Inverse Columnar-Equiaxed Transition (CET) in 304 and 316L Stainless Steels Melt by Electron Beam for Additive Manufacturing (AM)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Experimental Methods
2.2. Simulation Methods
3. Results and Discussion
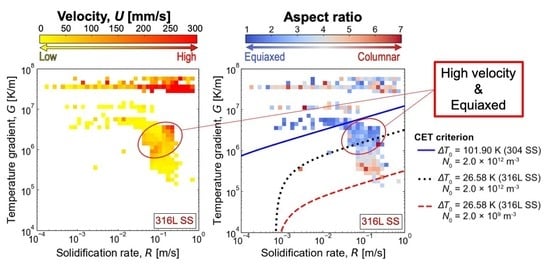
3.1. Experimental Results
3.2. Computational Thermal-Fluid Dynamic (CtFD) Simulation
3.3. Relationships between Microstructures and Solidification Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sow, M.C.; De Terris, T.; Castelnau, O.; Hamouche, Z.; Coste, F.; Fabbro, R.; Peyre, P. Influence of beam diameter on Laser Powder Bed Fusion (L-PBF) process. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 36, 101532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, J.C.; Chen, X.; Azizi, A.; Daeumer, M.A.; Zavalij, P.Y.; Zhou, G.; Schiffres, S.N. Influence of processing and microstructure on the local and bulk thermal conductivity of selective laser melted 316L stainless steel. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 32, 100996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dryepondt, S.; Nandwana, P.; Fernandez-Zelaia, P.; List, F. Microstructure and high temperature tensile properties of 316L fabricated by laser powder-bed fusion. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 37, 101723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.H.; Ishimoto, T.; Hagihara, K.; Tsutsumi, Y.; Hanawa, T.; Nakano, T. Excellent mechanical and corrosion properties of austenitic stainless steel with a unique crystallographic lamellar microstructure via selective laser melting. Scr. Mater. 2019, 159, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, T.; Ishimoto, T.; Oishi, T.; Manaka, T.; Chen, P.; Ashida, M.; Doi, K.; Katayama, H.; Hanawa, T.; Nakano, T. Crystallographic textureand grain boundary density-independent improvement of corrosion resistance in austenitic 316L stainless steel fabricated via laser powder bed fusion. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 45, 102066. [Google Scholar]
- Ishimoto, T.; Wu, S.; Ito, Y.; Sun, S.-H.; Amano, H.; Nakano, T. Crystallographic Orientation Control of 316L Austenitic Stainless Steel via Selective Laser Melting. ISIJ Int. 2020, 60, 1758–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishimoto, T.; Hagihara, K.; Hisamoto, K.; Sun, S.H.; Nakano, T. Crystallographic texture control of beta-type Ti–15Mo–5Zr–3Al alloy by selective laser melting for the development of novel implants with a biocompatible low Young’s modulus. Scr. Mater. 2017, 132, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Koizumi, Y.; Wei, D.; Chiba, A. Effect of process parameters on melt pool geometry and microstructure development for electron beam melting of IN718: A systematic single bead analysis study. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 26, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karayagiz, K.; Johnson, L.; Seede, R.; Attari, V.; Zhang, B.; Huang, X.; Ghosh, S.; Duong, T.; Karaman, I.; Elwany, A.; et al. Finite interface dissipation phase field modeling of Ni–Nb under additive manufacturing conditions. Acta Mater. 2020, 185, 320–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirka, M.M.; Lee, Y.; Greeley, D.A.; Okello, A.; Goin, M.J.; Pearce, M.T.; Dehoff, R.R. Strategy for Texture Management in Metals Additive Manufacturing. JOM 2017, 69, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babu, S.S.; Raghavan, N.; Raplee, J.; Foster, S.J.; Frederick, C.; Haines, M.; Dinwiddie, R.; Kirka, M.K.; Plotkowski, A.; Lee, Y.; et al. Additive Manufacturing of Nickel Superalloys: Opportunities for Innovation and Challenges Related to Qualification. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2018, 49, 3764–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Koizumi, Y.; Aoyagi, K.; Kii, T.; Sasaki, N.; Hayasaka, Y.; Yamanaka, K.; Chiba, A. Microstructural control of alloy 718 fabricated by electron beam melting with expanded processing window by adaptive offset method. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 764, 138058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotterbarm, M.R.; Rausch, A.M.; Körner, C. Fabrication of Single Crystals through a µ-Helix Grain Selection Process during Electron Beam Metal Additive Manufacturing. Metals 2020, 10, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunt, J.D.D. Steady state columnar and equiaxed growth of dendrites and eutectic. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1984, 65, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, W.; Bezencon, C.; Gäumann, M. Columnar to equiaxed transition in solidification processing. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2001, 2, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontha, S.; Klingbeil, N.W.; Kobryn, P.A.; Fraser, H.L. Effects of process variables and size-scale on solidification microstructure in beam-based fabrication of bulky 3D structures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 513–514, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoinochoritis, B.; Chantzis, D.; Salonitis, K. Simulation of metallic powder bed additive manufacturing processes with the finite element method: A critical review. Proc. Instit. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2017, 231, 96–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Koizumi, Y.; Aoyagi, K.; Wei, D.; Yamanaka, K.; Chiba, A. Molten pool behavior and effect of fluid flow on solidification conditions in selective electron beam melting (SEBM) of a biomedical Co-Cr-Mo alloy. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 26, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Tan, J.L.; Wong, C.H. A numerical investigation on the physical mechanisms of single track defects in selective laser melting. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 126, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technical Data for Iron. Available online: http://periodictable.com/Elements/026/data.html (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Raghavan, N.; Dehoff, R.; Pannala, S.; Simunovic, S.; Kirka, M.; Turner, J.; Carlson, N.; Babu, S.S. Numerical modeling of heat-transfer and the influence of process parameters on tailoring the grain morphology of IN718 in electron beam additive manufacturing. Acta Mater. 2016, 112, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hellawell, A.; Liu, S.; Lu, S.Z. Dendrite fragmentation and the effects of fluid flow in castings. JOM 1997, 49, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, T.; Charbon, C.; Rappaz, M. Grain refinement induced by electromagnetic stirring: A dendrite fragmentation criterion. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2004, 35, 3201–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Line Energy, Eline (J/mm) | Scanning Speed, V (mm/s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 300 | 1000 | 3000 | ||
| Beam power, P (W) | 600 | 6 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.2 |
| 900 | 9 | 3 | 0.9 | 0.3 | |
| 1200 | 12 | 4 | 1.2 | 0.4 | |
| Name | Symbol | Value for 316L SS | Value for 304 SS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density at 298.15 K | ρ (kg/m3) | 8000 a | 7892.77 a |
| Liquidus temperature | TL (K) | 1710.26 a | 1721.05 a |
| Solidus temperature | TS (K) | 1683.68 a | 1619.15 a |
| Viscosity at TL | η (g/m∙s) | 7.83 a | 7.35 a |
| Specific heat at 298.15 K | CP (J/kg∙K) | 440 a | 453.66 a |
| Thermal conductivity at 298.15 K | λ (W/m∙K) | 13.58 a | 15.066 a |
| Surface tension at TL | γL (J/m2) | 1.80216 a | 1.78225 a |
| Temperature coefficient of surface tension | dγL/dT (J/m2∙K) | −3.6616 × 10−4 a | −3.5992 × 10−4 a |
| Emissivity | Ε | 0.27 [19] | |
| Stefan–Boltzmann constant | σ (W/m2∙K4) | 5.67 × 10−8 [19] | |
| Heat of vaporization | ΔHLV (J/kg) | 6.21 × 10⁶ [20] | |
| Vaporization temperature | TV (K) | 3134 [20] | |
| Name | Symbol | Value for 316L SS | Value for 304 SS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liquidus temperature | TL | 1710.26 K a | 1721.05 K a |
| Solidus temperature | TS | 1683.68 K a | 1619.15 K a |
| Temperature difference between TL and TS | ΔT0 | 26.58 K | 101.90 K |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miyata, Y.; Okugawa, M.; Koizumi, Y.; Nakano, T. Inverse Columnar-Equiaxed Transition (CET) in 304 and 316L Stainless Steels Melt by Electron Beam for Additive Manufacturing (AM). Crystals 2021, 11, 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080856
Miyata Y, Okugawa M, Koizumi Y, Nakano T. Inverse Columnar-Equiaxed Transition (CET) in 304 and 316L Stainless Steels Melt by Electron Beam for Additive Manufacturing (AM). Crystals. 2021; 11(8):856. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080856
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiyata, Yuichiro, Masayuki Okugawa, Yuichiro Koizumi, and Takayoshi Nakano. 2021. "Inverse Columnar-Equiaxed Transition (CET) in 304 and 316L Stainless Steels Melt by Electron Beam for Additive Manufacturing (AM)" Crystals 11, no. 8: 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080856
APA StyleMiyata, Y., Okugawa, M., Koizumi, Y., & Nakano, T. (2021). Inverse Columnar-Equiaxed Transition (CET) in 304 and 316L Stainless Steels Melt by Electron Beam for Additive Manufacturing (AM). Crystals, 11(8), 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11080856