Mixed Sr and Ba Tri-Stannides/Plumbides AII(Sn1−xPbx)3
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Synthesis and Phase Widths
2.2. Single Crystal Structure Refinements
2.3. Rietveld Refinements
2.4. Band Structure Calculations
3. Results and Discussion
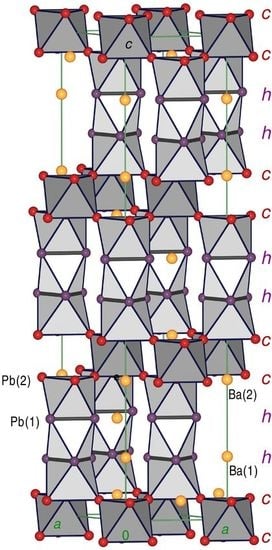
3.1. Description of the Crystal Structures and Their Respective Phase Widths
3.1.1. NiSn-Type Compounds
3.1.2. BaSnBi-Type Compounds
3.1.3. BaPb-Type Compounds
3.1.4. MgIn-Type Compounds
3.1.5. PuAl-Type Compounds
3.1.6. CuAu-Type Compounds
3.2. Stacking Sequences: Geometric Aspects
3.3. Molar Volumes and Variation of the Ratio
3.4. Sn/Pb Distribution: ‘Coloring’ Aspects
3.5. Chemical Bonding, Electronic Structure
3.5.1. Electron Count (Zintl/Wade/mno)
- c
- The bonding within c stacked compounds like e.g., SrPb3, in which [Pb6] octahedra are fused via common corners (Figure 7), can be explained by a direct comparison with the electron-precise boride CaB6 containing also octahedral closo clusters B62- (20 v.e.), which are in this case connected via 2e2c bonds (exo-bonds). Subtracting the six v.e. needed for these exo-bonds, each boron atom contributes 2 v.e. to stabilize one octahedral closo cluster. In tri-tetrelides two octahedra are directly fused via corners, i.e., each Pb atom participates in two closo octahedral clusters. Thus, the polyanion needs 2 × 2 = 4 v.e./Pb to obey Wade’s rule. This corresponds to the observed v.e. number (2 SrPb3 → 2 Sr2+ + Pb64−: 6×4 + 4 v.e./f.u. ≡ 4 v.e./Pb). and to the fact, that the tDOS exhibits a very pronounced minimum close to the Fermi level, at 13.9 v.e./f.u. (bottom of Figure 12, black arrow).
- h
- The mno rules and the similarities to the ‘polyaromatic’ bonding in borides and molecular boranes/boranates can be also used to explain the electron count of the h stacked atoms: Figure 11 shows the formal splitting of the v.e. in the boranate [B9H6]-, which satisfies the mno rules [46] (9 + 2 + 0 = 11 s.e.p. (s.e.p.: skeleton electron pairs): + + - = 22 s.e. = 11 s.e.p.). For the formal splitting of these overall number of s.e. to individual B atoms, the six BH atoms contribute 14 s.e. (, see above). The remaining 8 s.e. result in v.e. for each of the three central (h stacked) B atoms ( s.e./octahedron). Transfered to the electron balance of BaSn3, where each of the Sn atoms carries an additional lone-electron pair ( electrons), we expect v.e./Sn (i.e., 14 v.e./f.u.) to result in a stable cluster.
