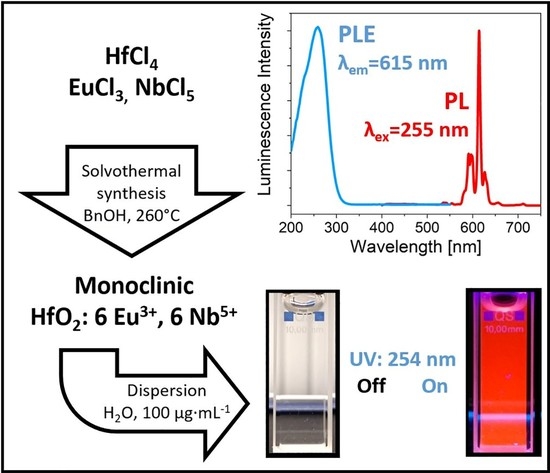
Charge Compensation in Europium-Doped Hafnia Nanoparticles: Solvothermal Synthesis and Colloidal Dispersion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of HfO2:Eu Dispersions
2.2. Characterisation Methods
3. Results
3.1. Structural Analysis of the Nanocrystals
3.2. STEM-EDX Elemental Analysis
3.3. Evaluation of the Particle Dispersion
3.4. Optical Charcterization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lauria, A.; Villa, I.; Fasoli, M.; Niederberger, M.; Vedda, A. Multifunctional Role of Rare Earth Doping in Optical Materials: Nonaqueous Sol–Gel Synthesis of Stabilized Cubic HfO2 Luminescent Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 7041–7052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laganovska, K.; Bite, I.; Zolotarjovs, A.; Smits, K. Niobium enhanced europium ion luminescence in hafnia nanocrystals. J. Lumin. 2018, 203, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeLuyer, C.; Villanueva-Ibañez, M.; Pillonnet, A.; Dujardin, C. HfO2:X (X = Eu3+, Ce3+, Y3+) Sol Gel Powders for Ultradense Scintillating Materials. J. Phys. Chem. A 2008, 112, 10152–10155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerken, L.R.H.; Keevend, K.; Zhang, Y.; Starsich, F.H.L.; Eberhardt, C.; Panzarasa, G.; Matter, M.T.; Wichser, A.; Boss, A.; Neels, A.; et al. Lanthanide-Doped Hafnia Nanoparticles for Multimodal Theranostics: Tailoring the Physicochemical Properties and Interactions with Biological Entities. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva-Ibañez, M.; Le Luyer, C.; Marty, O.; Mugnier, J. Annealing and doping effects on the structure of europium-doped HfO2 sol-gel material. Opt. Mater. (Amst.) 2003, 24, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimori, H.; Yashima, M.; Sasaki, S.; Kakihana, M.; Mori, T.; Tanaka, M.; Yoshimura, M. Cubic-tetragonal phase change of yttria-doped hafnia solid solution: High-resolution X-ray diffraction and Raman scattering. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2001, 346, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Wang, Y.; Wan, D.; Huang, F.; Yao, J. Red-luminescence enhancement of ZrO2-based phosphor by codoping Eu3+ and M5+ (M = Nb, Ta). Opt. Mater. (Amst.) 2012, 34, 1353–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Y.; Zou, B.; Liu, S.; Zhao, S.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, X.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Cao, X. Effects of Eu3+-doping and annealing on structure and fluorescence of zirconia phosphors. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 2760–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, K.; Olsteins, D.; Zolotarjovs, A.; Laganovska, K.; Millers, D.; Ignatans, R.; Grabis, J. Doped zirconia phase and luminescence dependence on the nature of charge compensation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bugrov, A.N.; Smyslov, R.Y.; Zavialova, A.Y.; Kopitsa, G.P.; Khamova, T.V.; Kirilenko, D.A.; Kolesnikov, I.E.; Pankin, D.V.; Baigildin, V.A.; Licitra, C. Influence of Stabilizing Ion Content on the Structure, Photoluminescence and Biological Properties of Zr1−xEuxO2−0.5x Nanoparticles. Crystals 2020, 10, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, K.; Sarakovskis, A.; Grigorjeva, L.; Millers, D.; Grabis, J. The role of Nb in intensity increase of Er ion upconversion luminescence in zirconia. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 213520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiatrowska, A.; Zych, E. Modeling Luminescent Properties of HfO2:Eu Powders with Li, Ta, Nb, and V Codopants. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 6409–6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiisk, V.; Puust, L.; Mändar, H.; Ritslaid, P.; Rähn, M.; Bite, I.; Jankovica, D.; Sildos, I.; Jaaniso, R. Phase stability and oxygen-sensitive photoluminescence of ZrO2:Eu,Nb nanopowders. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 214, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primc, D.; Zeng, G.; Leute, R.; Walter, M.; Mayrhofer, L.; Niederberger, M. Chemical Substitution—Alignment of the Surface Potentials for Efficient Charge Transport in Nanocrystalline TiO2 Photocatalysts. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 4223–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Keukeleere, K.; De Roo, J.; Lommens, P.; Martins, J.C.; Van Der Voort, P.; Van Driessche, I. Fast and Tunable Synthesis of ZrO2 Nanocrystals: Mechanistic Insights into Precursor Dependence. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 3469–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olliges-Stadler, I.; Rossell, M.D.; Niederberger, M. Co-operative Formation of Monolithic Tungsten Oxide-Polybenzylene Hybrids via Polymerization of Benzyl Alcohol and Study of the Catalytic Activity of the Tungsten Oxide Nanoparticles. Small 2010, 6, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braendle, A.; Perevedentsev, A.; Cheetham, N.J.; Stavrinou, P.N.; Schachner, J.A.; Mösch-Zanetti, N.C.; Niederberger, M.; Caseri, W.R. Homoconjugation in poly(phenylene methylene)s: A case study of non-π-conjugated polymers with unexpected fluorescent properties. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2017, 55, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, C.; Lauria, A.; Manzano, C.V.; Guerra-Nuñez, C.; Niederberger, M.; Storrer, C.; Michler, J.; Philippe, L. Nonaqueous Sol-Gel Synthesis of Anatase Nanoparticles and Their Electrophoretic Deposition in Porous Alumina. Langmuir 2017, 33, 12404–12418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binnemans, K.; Görller-Walrand, C. A simple model for crystal field splittings of the 7F1 and 5D1 energy levels of Eu3+. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1995, 245, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bünzli, J.-C.G.; Chauvin, A.-S.; Vandevyver, C.D.B.; Bo, S.; Comby, S. Lanthanide Bimetallic Helicates for in Vitro Imaging and Sensing. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1130, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binnemans, K. Interpretation of europium(III) spectra. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 295, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, S.K.; Reghukumar, C.; Kadam, R.M. Eu3+ local site analysis and emission characteristics of novel Nd2Zr2O7:Eu phosphor: Insight into the effect of europium concentration on its photoluminescence properties. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 53614–53624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Element | HfO2: 6 Eu, 6 Nb | HfO2: 6 Eu, 6 Ta |
|---|---|---|
| Hf | Nominal 88.0 measured 88.2 ± 1 at.% | Nominal 88.0 measured 85.7 ± 1 at.% |
| Eu | Nominal 6.0 measured 5.8 ± 1 at.% | Nominal 6.0 measured 6.1 ± 1 at.% |
| Nd | Nominal 6.0 measured 6.0 ± 1 at.% | - |
| Ta | - | Nominal 6.0 measured 8.2 ± 1 at.% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guichard, X.H.; Bernasconi, F.; Lauria, A. Charge Compensation in Europium-Doped Hafnia Nanoparticles: Solvothermal Synthesis and Colloidal Dispersion. Crystals 2021, 11, 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091042
Guichard XH, Bernasconi F, Lauria A. Charge Compensation in Europium-Doped Hafnia Nanoparticles: Solvothermal Synthesis and Colloidal Dispersion. Crystals. 2021; 11(9):1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091042
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuichard, Xavier H., Francesco Bernasconi, and Alessandro Lauria. 2021. "Charge Compensation in Europium-Doped Hafnia Nanoparticles: Solvothermal Synthesis and Colloidal Dispersion" Crystals 11, no. 9: 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091042
APA StyleGuichard, X. H., Bernasconi, F., & Lauria, A. (2021). Charge Compensation in Europium-Doped Hafnia Nanoparticles: Solvothermal Synthesis and Colloidal Dispersion. Crystals, 11(9), 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11091042