CO2 Capture and Crystallization of Ammonia Bicarbonate in a Lab-Scale Scrubber
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Absorption Model and Solution Chemistry
3. Experimental Procedure
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Effect of Process Variables on E
4.2. Effect of Process Variables on the RA and KGa
4.3. Characterization of ABC Crystals
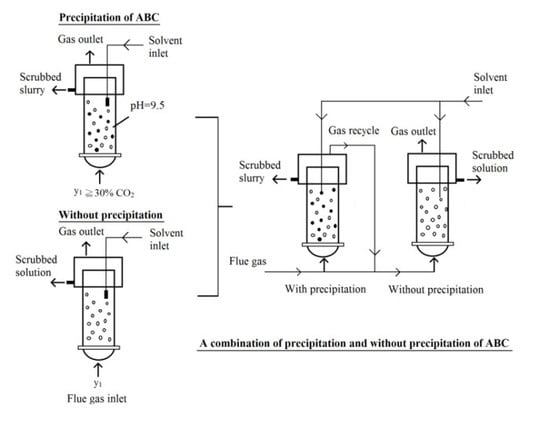
4.4. Strategy of CO2 Capture Using Aqueous Ammonia Solution
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, K.; Ahn, C.K.; Lee, M.S. Performance of an ammonia-based CO2 capture pilot facility in iron and steel industry. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2014, 27, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.Y.C.; Caramanna, C.; Maroto-Valer, M.M. An overview of current status of carbon dioxide capture and storage technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 39, 426–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeh, A.C.; Bai, H. Comparison of ammonia and monoethanolamine solvents to reduce CO2 greenhouse gas emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 228, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.C.; Lin, L.C. Capture of carbon dioxide using aqueous ammonia in a lab-scale stirred-tank scrubber. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 955–959, 1927–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.C.; Shi, W.; Du, R.; Chen, V. Scrubbing of CO2 greenhouse gases, accompanied by precipitation in a continuous bubble-column scrubber. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 6336–6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borhani, T.N.G.; Azarpour, A.; Akbari, V.; Wan Alwi, S.R.; Manan, Z.A. CO2 capture with potassium carbonate solutions: A state-of-the-art review. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2015, 41, 142–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Yeh, A.C. Removal of CO2 greenhouse gas by ammonia scrubbing. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1997, 36, 2490–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, N.; Do, T.; Puxty, G.; Rowland, R.; Feron, P.H.M.; Attalla, M.I. CO2 capture by aqueous amines and aqueous ammonia—A Comparison. Energy Procedia 2009, 1, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Y.F.; Zheng, X.Y.; He, B.S.; Chen, C.H.; Xu, X.C. Experimental study on capuring CO2 greenhouse gas by ammonia scrubbing. Energy Convers. Manag. 2004, 45, 2283–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chang, S.G. Method to regenerate ammonia for the capture of carbon dioxide. Energy Fuels 2002, 16, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darde, V.; Thomsen, K.; van Well, W.J.M.; Stenby, E.H. Chilled ammonia process for CO2 capture. Energy Procedia 2009, 1, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resnik, K.P.; Yeh, J.T.; Pennline, H.W. Aqua ammonia process for simultaneous removal of CO2, SO2 and NOx. Int. J. Environ. Technonl. Manag. 2004, 4, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhao, B.; Tong, H.; Chen, C. Absorption of carbon dioxide in aqueous ammonia. Energy Procedia 2009, 1, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.T.; Resnik, K.P.; Rygle, K.; Pennline, H.W. Semi-batch absorption and regeneration studies for CO2 capture by aqueous ammonia. Fuel Process. Technol. 2005, 86, 1533–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.C.; Liu, S.M.; Jang, C.J.; Hwang, R.C.; Yang, Y.L.; Lee, J.S.; Jang, J.S. Interpretation of gas-liquid reactive crystallization data using a size-independent agglomeration model. J. Cryst. Growth 2003, 257, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, F.M.M. Principles of Aqueous Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1983; Chapter 4; pp. 127–177. ISBN 0-471-08683-5. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.F.; Yang, Y.M.; Ma, J.R. Promotion mechanism for CO2 absorption into partially carbonated ammonia solutions. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 1999, 32, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Li, C.C.; Li, M.H. Kinetics of absorption of carbon dioxide into aqueous solutions of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanol + monoethanolamin. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2000, 55, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Burris, S.; Bui, H.; Pan, W.P. Development of an analytical method for distinguishing ammonia bicarbonate form the products of an aqueous ammonia CO2 scrubber. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 5947–5952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Zang, B.; Song, H.; Chen, G.; Yang, J. Research on mass transfer of CO2 absorption using ammonia solution in spray tower. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 67, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.C. Absorption of Carbon Dioxide in a Bubble Column Scrubber. Greenhouse Gases; Liu, G., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; Chapter 5; pp. 95–116. [Google Scholar]