3.5.2. Bandstructure Calculations (DOS, Electron Densities)
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Fässler, T.F.; Hoffmann, S. Valence compounds at the border to intermetallics: alkali and alkaline earth metal stannides and plumbides. Z. Kristallogr. 1999, 214, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hume-Rothery, W. Formation of intermetallic compounds. Part IV: The System Calcium-Tin and the compounds CaSn3, CaSn and Ca2Sn. J. Inst. Met. 1926, 35, 319–335. [Google Scholar]
- Fässler, T.F.; Hoffmann, S. SrSn3–eine supraleitende Legierung mit freien Elektronenpaaren. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2000, 626, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, K.W.; Thompson, R.G. Study of barium-tin alloys. Met. Alloys 1930, 1, 314–316. [Google Scholar]
- Fässler, T.F.; Kronseder, C. BaSn3, ein Supraleiter im Grenzbereich zwischen Zintl-Phasen und intermetallischen Verbindungen: Realraumanalyse von Bandstrukturen. Angew. Chem. 1997, 109, 2800–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damsma, W.; Havinga, E.E. Influence of small lattice deformation on the superconductive critical temperature of alloys with the Cu3Au type structure. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1972, 34, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vucht, J.H.N. Influence of radius ratio on the structure of intermetallic compounds of the AB3 type. J. Less Common Met. 1966, 11, 308–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havinga, E.E. Influence of repulsive energy on structural parameters of the close-packed metal structures. J. Less Common Met. 1975, 41, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sands, D.E.; Wood, D.H.; Ramsey, W.J. The structures of Ba5Pb3, BaPb and BaPb3. Acta Crystallogr. 1964, 17, 986–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendorff, M.; Röhr, C. Gemischte Tristannide der Reihe CaSn3–SrSn3–BaSn3: Synthesen, Kristallstrukturen, Chemische Bindung. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2011, 637, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendorff, M.; Röhr, C. Gemischte Plumbide (Ca/Sr)xBa1−xPb3. Strukturchemie und chemische Bindung. Z. Naturforsch. 2008, 63, 1383–1394. [Google Scholar]
- Havinga, E.E. W-like dependence of critical temperature on number of valence electrons in non-transition metal Cu3Au-type alloys. Phys. Lett. A 1968, 28, 350–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havinga, E.E.; Damsma, W.; van Maaren, M.H. Oscillatory dependence of superconductive critical temperature on number of valency electrons in Cu3Au type alloys. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1970, 31, 2653–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranovskiy, A.E.; Grechnev, G.E.; Svechkarev, I.V. Features of the electronic spectrum and anomalous magnetism in the compounds YbPb3, YbSn3, CaPb3 and CaSn3. Low Temp. Phys. 2006, 32, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranovskiy, A.E.; Grechnev, G.E.; Mikitik, G.P.; Svechakarev, I.V. Anomalous diamagnetism in the intermetallic compounds CaPb3 and YbPb3. Low Temp. Phys. 2003, 29, 356–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havinga, E.E.; van Vucht, J.H.N. The crystal structure of Ba(Pb0.8Tl0.2)3. Acta Crystallogr. 1970, B26, 653–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Single crystal structure refinement of the strucuture of BaIn0.15Pb2.85: Hexagonal, space group P63/mmc, a = 733(1), c = 3991(5) pm, Z = 14, R1 = 0.0494.
- Ponou, S.; Fässler, T.F.; Kienle, L. Structural complexity in intermetallic alloys: Long-periodic order beyound 10 nm in the system BaSn3/BaBi3. Angew. Chem. 2008, 47, 3999–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, G.J. The “Coloring Problem” in solids: How it affects structure, composition and properties. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 1998, 5, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yvon, K.; Jeitschko, W.; Parthé, E. Program LAZY-PULVERIX; University Geneve: Geneva, Switzerland, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- STOE & Cie GmbH. X-SHAPE (Version 1.03), Crystal Optimization for Numerical Absorption Correction; STOE & Cie GmbH: Darmstadt, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SADABS: Program for Absorption Correction for Data from Area Detector Frames; Bruker Analytical X-ray Systems, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of Shelx. Acta Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelato, L.M.; Parthé, E. Structure Tidy: A computer program to standardize structure data. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1990, A46, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Further details on the crystal structure investigation are available from the Fachinformationszentrum Karlsruhe, Gesellschaft für wissenschaftlich-technische Information mbH, D-76344 Eggenstein-Leopoldshafen 2 on quoting the depository numbers CSD 431093 (BaPb3-II), 431094 (BaSn0.65Pb2.35) 431095 (BaSn1.01Pb1.99) 431096 (BaSn1.52Pb1.42) 431097 (BaSn2.20Pb0.80) and 431098 (SrSn2.05Pb0.95), the names of the authors, and citation of the paper (E-mail: [email protected]).
