.; Inatomi, Y.; Huang, W.D.; Kuribayashi, K. Strong magnetic field effect on the dissolution process of tetragonal lysozyme crystals. Gravit. Eff. Phys. Chem. Process. 2003, 32, 217–223. [Google Scholar]
- Sazaki, G. Crystal quality enhancement by magnetic fields. Prog. Biophys Mol. Biol. 2009, 101, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pareja-Rivera, C.; Cuéllar-Cruz, M.; Esturau-Escofet, N.; Demitri, N.; Polentarutti, M.; Stojanoff, V.; Moreno, A. Recent advances in the understanding of the influence of electric and magnetic fields on protein crystal growth. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 17, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.-C. Protein crystallization in a magnetic field. Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. Mater. 2015, 61, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, E.J.L.; Ramalho, T.C.; Magriotis, Z.M. Influence of magnetic field on physical–chemical properties of the liquid water: Insights from experimental and theoretical models. J. Mol. Struct. 2008, 888, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagiya, S.; Sazaki, G.; Durbin, S.D.; Miyashita, S.; Nakajima, K.; Komatsu, H.; Watanabe, K.; Motokawa, M. Effects of a magnetic field on the growth rate of tetragonal lysozyme crystals. J. Cryst. Growth 2000, 208, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Z.; Yin, D.C.; Cao, H.L.; Shi, J.Y.; Zhang, C.Y.; Liu, Y.M.; Huang, H.H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, W.H.; et al. Evaporation rate of water as a function of a magnetic field and field gradient. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 16916–16928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gavira, J.A.; Garcia-Ruiz, J.M. Effects of a magnetic field on lysozyme crystal nucleation and growth in a diffusive environment. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 2610–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.-C.; Lu, H.-M.; Geng, L.-Q.; Shi, Z.-H.; Luo, H.-M.; Li, H.-S.; Ye, Y.-J.; Guo, W.-H.; Shang, P.; Wakayama, N.I. Growing and dissolving protein crystals in a levitated and containerless droplet. J. Cryst. Growth 2008, 310, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataka, M.; Katoh, E.; Wakayama, N.I. Magnetic orientation as a tool to study the initial stage of crystallization of lysozyme. J. Cryst. Growth 1997, 173, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.W.; Wakayama, N.I.; Ataka, M. Magnetic suppression of convection in protein crystal growth processes. J. Cryst. Growth 2001, 232, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saijo, S.; Yamada, Y.; Sato, T.; Tanaka, N.; Matsui, T.; Sazaki, G.; Nakajima, K.; Matsuura, Y. Structural consequences of hen egg-white lysozyme orthorhombic crystal growth in a high magnetic field: Validation of x-ray diffraction intensity, conformational energy searching and quantitative analysis of b factors and mosaicity. Acta Cryst. D Biol. Cryst. 2005, 61, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, T.; Yamada, Y.; Saijo, S.; Hori, T.; Hirose, R.; Tanaka, N.; Sazaki, G.; Nakajima, K.; Igarashi, N.; Tanaka, M.; et al. Enhancement in the perfection of orthorhombic lysozyme crystals grown in a high magnetic field (10 T). Acta Cryst. D Biol. Cryst. 2000, 56, 1079–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sazaki, G.; Yoshida, E.; Komatsu, H.; Nakada, T.; Miyashita, S.; Watanabe, K. Effects of a magnetic field on the nucleation and growth of protein crystals. J. Cryst. Growth 1997, 173, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, E.; Magazù, S. Electromagnetic fields effects on the secondary structure of lysozyme and bioprotective effectiveness of trehalose. Adv. Phys. Chem. 2012, 2012, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okutsu, T.; Furuta, K.; Terao, M.; Hiratsuka, H.; Yamano, A.; Ferte, N.; Veesler, S. Light-induced nucleation of metastable hen egg-white lysozyme solutions. Cryst. Growth Des. 2005, 5, 1393–1398. [Google Scholar]
