Tailoring Water Adsorption Capacity of APO-Tric †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
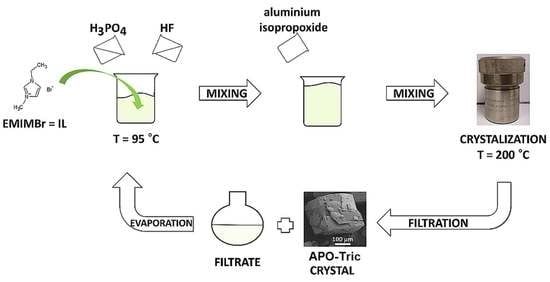
2.2. Synthesis
2.3. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Henninger, S.K.; Schmidt, F.P.; Henning, H.M. Water adsorption characteristics of novel materials for heat transformation applications. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2010, 30, 1692–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasta, S.; Brancato, V.; La Rosa, D.; Palomba, V.; Restuccia, G.; Sapienza, A.; Frazzica, A. Adsorption Heat Storage: State-of-the-Art and Future Perspectives. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ng, E.P.; Mintova, S. Nanoporous materials with enhanced hydrophilicity and high water sorption capacity. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 114, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Salles, F.; Zajac, J. A Critical Review of Solid Materials for Low-Temperature Thermochemical Storage of Solar Energy Based on Solid-Vapour Adsorption in View of Space Heating Uses. Molecules 2019, 24, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, J.; Li, H.; Zhao, S.; Guo, W.; Wang, R.; Ying, M. Characteristics and performance of SAPO-34 catalyst for methanol-to-olefin conversion. Appl. Catal. 1990, 64, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.T.; Lok, B.M.; Messina, C.A.; Cannan, T.R.; Flanigen, E.M. Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieves: A New Class of Microporous Crystalline Inorganic Solids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982, 104, 1146–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stach, H.; Mugele, J.; Jänchen, J.; Weiler, E. Influence of cycle temperatures on the thermochemical heat storage densities in the systems water/microporous and water/mesoporous adsorbents. Adsorption 2005, 11, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccorsi, L.; Calabrese, L.; Freni, A.; Proverbio, E.; Restuccia, G. Zeolites direct synthesis on heat exchangers for adsorption heat pumps. In Proceedings of the Applied Thermal Engineering; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 50, pp. 1590–1595. [Google Scholar]
- Ristić, A.; Logar, N.Z.; Henninger, S.K.; Kaučič, V. The performance of small-pore microporous aluminophosphates in low-temperature solar energy storage: The structure-property relationship. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 1952–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancato, V.; Frazzica, A. Characterisation and comparative analysis of zeotype water adsorbents for heat transformation applications. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2018, 180, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, L.; De Antonellis, S.; Vasta, S.; Brancato, V.; Freni, A. Modified silicone-SAPO34 composite materials for adsorption thermal energy storage systems. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajnc, A.; Varlec, J.; Mazaj, M.; Ristić, A.; Logar, N.Z.; Mali, G. Superior Performance of Microporous Aluminophosphate with LTA Topology in Solar-Energy Storage and Heat Reallocation. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1601815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henninger, S.K.; Munz, G.; Ratzsch, K.F.; Schossig, P. Cycle stability of sorption materials and composites for the use in heat pumps and cooling machines. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 3043–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drylie, E.A.; Wragg, D.S.; Parnham, E.R.; Wheatley, P.S.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Warren, J.E.; Morris, R.E. Ionothermal synthesis of unusual choline-templated cobalt aluminophosphates. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 7839–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, R.D.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic Liquids—Solvents of the Future? Science (80-.) 2003, 302, 792–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Xiao, F.S. Green routes for synthesis of zeolites. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 1521–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, R.; Warr, G.G.; Atkin, R. Structure and Nanostructure in Ionic Liquids. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 6357–6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, E.R.; Andrews, C.D.; Wheatley, P.S.; Webb, P.B.; Wormald, P.; Morris, R.E. Ionic liquids and eutectic mixtures as solvent and template in synthesis of zeolite analogues. Nature 2004, 430, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baerlocher, C.; Meier, W.M.; Olson, D.H. Atlas of Zeolite Framework Types; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Musa, M.; Dawson, D.M.; Ashbrook, S.E.; Morris, R.E. Ionothermal synthesis and characterization of CoAPO-34 molecular sieve. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 239, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rigaku Oxford Diffraction. CrysAlis Pro. Version 1.171.38.46; Rigaku Corporation: Oxford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Altomare, A.; Burla, M.C.; Camalli, M.; Cascarano, G.L.; Giacovazzo, C.; Guagliardi, A.; Moliterni, A.G.G.; Polidori, G.; Spagna, R. SIR97: A new tool for crystal structure determination and refinement. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1999, 32, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Found. Crystallogr. 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farrugia, L.J. ORTEP-3 for windows—A version of ORTEP-III with a graphical user interface (GUI). J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1997, 30, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrae, C.F.; Edgington, P.R.; McCabe, P.; Pidcock, E.; Shields, G.P.; Taylor, R.; Towler, M.; Van De Streek, J. Mercury: Visualization and analysis of crystal structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2006, 39, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harding, M.M.; Kariuki, B.M. Microcrystal structure determination of AlPO4-CHA using synchrotron radiation. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Cryst. Struct. Commun. 1994, 50, 852–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnham, E.R.; Morris, R.E. 1-Alkyl-3-methyl imidazolium bromide ionic liquids in the ionothermal synthesis of aluminium phosphate molecular sieves. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 4882–4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnham, E.R.; Morris, R.E. Ionothermal synthesis of zeolites, metal-organic frameworks, and inorganic-organic hybrids. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, J.M.; Clark, L.; Seymour, V.R.; Aldous, D.W.; Dawson, D.M.; Iuga, D.; Morris, R.E.; Ashbrook, S.E. Ionothermal 17O enrichment of oxides using microlitre quantities of labelled water. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 2293–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristić, A.; Fischer, F.; Hauer, A.; Zabukovec Logar, N. Improved performance of binder-free zeolite y for low-temperature sorption heat storage. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 11521–11530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varlec, J.; Krajnc, A.; Mazaj, M.; Ristić, A.; Vanatalu, K.; Oss, A.; Samoson, A.; Kaučič, V.; Mali, G. Dehydration of AlPO 4 -34 studied by variable-temperature NMR, XRD and first-principles calculations. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 4178–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristić, A.; Tušar, N.N.; Arčon, I.; Thibault-Starzyk, F.; Hanžel, D.; Czyzniewska, J.; Kaučič, V. Synthesis and characterization of triclinic MeAPO-34 (Me = Zn, Fe) molecular sieves. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2002, 56, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuel, A.; Caldarelli, S.; Meden, A.; McCusker, L.B.; Baerlocher, C.; Ristic, A.; Rajic, N.; Mali, G.; Kaucic, V. NMR characterization and rietveld refinement of the structure of rehydrated AlPQ4-34. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 5697–5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M. Template effects on the pressure-dependent behavior of chabazite-type fluoroaluminophosphates: A computational approach. Phys. Chem. Miner. 2019, 46, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, D.M.; Griffin, J.M.; Seymour, V.R.; Wheatley, P.S.; Amri, M.; Kurkiewicz, T.; Guillou, N.; Wimperis, S.; Walton, R.I.; Ashbrook, S.E. A multinuclear NMR study of six forms of AlPO-34: Structure and motional broadening. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 1781–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]










Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mal, S.; Ristić, A.; Golobič, A.; Zabukovec Logar, N. Tailoring Water Adsorption Capacity of APO-Tric. Crystals 2021, 11, 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11070773
Mal S, Ristić A, Golobič A, Zabukovec Logar N. Tailoring Water Adsorption Capacity of APO-Tric. Crystals. 2021; 11(7):773. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11070773
Chicago/Turabian StyleMal, Suzana, Alenka Ristić, Amalija Golobič, and Nataša Zabukovec Logar. 2021. "Tailoring Water Adsorption Capacity of APO-Tric" Crystals 11, no. 7: 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11070773
APA StyleMal, S., Ristić, A., Golobič, A., & Zabukovec Logar, N. (2021). Tailoring Water Adsorption Capacity of APO-Tric. Crystals, 11(7), 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11070773