- Larson, A.C.; Dreele, R.B.V. General Structure Analysis System (GSAS); Los Alamos National Laboratory Report LAUR 86-748; Los Alamos National Laboratory: Los Alamos, NM, USA, 2000.
- Toby, B.H. Expgui, a graphical user interface for Gsas. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2001, 34, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, K.; Gauzzi, F.; Frank, K. Kristallstruktur einiger Mg-B3-Phasen. Z. Metallk. 1963, 54, 422–429. [Google Scholar]
- Blaha, P.; Schwarz, K.; Madsen, G.K.H.; Kvasnicka, D.; Luitz, J. WIEN2K, An Augmented Plane Wave and Local Orbital Program for Calculating Crystal Properties; TU Wien: Vienna, Austria, 2006; ISBN 3-9501031-1-2. [Google Scholar]
- Dewhurst, J.K.; Sharma, S.; Nordstrom, L.; Cricchio, F.; Bultmark, F.; Gross, E.K.U. Elk (Vers. 2.1.15), The Elk–FP-LAPW Code. 2013. Available online: http://elk.sourceforge.net (accessed on 5 May 2018).
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, S.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, G.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wagner, F.R. Chemical bonding in solids. In Handbook of Solid State Chemistry; Dronskoski, R., Kikkawa, S., Stein, A., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2017; Volume 5, pp. 405–489. [Google Scholar]
- Savin, A.; Nesper, R.; Wengert, S.; Fässler, T.F. ELF: The electron localization function. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1997, 36, 1808–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokalj, A. Program XCrySDen. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 1999, 17, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finger, L.W.; Kroeker, M.; Toby, B.H. Drawxtl: An open-source computer program to produce crystal structure drawings. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.W.F. Atoms in Molecules. A Quantum Theory; International Series of Monographs on Chemistry; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- De-la Roza, A.O.; Blanco, M.A.; Martá, A.; Pendás, A.M.; Luaña, V. Program Critic2 (Vers. 1.0). Comput. Phys. Commun. 2009, 180, 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- De-la Roza, A.O.; Luaña, V. A fast and accurate algorithm for QTAIM integrations in solids. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 32, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FIZ Karlsruhe. Inorganic Crystal Structure Database; FIZ Karlsruhe: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cirafici, S.; Franceschi, E. Stacking of close-packed AB3 layers in RGa3 compounds (R = heavy rare earth). J. Less Common Met. 1981, 77, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, A.C.; Cromer, D.T.; Stambaugh, C.K. The crystal structure of PuAl3. Acta Crystallogr. 1957, 10, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. 