Improving the Solubility of Aripiprazole by Multicomponent Crystallization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Multicomponent Crystals
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Single Crystal X-ray Diffraction (SXRD)
2.3.2. Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD)
2.3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.4. Computational Studies
2.4.1. Acid Dissociation Constant (pKa)
2.4.2. Molecular Electrostatic Potential Surface (MEPS)
2.4.3. Hirshfeld Surface Analysis (HSA)
2.5. Powder Hygroscopicity
2.6. Stability Test
2.7. Solubility Experiment
2.7.1. Solubility Test
2.7.2. Intrinsic Dissolution Rate (IDR) Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
3.1.1. SXRD Analysis
3.1.2. PXRD Analysis
3.1.3. DSC Analysis
3.2. Theoretical Calculation
3.2.1. Acid Dissociation Constant (pKa)
3.2.2. Molecular Electrostatic Potential Surface
3.2.3. Hirshfeld Surface Analysis
3.3. Powder Hygroscopicity
3.4. Stability Test
3.5. Solubility
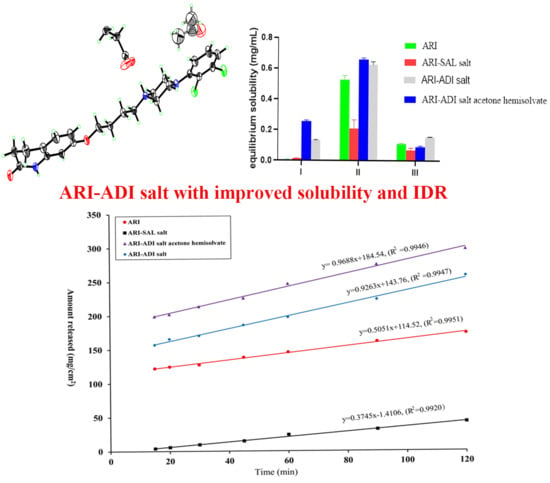
3.5.1. Equilibrium Solubility Test
3.5.2. IDR Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Sethiya, A.; Agarwal, D.K.; Agarwal, S. Current Trends in Drug Delivery System of Curcumin and its Therapeutic Applications. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2020, 13, 1190–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, D.J.; Steed, J.W. Pharmaceutical cocrystals, salts and multicomponent systems; intermolecular interactions and property based design. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 117, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diniz, L.F.; Carvalho, P.S., Jr.; Pena, S.A.C.; Gonçalves, J.E.; Souza, M.A.C.; de Souza Filho, J.D.; Bomfim Filho, L.F.O.; Franco, C.H.J.; Diniz, R.; Fernandes, C. Enhancing the solubility and permeability of the diuretic drug furosemide via multicomponent crystal forms. Int. J. Pharm. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clements, M.; Roex, T.L.; Blackie, M. Multicomponent Crystal Systems of Known Antimalarial Drug Molecules. ChemMedChem 2015, 10, 1786–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanphui, P.; Mishra, M.K.; Ramamurty, U.; Desiraju, G.R. Tuning mechanical properties of pharmaceutical crystals with multicomponent crystals: Voriconazole as a case study. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elder, D.P.; Holm, R.; Diego, H.L. Use of pharmaceutical salts and cocrystals to address the issue of poor solubility. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prommer, E. Aripiprazole. Am. J. Hosp. Palliat. Care 2017, 34, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuomo, A.; Beccarini Crescenzi, B.; Goracci, A.; Bolognesi, S.; Giordano, N.; Rossi, R.; Facchi, E.; Neal, S.M.; Fagiolini, A. Drug safety evaluation of aripiprazole in bipolar disorder. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2019, 18, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego-Sánchez, A.; Sánchez-Espejo, R.; Albertini, B.; Passerini, N.; Cerezo, P.; Viseras, C.; Sainz-Díaz, C.I. Ground Calcium Carbonate as a Low Cost and Biosafety Excipient for Solubility and Dissolution Improvement of Praziquantel. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyszczarz, E.; Hofmanova, J.; Szafraniec-Szczesny, J.; Jachowicz, R. Orodispersible films containing ball milled aripiprazole-poloxamer(R)407 solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, X.R.; Chen, Y.F.; Liao, Z.L. A new febuxostat imidazolium salt hydrate: Synthesis, crystal structure, solubility, and dissolution study. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1176, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miraglia, N.; Agostinetto, M.; Bianchi, D.; Valoti, E. Enhanced oral bioavailability of a novel folate salt: Comparison with folic acid and a calcium folate salt in a pharmacokinetic study in rats. Minerva Ginecol. 