- Petrov, P.; Ewert, G.; Rohm, H.J. Chemisorptive removal of carbon dioxide from process streams using a reactive bubble column with simultaneous production of usable materials. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2006, 29, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, O.; Michaud, S.; Escudié, R.; Delgenès, J.-P.; Bernet, N. Liquid mixing and gas–liquid mass transfer in a three-phase inverse turbulent bed reactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2005, 114, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Su, Y.; Peng, Y.C. Effect of reactor geometry on aqueous ammonia-based carbon dioxide capture in bubble column reactors. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2013, 17, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathias, P.M.; Reddy, S.; Connell, J.P.O. Quantitative evaluation of the aqueous-ammonia process for CO2 capture using fundamental data and thermodynamic analysis. Energy Procedia 2009, 1, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puxty, G.; Rowland, R.; Attalla, M. Comparison of the rate of CO2 absorption into ammonia and manoethanolamine. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Lee, B.; Lee, J.H.; You, J.K.; Park, K.T.; Baek, I.H.; Hur, N.H. Aqueous hydrazine as a promising candidate for capyuring carbon dioxide. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2014, 29, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.C.; Luo, Y.X.; Cai, P.W. CO2 Capture using monoethanolamine in a bubble-column scrubber. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2015, 38, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L. Development of an Analytical Method for Distinguishing Ammonium Bicarbonate from the Products of an Aqueous Ammonia CO2 Scrubber and the Characterization of Ammonium Bicarbonate. Master’s Thesis, Western Kentucky University, Bowling Green, KY, USA, December 2004. [Google Scholar]












| (5) | |
| (6) | |
| (7) | |
| (8) | |
| (9) | |
| (10) |
| (11) | |
| (12) | |
| (13) | |
| (14) | |
| (15) | |
| (16) |
| Operating Condition | |
| Gas-flow rate (L/min) | 3–5 |
| Concentration of CO2 | 15–60% |
| pH | 9.5 |
| Operating time (h) | 5–7 |
| Gas inlet temperature (°C) | 55 |
| Working temperature in the scrubber (°C) | 25–60 |
| Physical Property of ABC | |
| Density (kg/m3) | 1.58 |
| Molecular weight | 79.06 |
| Solubility (g/L-H2O) (20 (°C)) | 220 |
| Decomposition temperature (°C) | 35–60 |
| No. | pH | Qg (L/min) | y1 (%) | y2 (%) | T (°C) | QL (mL/min) | γ (-) | RA × 104 (mol/(s·L)) | KGa (1/s) | E (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9.5 | 3 | 15 | 7.95 | 25 | 3.66 | 0.58 | 3.9178 | 0.0794 | 47.0 |
| 2 | 9.5 | 3 | 30 | 17.7 | 25 | 3.30 | 1.33 | 5.1831 | 0.0447 | 41.3 |
| 3 | 9.5 | 3 | 50 | 38.8 | 25 | 4.90 | 1.50 | 5.7170 | 0.0194 | 22.4 |
| 4 | 9.5 | 3 | 60 | 53.5 | 25 | 4.96 | 1.75 | 7.1506 | 0.0143 | 10.9 |
| 5 | 9.5 | 4 | 15 | 8.7 | 25 | 2.22 | 1.33 | 3.5858 | 0.0692 | 42.1 |
| 6 | 9.5 | 4 | 30 | 22 | 25 | 3.51 | 1.71 | 5.0876 | 0.0327 | 26.7 |
| 7 | 9.5 | 4 | 50 | 39.3 | 25 | 4.73 | 2.05 | 7.0207 | 0.0136 | 21.4 |
| 8 | 9.5 | 4 | 60 | 51.7 | 25 | 6.63 | 1.77 | 9.3765 | 0.0199 | 13.8 |
| 9 | 9.5 | 5 | 15 | 7.56 | 25 | 3.30 | 1.11 | 5.4895 | 0.1142 | 49.6 |
| 10 | 9.5 | 5 | 30 | 22.9 | 25 | 0.60 | 12.24 | 7.0572 | 0.0506 | 23.6 |
| 11 | 9.5 | 5 | 50 | 39.6 | 25 | 7.28 | 1.69 | 9.0338 | 0.0299 | 20.8 |
| 12 | 9.5 | 5 | 60 | 50.6 | 25 | 7.10 | 2.07 | 10.999 | 0.0241 | 15.8 |
| 13 | 10.0 | 3 | 15 | 10.0 | 25 | 2.96 | 0.75 | 3.2122 | 0.0608 | 33.3 |
| 14 | 10.5 | 3 | 15 | 5.3 | 25 | 8.89 | 0.24 | 4.1095 | 0.1020 | 64.6 |
| 15 | 11.0 | 3 | 15 | 3.7 | 25 | 9.73 | 0.22 | 4.8295 | 0.1573 | 75.3 |
| 16 | 11.5 | 3 | 15 | 0 | 25 | 37.63 | 0.058 | 6.3943 | 0.2083 | 100 |
| 17 | 10.0 | 4 | 15 | 5.5 | 25 | 7.08 | 0.41 | 7.4126 | 0.1808 | 63.3 |
| 18 | 10.0 | 4 | 15 | 0 | 40 | 4.14 | 0.67 | 5.9145 | 0.1963 | 96.7 |
| 19 | 10.0 | 4 | 15 | 0 | 50 | 8.71 | 0.31 | 6.7421 | 0.2381 | 100 |
| 20 | 10.0 | 4 | 15 | 0 | 60 | 46.13 | 0.053 | 9.0425 | 0.3302 | 100 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, P.C.; Yu, S.C. CO2 Capture and Crystallization of Ammonia Bicarbonate in a Lab-Scale Scrubber. Crystals 2018, 8, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8010039
Chen PC, Yu SC. CO2 Capture and Crystallization of Ammonia Bicarbonate in a Lab-Scale Scrubber. Crystals. 2018; 8(1):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8010039
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Pao Chi, and Shun Chao Yu. 2018. "CO2 Capture and Crystallization of Ammonia Bicarbonate in a Lab-Scale Scrubber" Crystals 8, no. 1: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8010039
APA StyleChen, P. C., & Yu, S. C. (2018). CO2 Capture and Crystallization of Ammonia Bicarbonate in a Lab-Scale Scrubber. Crystals, 8(1), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8010039