1976, A32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, W.B. The Crystal Chemistry and Physics of Metals and Alloys; Wiley Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Wendorff, M.; Röhr, C. Alkaline-earth tri-mercurides AIIHg3 (AII=Ca, Sr, Ba): Binary intermetallic compounds with a common and a new structure type. Z. Kristallogr. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Wade, K. Structural and bonding patterns in cluster chemistry. Adv. Inorg. Chem. Radiochem. 1976, 18, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Jemmis, E.D.; Balakrishnarajan, M.M.; Pancharatna, P.D. Electronic requirements for macropolyhedral boranes. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 93–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorov, E.; Sevov, S.C. Deltahedral clusters in neat solids: Synthesis and structure of the Zintl phase Cs4Pb9 with discrete clusters. Inorg. Chem. 1998, 37, 3889–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fässler, T.F. The renaissance of homoatomic nine-atom polyhedra of the heavier carbon-group element Si-Pb. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2001, 215, 347–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoch, C.; Röhr, C.; Wendorff, M. Crystal structure of K4Sn9. Acta Crystallogr. 2002, C58, 45–46. [Google Scholar]
- Bobev, S.; Sevov, S.C. Isolated deltaheral clusters of leadin the solid state: synthesis and characterization of Rb4Pb9 and Cs10K6Pb36 with , and A″Pb4 (A’ = Cs, Rb, K; A” = Na, Li) with . Polyhedron 2002, 21, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fässler, T.F.; Hunziker, M. The nido- and the Jahn-Teller Distorted closo- Zintl-Anions: Syntheses, X-ray Structures and Theoretical Studies. Inorg. Chem. 1995, 33, 5798–5809. [Google Scholar]
- Hoch, C.; Wendorff, M.; Röhr, C. Synthesis and Crystal Structure of the Plumbides A4Pb9 and the Tetrelides A12M17 (A=Na, K, Rb, Cs; M=Si, Ge, Sn). J. Alloys Compd. 2003, 361, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sample | Structure | Single | Pb | Weighed Elements | Temperature Program | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition | Type | Crystal | Content | Sr/Ba | Sn | Pb | T | ||||||||
| No. | [%] | [mg] | [mmol] | [mg] | [mmol] | [mg] | [mmol] | (in [ C] and [C/h]) | |||||||
| BaSn2Pb | Ni3Sn | 1 | 28 | 253.7 | 1.85 | 407.0 | 3.43 | 356.8 | 1.72 | 750 | 30 | 500 | 200 | ||
| BaSn1.5Pb1.5 | BaSn2.6Bi0.4 | 2 | 47.4 | 220.7 | 1.61 | 284.7 | 2.40 | 496.7 | 2.40 | 750 | 200 | 650 | 2 | 500 | 200 |
| BaSnPb2 | BaSn2.6Bi0.4 | 3 | 66.3 | 205.2 | 1.49 | 176.0 | 1.48 | 619.4 | 2.99 | 750 | 20 | 500 | 200 | ||
| BaSn0.75Pb2.25 | BaPb3 | 4 | 78.3 | 199.6 | 1.45 | 129.1 | 1.09 | 675.9 | 3.26 | 750 | 200 | 650 | 2 | 500 | 200 |
| BaSn0.5Pb2.5 | BaPb3 | 4p | 85 | 192.2 | 1.40 | 88.1 | 0.74 | 724.3 | 3.50 | 750 | 30 | 500 | 200 | ||