- Russo Krauss, I.; Merlino, A.; Vergara, A.; Sica, F. An overview of biological macromolecule crystallization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 11643–11691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, B.G.; Kim, M.K.; Song, H.K. Structural insights into the conformational diversity of clpp from bacillus subtilis. Mol. Cells 2011, 32, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.G.; Park, E.Y.; Lee, K.E.; Jeon, H.; Sung, K.H.; Paulsen, H.; Rubsamen-Schaeff, H.; Brotz-Oesterhelt, H.; Song, H.K. Structures of clpp in complex with acyldepsipeptide antibiotics reveal its activation mechanism. Nat. Struct Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, D.H.; Park, O.H.; Kim, L.; Jung, Y.O.; Park, Y.; Jeong, H.; Hyun, J.; Kim, Y.K.; Song, H.K. Insights into degradation mechanism of n-end rule substrates by p62/sqstm1 autophagy adapter. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Q.; Gruner, S.M.; Kim, C.U.; Mao, Y.; Wu, X.; Szebenyi, D.M. Reduction of lattice disorder in protein crystals by high-pressure cryocooling. J. Appl. Cryst. 2016, 49, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.K.; Lomelino, C.L.; Avvaru, B.S.; Mahon, B.P.; McKenna, R.; Park, S.; Kim, C.U. Active-site solvent replenishment observed during human carbonic anhydrase ii catalysis. IUCRJ 2018, 5, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magay, E.; Cho, S.J.; Kim, S.A. Enhancing the volume and the optical quality of hen egg-white lysozyme crystals by coupling the salt concentration gradient crystallization method with a magnetic field. J. Appl. Cryst. 2012, 45, 1066–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suk-Youl, P.; Sung-Chul, H.; Yeon-Gil, K. The protein crystallography beamlines at the pohang light source ii. Biodesign 2017, 5, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Wlodawer, A.; Minor, W.; Dauter, Z.; Jaskolski, M. Protein crystallography for aspiring crystallographers or how to avoid pitfalls and traps in macromolecular structure determination. Febs J. 2013, 280, 5705–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Powell, H.R. X-ray data processing. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arndt, U.W.; Crowther, R.A.; Mallett, J.F.W. A computer-linked cathode-ray tube microdensitometer for x-ray crystallography. J. Phys. E-Sci. Instrum. 1968, 1, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Data Collection | Proteins | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEWL | ENR | |||
| Magnetic Strength (mT) | 0 | 200 | 0 | 200 |
| Diffraction source | 7A, PAL | 7A, PAL | 7A, PAL | 7A, PAL |
| Wavelength (Å) | 0.97935 | 0.97935 | 0.97933 | 0.97933 |
| Temperature (K) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Distance (mm) | 150 | 150 | 300 | 300 |
| Space group | P43212 | P43212 | P212121 | P212121 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 77.383 | 76.893 | 109.016 | 108.710 |
| 77.369 | 76.893 | 78.667 | 78.546 | |
| 37.032 | 36.975 | 113.883 | 119.951 | |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90.000 | 90.000 | 90.000 | 90.000 |
| 90.000 | 90.000 | 90.000 | 90.000 | |
| 90.000 | 90.000 | 90.000 | 90.000 | |
| Resolution range 1 (Å) (outer shell) | 50.0–1.78 | 50.0–1.08 | 50.0–2.56 | 50.0–2.27 |
| (1.81–1.78) | (1.10–1.08) | (2.60–2.56) | (2.31–2.27) | |
| No. of total reflections | 314,860 | 1,076,894 | 413,142 | 650,615 |
| Completeness (%) | 100 (100) | 93.3 (33.2) | 100 (99.9) | 100.0 (99.9) |
| 2 | 0.054 (0.115) | 0.089 (0.695) | 0.114 (0.315) | 0.139 (0.470) |
| 67.192 (22.444) | 36.846 (0.583) | 18.362 (5.500) | 21.567 (4.421) | |
| Mosaicity (°) | 0.622 | 0.333 | 0.650 | 0.398 |
| Redundancy | 14.4 (14.5) | 24.0 (2.0) | 7.6 (7.1) | 14.5 (11.5) |
| Protein | Magnetic Field (mT) | Number of Nucleation (Average) | Increasing Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| HEWL | 0 | 11.1 | +1.71 |
| 200 | 19.0 | ||
| ENR | 0 | 9.5 | +2.26 |
| 200 | 21.5 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryu, S.Y.; Oh, I.H.; Cho, S.J.; Kim, S.A.; Song, H.K. Enhancing Protein Crystallization under a Magnetic Field. Crystals 2020, 10, 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10090821
Ryu SY, Oh IH, Cho SJ, Kim SA, Song HK. Enhancing Protein Crystallization under a Magnetic Field. Crystals. 2020; 10(9):821. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10090821
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyu, Sun Young, In Hwan Oh, Sang Jin Cho, Shin Ae Kim, and Hyun Kyu Song. 2020. "Enhancing Protein Crystallization under a Magnetic Field" Crystals 10, no. 9: 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10090821
APA StyleRyu, S. Y., Oh, I. H., Cho, S. J., Kim, S. A., & Song, H. K. (2020). Enhancing Protein Crystallization under a Magnetic Field. Crystals, 10(9), 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10090821