2016, 68, 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- Freire, E.; Polla, G.; Baggio, R. Aripiprazole salts I Aripiprazole nitrate. Acta Crystallogr. C 2012, 68 Pt 4, o170–o173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, E.; Polla, G.; Baggio, R. Aripiprazole salts. II. Aripiprazole perchlorate. Acta Crystallogr. C 2012, 68 Pt 6, o235–o239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, E.; Polla, G.; Baggio, R. Aripiprazole salts. III. Bis(aripiprazolium) oxalate-oxalic acid (1/1). Acta Crystallogr. C 2013, 69 Pt 2, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, E.; Polla, G.; Baggio, R. Aripiprazole salts IV. Anionic plus solvato networks defining molecular conformation. J. Mol. Struct. 2014, 1068, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanubolu, J.B.; Sridhar, B.; Ravikumar, K.; Cherukuvada, S. Adaptability of aripiprazole towards forming isostructural hydrogen bonding networks in multi-component salts: A rare case of strong O–H⋯O− ↔ weak C–H⋯O mimicry. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 4321–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, B.; Jia, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Yang, H.; Qiao, Y.; Gong, J.; Tang, W. Tuning Physicochemical Properties of Antipsychotic Drug Aripiprazole with Multicomponent Crystal Strategy Based on Structure and Property Relationship. Cryst. Growth. Des. 2020, 20, 3747–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAINT Version 7.68A. Software for the CCD Detector System; Bruker AXS Inc: Madison, WI, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SADABS, Bruker/Siemens Area Detector Absorption Correction Program; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXL2015, Program for Crystal Structure Refinement; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pennington, W. DIAMOND—Visual Crystal Structure Information System. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1999, 32, 1028–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sedghiniya, S.; Soleimannejad, J.; Janczak, J. The salt-cocrystal spectrum in salicylic acid-adenine: The influence of crystal structure on proton-transfer balance. Acta Crystallogr. C Struct. Chem. 2019, 75 Pt 4, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanphui, P.; Bolla, G.; Nangia, A. High Solubility Piperazine Salts of the Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (NSAID) Meclofenamic Acid. Cryst. Growth. Des. 2012, 12, 2023–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.F.; Nahar, N.; Rashid, R.B.; Chowdhury, A.; Rashid, M.A. Computational investigations of physicochemical, pharmacokinetic, toxicological properties and molecular docking of betulinic acid, a constituent of Corypha taliera (Roxb.) with Phospholipase A2 (PLA2). BMC complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F. Multiwfn: A multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzetti, S.; Lu, T. The geometry and electronic structure of Aristolochic acid: Possible implications for a frozen resonance. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2013, 26, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, L.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yin, Q. Insight into the Role of Hydrogen Bonding in the Molecular Self-Assembly Process of Sulfamethazine Solvates. Cryst. Growth. Des. 2017, 17, 6151–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spackman, M.A.; Jayatilaka, D. Hirshfeld Surface Analysis. CrystEngComm 2009, 11, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Cao, J.; Jiao, L.; Yang, S.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Y.; Du, G. Solubility and stability advantages of a new cocrystal of berberine chloride with fumaric acid. ACS Omega 2020, 4, 8283–8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steiner, T. Competition of hydrogen-bond acceptors for the strong carboxyl donor. Acta Crystallogr. B 2001, 57, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Newman, A.W.; Reutzel-Edens, S.M.; Zografi, G. Characterization of the “hygroscopic” properties of active pharmaceutical ingredients. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 1047–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevchenko, A.; Bimbo, L.M.; Miroshnyk, I.; Haarala, J.; Jelínková, K.; Syrjänen, K.; Veen, B.; Kiesvaara, J.; Santos, H.A.; Yliruusi, J. A new cocrystal and salts of itraconazole: Comparison of solid-state properties stability and dissolution behavior. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 436, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Compound Reference | ARI-SAL Salt | ARI-ADI Salts Acetone Hemisolvate |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C23H28Cl2N3O2·C7H5O3 | C23H28Cl2N3O2·0.5(C6H8O4)·0.5(C3H6O) |
| Formula mass | 586.49 | 550.48 |
| Crystal system | monoclinic | triclinic |
| Space group | P 21/c | P-1 |
| a/Å | 15.082 (2) | 7.6388(12) |
| b/Å | 9.6912 (13) | 10.7268(17) |
| c/Å | 21.220 (3) | 18.390(3) |
| α/° | 90 | 97.229(3) |
| β/° | 106.743 (2) | 93.641(3) |
| γ/° | 90 | 105.529(3) |
| Unit cell volume/Å3 | 2970.1 (7) | 1432.9(4) |
| Temperature/k | 296(2) | 296(2) |
| No. of formula units per unit cell, Z | 4 | 2 |
| Crystal density (g/cm3) | 1.312 | 1.276 |
| No. of reflections measured | 9612 | 7725 |
| No. of independent reflections | 6483 | 4047 |
| Rint | 0.0289 | 0.0321 |
| Final R1 values (I > 2σ(I)) | 0.0806 | 0.0689 |
| Final wR (F2) values (I > 2σ(I)) | 0.2526 | 0.2135 |
| Final R1 values (all data) | 0.1127 | 0.1308 |
| Final wR (F2) values (all data) | 0.2848 | 0.2725 |
| F(000) | 1232 | 582 |
| Goodness of fit on F2 | 1.084 | 0.963 |
| CCDC Number | 1991810 | 2023732 |
| D-H⋯A | D-H/Å | H⋯A/Å | D⋯A/Å | D-H⋯A/° | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARI-SAL Salt | C16-H16A⋯Cl1 | 0.97 | 2.675 | 3.248 | 118 |
| O5-H5⋯O4 | 0.82 | 1.789 | 2.497 | 143 | |
| N2-H2⋯O3 | 0.98 | 1.691 | 2.670 | 177 | |
| N2-H2⋯O4 | 0.98 | 2.503 | 3.122 | 121 | |
| N1-H1⋯O1i | 0.86 | 2.062 | 2.908 | 168 | |
| C17-H17A⋯O5ii | 0.97 | 2.542 | 3.467 | 160 | |
| C27-H27⋯O1iii | 0.93 | 2.360 | 3.287 | 174 | |
| Symmetry transformation: i: −x+2, −y, −z+1; ii: −x+1, y−1/2, −z+3/2; iii: −x+2, y+1/2, −z+3/2. | |||||
| ARI-ADI salt acetone hemisolvate | C16-H16A⋯Cl1 | 0.97 | 2.595 | 3.214 | 121 |
| N1-H1⋯O1i | 0.86 | 2.023 | 2.869 | 167 | |
| N2-H2⋯O3 | 0.98 | 1.729 | 2.685 | 164 | |
| C15-H15A⋯Cl1ii | 0.97 | 2.957 | 3.448 | 112 | |
| C11-H11A⋯π(Cg)iii | 0.97 | 2.96 | 3.843 | 151 | |
| Symmetry transformation i: −x+1, −y−1, −z; ii: x+1, y, z; ii: x, −1+y, z. Cg is the centroid of C18/C19/C20/C21/C22/C23 atoms | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Q.; Tan, Z.; Yang, D.; Tu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gan, G. Improving the Solubility of Aripiprazole by Multicomponent Crystallization. Crystals 2021, 11, 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11040343
Zhou Q, Tan Z, Yang D, Tu J, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Gan G. Improving the Solubility of Aripiprazole by Multicomponent Crystallization. Crystals. 2021; 11(4):343. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11040343
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Qi, Zhongchuan Tan, Desen Yang, Jiyuan Tu, Yezi Wang, Ying Zhang, Yanju Liu, and Guoping Gan. 2021. "Improving the Solubility of Aripiprazole by Multicomponent Crystallization" Crystals 11, no. 4: 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11040343
APA StyleZhou, Q., Tan, Z., Yang, D., Tu, J., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., & Gan, G. (2021). Improving the Solubility of Aripiprazole by Multicomponent Crystallization. Crystals, 11(4), 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11040343