| BaGePb2 | Mg3In | 5 | 100 | 220.6 | 1.61 | 116.9 | 1.61 | 663.6 | 3.20 | 750 | 30 | 500 | 200 | ||
| SrSn2.5Pb0.5 | Mg3In | 5p | 14 | 179.7 | 2.05 | 608.8 | 5.13 | 212.3 | 1.02 | 800 | 200 | 750 | 2 | 625 | 200 |
| SrSn2Pb | PuAl3 | 6 | 32 | 164.8 | 1.88 | 445.5 | 3.75 | 389.6 | 1.88 | 800 | 200 | 750 | 2 | 625 | 200 |
| SrSn1.5Pb1.5 | PuAl3 | 6p | 34 | 152.0 | 1.73 | 307.9 | 2.59 | 539.0 | 2.60 | 700 | 20 | 500 | 200 | ||
| SrSn0.75Pb2.25 | Cu3Au | 7 | 75 | 137.1 | 1.56 | 138.7 | 1.17 | 726.0 | 3.50 | 700 | 20 | 500 | 200 | ||
| A | ⊢ Ba Compounds ⊣ | ⊢ Sr Compounds ⊣ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| Pb content, % | 28 | 47.4 | 66.3 | 78.3 | 100 | 32 | 75 | |
| Structure type | Ni3Sn | ⊢ BaSn2.6Bi0.4 ⊣ | BaPb3 | Mg3In | PuAl3 | Cu3Au | ||
| Stacking sequence | ⊢ ⊣ | |||||||
| Crystal system | ⊢ hexagonal ⊣ | ⊢ rhombohedric ⊣ | hexagonal | cubic | ||||
| Space group | ⊢ ⊣ | ⊢ ⊣ | ||||||
| ⊢ no. 194 ⊣ | ⊢ no. 166 ⊣ | no. 194 | no. 221 | |||||
| Pearson symbol | 8 | ⊢ 32 ⊣ | ⊢ 36 ⊣ | 48 | 4 | |||
| Lattice parameters, pm | a | 726.12(6) | 726.80(3) | 728.12(4) | 728.77(3) | 728.7(2) | 696.97(6) | 495.46(9) |
| c | 556.51(6) | 2235.78(14) | 2254.81(13) | 2540.6(2) | 3420.3(12) | 1675.5(2) | ||
| Volume of the u.c., pm | 254.11(5) | 1022.80(11) | 1035.25(13) | 1168.55(12) | 1572.8(11) | 704.87(15) | ||
| Volume/f.u., pm | 127.06 | 127.85 | 129.41 | 129.84 | 131.07 | 117.49 | 121.63(7) | |
| c/a | 1.5328 | 1.5380 | 1.5484 | 1.5494 | 1.5646 | 1.6027 | 1.63 | |
| Z | 2 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 12 | 6 | 1 | |
| Density (X-ray), gcm | 7.38 | 8.04 | 8.59 | 8.97 | 9.62 | 7.46 | 8.78 | |
| Diffractometer | ⊢ Stoe IPDS-II ⊣ | ⊢ APEX-II ⊣ | ||||||
| ⊢ Mo-K radiation ⊣ | ||||||||
| Absorption coefficient , mm | 44.7 | 61.7 | 76.6 | 86.2 | 103.3 | 55.7 | 92.1 | |
| range, deg | 3.2–29.1 | 1.8–29.3 | 1.8–29.3 | 2.4–29.1 | 1.8–30.0 | 3.4–29.9 | 4.1–32.5 | |
| No. of reflections collected | 3737 | 7730 | 9690 | 5106 | 5074 | 6364 | 730 | |
| No. of independent reflections | 155 | 582 | 593 | 431 | 628 | 433 | 69 | |
| 0.0723 | 0.0732 | 0.1072 | 0.2342 | 0.1131 | 0.1023 | 0.0860 | ||
| Corrections | ⊢ Lorentz, Polarisation, Absorption ⊣ | |||||||
| ⊢ XShape [21] ⊣ | ⊢ Sadabs [22] ⊣ | |||||||
| Structure refinement | ⊢ Shelxl-2013 [23] ⊣ | |||||||
| No. of free parameter | 9 | 25 | 25 | 18 | 20 | 18 | 6 | |
| Goodness-of-fit on | 1.248 | 1.372 | 1.383 | 1.116 | 0.969 | 1.243 | 1.263 | |
| R Values [for refl. with I ≥ 2(I)] | R1 | 0.0264 | 0.0437 | 0.0423 | 0.0660 | 0.0499 | 0.1182 | 0.0571 |
| wR2 | 0.0644 | 0.0934 | 0.0566 | 0.1738 | 0.1166 | 0.3585 | 0.1610 | |
| R Values (all data) | R1 | 0.0266 | 0.0485 | 0.0506 | 0.0683 | 0.0772 | 0.1270 | 0.0572 |
| wR2 | 0.0644 | 0.0948 | 0.0578 | 0.1761 | 0.1258 | 0.3642 | 0.1610 | |
| Residual elect. density, e pm | +1.2/−1.5 | +2.2/−1.8 | +2.7/−1.8 | +5.6/−1.9 | +6.4/−3.1 | +9.8/−3.7 | +7.4/−4.0 | |
| Compound | No. | Atoms | Wyckoff Position | Point Group Symmetry | Stacking Sequence | Pb Prop. /% | x | y | z | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BaSn2.16Pb0.84 | 1 | Ba | 2d | 1/3 | 2/3 | 3/4 | 263(6) | |||
| M | 6h | h | 28.0(14) | 0.14395(7) | 2x | 1/4 | 244(4) | |||
| BaSn1.58Pb1.42 | 2 | Ba(1) | 2a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 250(6) | |||
| Ba(2) | 2b | 0 | 0 | 1/4 | 201(5) | |||||
| Ba(3) | 4f | 1/3 | 2/3 | 0.13534(8) | 176(4) | |||||
| M(1) | 6h | h | 9.5(13) | 0.52781(12) | 2x | 1/4 | 202(6) | |||
| M(2) | 12k | h | 40.1(12) | 0.18965(8) | 2x | 0.62443(4) | 227(4) | |||
| Pb(3) | 6g | c | 1/2 | 0 | 0 | 266(3) | ||||
| BaSn1.01Pb1.99 | 3 | Ba(1) | 2a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 268(5) | |||
| Ba(2) | 2b | 0 | 0 | 1/4 | 211(5) | |||||
| Ba(3) | 4f | 1/3 | 2/3 | 0.13465(6) | 189(3) | |||||
| M(1) | 6h | h | 23.7(1) | 0.52645(9) | 2x | 1/4 | 210(4) | |||
| M(2) | 12k | h | 70.6(9) | 0.18753(5) | 2x | 0.62418(3) | 232(2) | |||
| Pb(3) | 6g | c | 1/2 | 0 | 0 | 262(2) | ||||
| BaSn0.65Pb2.35 | 4 | Ba(1) | 3a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 374(9) | |||
| Ba(2) | 6c | 0 | 0 | 0.21602(10) | 324(7) | |||||
| M(1) | 18h | h | 67(2) | 0.47707(12) | 0.22315(4) | 364(6) | ||||
| Pb(2) | 9e | c | 1/2 | 0 | 0 | 388(6) | ||||
| BaPb3 | 5 | Ba(1) | 6c | 0 | 0 | 0.13034(7) | 220(5) | |||
| Ba(2) | 6c | 0 | 0 | 0.28912(7) | 234(5) | |||||
| Pb(1) | 18h | h | 0.47742(8) | 0.12358(3) | 252(3) | |||||
| Pb(2) | 18h | c | 0.50625(8) | 0.29199(3) | 297(3) | |||||
| SrSn2.05Pb0.95 | 6 | Sr(1) | 2b | 0 | 0 | 1/4 | 180(20) | |||
| Sr(2) | 4f | 1/3 | 2/3 | 0.0930(5) | 185(18) | |||||
| Sn(1) | 6h | h | 0.5218(4) | 0.0436(8) | 1/4 | 182(15) | ||||
| M(2) | 12k | c | 47(4) | 0.16833(19) | 0.3367(4) | 0.58108(13) | 221(11) | |||
| SrSn0.75Pb2.25 | 7 | Sr | 1a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 500(20) | |||
| M | 3c | c | 75 | 0 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 159(9) |
| Compound | BaSn3 | BaPb3 | SrSn3 | SrPb3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structure type | Ni3Sn | BaPb3 | Mg3In | Mg3In | Cu3Au | |
| Crystal data | [5] | [11] | Table 2 and Table 3 | [3] | ||
| (all atoms) | ⊢ 127.0 pm (2.4 a.u.) ⊣ | |||||
| ⊢ 8.0 ⊣ | ||||||
| k-points/BZ | 820 | 1000 | ⊢ 1000 ⊣ | 1295 | ||
| k-points/IBZ | 72 | 110 | ⊢ 110 ⊣ | 75 | ||
| Monkhorst-Pack-Grid | 9 × 9 × 10 | 10 × 10 × 10 | ⊢ 10 × 10 × 10 ⊣ | 10 × 10 × 9 | ||
| DOS | ⊢ Figure 12 ⊣ | |||||
| Band structure | [3,10,11] | [3] | [10,11] | |||
| Bonds: | label | |||||
| Electron | a | 0.237 (305.9) | 0.204 (319.3) | 0.218 (315.0) | 0.245 (302.6) | 0.125 (351.4) |
| density | b | 0.171 (326.7) | 0.143 (343.7) | 0.138 (346.4) | 0.168 (339.2) | |
| at BCP/RCP(r) | c | 0.138 (345.3) | 0.136 (346.6) | 0.147 (329.2) | ||
| d | 0.109 (364.5) | 0.133 (347.8) | 0.159 (334.6) | |||
| (d [pm]) | e | 0.131 (350.7) | 0.150 (337.4) | |||
| f | 0.093 (378.0) | 0.116 (359.4) | ||||
| r | 0.190 | 0.152 | 0.164 | 0.198 | 0.088 | |
| Atoms: | label | |||||
| Charge | Sr/Ba(1) | +1.137 (28.6) | +1.093 (28.6) | +1.071 (28.5) | +1.255 (20.1) | +1.233 (20.3) |
| distribution | Sr/Ba(2) | +1.067 (28.4) | +1.069 (28.2) | +1.249 (19.8) | ||
| after Bader | Sn/Pb(1) | −0.379 (32.1) | −0.359 (34.0) | −0.370 (33.9) | −0.440 (31.5) | −0.418 (34.5) |
| ( ) | Sn/Pb(2) | −0.358 (34.5) | −0.344 (34.5) | −0.395 (31.6) | ||
| Atoms | Distance | freq. | CN | Atoms | Distance | lbl. | freq. | CN | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ba | –M | 364.2(1) | 6× | M | –M | 313.6(2) | a | 2× | ||
| –M | 366.3(1) | 6× | 12 | –M | 332.0(1) | b | 4× | |||
| –Ba | 364.2(1) | 2× | ||||||||
| –Ba | 366.3(1) | 2× | 10 | |||||||
| –M | 412.6(2) | 2× | +2 | |||||||
| Atoms | Distances in | freq. | CN | Atoms | Distances in | lbl. | freq. | CN | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | |||||||||
| Ba(1) | –Pb(3) | 363.4(1) | 364.1(1) | 6× | M(1) | –M(1) | 302.8(3) | 306.3(2) | a | 2× | ||
| –M(2) | 366.6(1) | 366.5(1) | 6× | 12 | –M(2) | 332.4(1) | 336.2(1) | b | 4× | |||
| –Ba(3) | 354.5(2) | 356.3(1) | 2× | |||||||||
| –Ba(2) | 365.1(1) | 365.6(1) | 2× | 6 + 4 | ||||||||
| Ba(2) | –M(1) | 365.1(1) | 365.6(2) | 6× | ||||||||
| –M(2) | 368.5(1) | 369.4(1) | 6× | 12 | M(2) | –M(2) | 313.3(2) | 318.5(1) | c | 2× | ||
| –M(1) | 332.4(1) | 336.2(1) | b | 2× | ||||||||
| Ba(3) | –M(1) | 354.5(2) | 356.3(1) | 3× | –Pb(3) | 340.9(1) | 343.1(1) | d | 2× | |||
| –M(2) | 365.4(1) | 365.8(1) | 6× | –Ba(3) | 365.4(1) | 365.8(1) | 2× | |||||
| –Pb(3) | 368.2(2) | 369.3(1) | 3× | 12 | –Ba(1) | 366.6(1) | 366.5(1) | |||||
| –Ba(2) | 368.5(1) | 369.4(1) | 6 + 4 | |||||||||
| Pb(3) | –M(2) | 340.9(1) | 343.1(1) | d | 4× | |||||||
| –Pb(3) | 363.4(1) | 364.1(1) | e | 4× | ||||||||
| –Ba(1) | 363.4(1) | 364.1(1) | 2× | |||||||||
| –Ba(3) | 368.2(2) | 369.3(1) | 2× | 8 + 4 | ||||||||
| Atoms | Distance | freq. | CN | Atoms | Distance | lbl. | freq. | CN | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ba(1) | –M(1) | 360.0(2) | 3× | M(1) | –M(1) | 314.2(3) | a | 2× | ||
| –Pb(2) | 364.8(2) | 3× | –M(1) | 339.5(2) | b | 2× | ||||
| –M(1) | 366.0(1) | 6× | 12 | –Pb(2) | 342.6(1) | c | 2× | |||
| –Ba(1) | 360.0(2) | |||||||||
| Ba(2) | –Pb(2) | 364.4(1) | 6× | –Ba(1) | 366.0(1) | 2× | ||||
| –M(1) | 368.3(1) | 6× | 12 | –Ba(2) | 368.3(1) | 6 + 4 | ||||
| Pb(2) | –M(1) | 342.6(1) | c | 4× | ||||||
| –Pb(2) | 364.4(1) | d | 4× | |||||||
| –Ba(2) | 364.4(1) | 2× | ||||||||
| –Ba(1) | 364.8(2) | 2× | 8 + 4 | |||||||
| Atoms | Distance | freq. | CN | Atoms | