Multi-Band Electromagnetically-Induced-Transparency Metamaterial Based on the Near-Field Coupling of Asymmetric Split-Ring and Cut-Wire Resonators in the GHz Regime
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
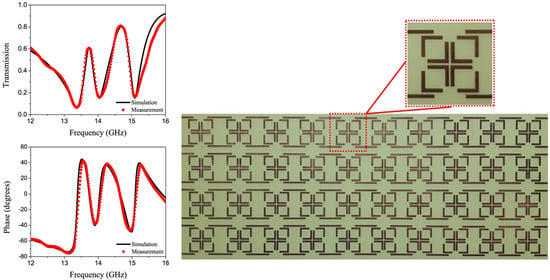
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Imamoğlu, A.; Boller, K.J.; Harris, S.E. Observation of electromagnetically induced transparency. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1991, 66, 2593–2596. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, S.E. Electromagnetically induced transparency. Phys. Today 1997, 50, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabinet, U.R.; Osuji, C.O. Optical materials and metamaterials from nanostructured soft matter. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 2172–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, L.; Tan, S.; Yahiaoui, R.; Yan, F.; Zhang, W.; Singh, R. Experimental demonstration of ultrasensitive sensing with terahertz metamaterial absorbers: A comparison with the metasurfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 031107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, A.; Erve, K.; Gerini, G. Ultra-narrowband polarization insensitive transmission filter using a coupled dielectric-metal metasurface. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 773–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souza, J.A.; Cabral, L.; Oliveira, R.R.; Villas-Boas, C.J. Electromagnetically-induced-transparency-related phenomena and their mechanical analogs. Phys. Rev. A 2015, 92, 023818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garrido Alzar, C.L.; Martinez, M.A.G.; Nussenzveig, P. Classical analog of electromagnetically induced transparency. Am. J. Phys. 2002, 70, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veselago, V.G. The electrodynamics of substances with simultaneously negative values of ε and μ. Usp. Fiz. Nauk 1968, 10, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendry, J.B.; Holden, A.J.; Stewart, W.J.; Youngs, I. Extremely low frequency plasmons in metallic mesostructures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 76, 4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pendry, J.B.; Holden, A.J.; Robbins, D.J.; Stewart, W.J. Magnetism from conductors and enhanced nonlinear phenomena. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1999, 47, 2075–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, D.R.; Padilla, W.J.; Vier, D.C.; Nemat-Nasser, S.C.; Schultz, S. Composite medium with simultaneously negative permeability and permittivity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Landy, N.I.; Sajuyigbe, S.; Mock, J.J.; Smith, D.R.; Padilla, W.J. Perfect metamaterial absorber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 207402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, B.S.; Khuyen, B.X.; Kim, Y.J.; Hwang, J.S.; Lam, V.D.; Chen, L.-Y.; Lee, Y.P. Manipulation of the near-field coupling in metamaterial for multi-band absorber. Waves Random Complex Media 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendry, J.B. Negative refraction makes a perfect lens. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblatt, G.; Orenstein, M. Perfect lensing by a single interface: Defying loss and bandwidth limitations of metamaterials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 195504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Park, Y.-S.; Li, J.; Lu, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X. Negative refractive index in chiral metamaterials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 023901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.; Liu, W.; Chun, Z.; Ling, Y.; Ding, J.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Li, H. Optical rotation and electromagnetically induced transparency in a chiral metamaterial with C4 symmetry. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 29496–29512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Teo, K.H.; Nishino, T.; Yerazunis, W.; Barnwell, J.; Zhang, J. Experiments on wireless power transfer with metamaterials. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 254101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pham, T.S.; Khuyen, B.X.; Tung, B.S.; Hoang, T.T.; Pham, V.D.; Ngo, Q.M.; Lam, V.D. Enhanced efficiency of asymmetric wireless power transmission using defects in 2D magnetic metamaterials. J. Electron. Mater. 2021, 50, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Genov, D.A.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, X. Plasmon-induced transparency in metamaterials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 047401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakanishi, T.; Otani, T.; Tamayama, Y.; Kitano, M. Storage of electromagnetic waves in a metamaterial that mimics electromagnetically induced transparency. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 161110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, W.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Yu, A.; Lu, W. Dynamic metamaterial based on the graphene split ring high-Q Fano-resonator for sensing applications. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 15196–15204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Lang, T.; Hong, Z.; Shen, C.; Shi, G. Comparison of electromagnetically induced transparency performance in metallic and all-dielectric metamaterials. J. Light. Technol. 2018, 36, 2083–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Takida, Y.; Minamide, H.; Hane, K.; Kanamori, Y. Actively tunable THz filter based on an electromagnetically induced transparency analog hybridized with a MEMS metamaterial. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, B.S.; Khuyen, B.X.; Linh, P.T.; Tung, N.T.; Manh, D.H.; Lam, V.D. Polarization-insensitive electromagnetically-induced transparency in planar metamaterial based on coupling of ring and zigzag spiral resonators. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2020, 34, 2050093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, P.; Liang, S.; Lan, F.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, T.; et al. Enhanced THz EIT resonance based on the coupled electric field dropping effect within the undulated meta-surface. Nanophotonics 2019, 8, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Z.; Yang, H.; Huang, X.; Xiang, T.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, Z. Electromagnetically induced transparency metamaterial with strong toroidal dipole response. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 035802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Kong, W. Actively mode tunable electromagnetically induced transparency in a polarization-dependent terahertz metamaterial. AIP Adv. 2020, 10, 045026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Xiao, Z.; Lv, F.; Cui, Z.; Xu, Q. Dynamically tunable dual-band electromagnetically induced transparency-like in terahertz metamaterial. Opt. Mater. 2020, 107, 110060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, J.; Han, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Chen, D.; Xu, S.; Xie, W. Actively tunable terahertz electromagnetically induced transparency analogue based on vanadium-oxide-assisted metamaterials. Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CST of America, Inc., 492 Old Connecticut Path, Suite 505, Framingham, MA 01701, USA. Available online: http://www.cst.com (accessed on 15 November 2020).
- Tung, B.S.; Khuyen, B.X.; Kim, Y.J.; Lam, V.D.; Kim, K.W.; Lee, Y.P. Polarization-independent, wide-incident-angle and dual-band perfect absorption, based on near-field coupling in a symmetric metamaterial. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, N.; Langguth, L.; Weiss, T.; Kästel, J.; Fleischhauer, M.; Pfau, T.; Giessen, H. Plasmonic analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency at the Drude damping limit. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Liu, X.; Mao, D. Plasmonic analog of electromagnetically induced transparency in multi-nanoresonator-coupled waveguide systems. Phys. Rev. A 2012, 85, 053803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nam, M.H.; Hanh, V.T.H.; Tuong, N.B.; Tung, B.S.; Khuyen, B.X.; Lam, V.D.; Chen, L.Y.; Lee, Y.P. Multi-Band Electromagnetically-Induced-Transparency Metamaterial Based on the Near-Field Coupling of Asymmetric Split-Ring and Cut-Wire Resonators in the GHz Regime. Crystals 2021, 11, 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11020164
Nam MH, Hanh VTH, Tuong NB, Tung BS, Khuyen BX, Lam VD, Chen LY, Lee YP. Multi-Band Electromagnetically-Induced-Transparency Metamaterial Based on the Near-Field Coupling of Asymmetric Split-Ring and Cut-Wire Resonators in the GHz Regime. Crystals. 2021; 11(2):164. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11020164
Chicago/Turabian StyleNam, Man Hoai, Vu Thi Hong Hanh, Nguyen Ba Tuong, Bui Son Tung, Bui Xuan Khuyen, Vu Dinh Lam, Liang Yao Chen, and Young Pak Lee. 2021. "Multi-Band Electromagnetically-Induced-Transparency Metamaterial Based on the Near-Field Coupling of Asymmetric Split-Ring and Cut-Wire Resonators in the GHz Regime" Crystals 11, no. 2: 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11020164
APA StyleNam, M. H., Hanh, V. T. H., Tuong, N. B., Tung, B. S., Khuyen, B. X., Lam, V. D., Chen, L. Y., & Lee, Y. P. (2021). Multi-Band Electromagnetically-Induced-Transparency Metamaterial Based on the Near-Field Coupling of Asymmetric Split-Ring and Cut-Wire Resonators in the GHz Regime. Crystals, 11(2), 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11020164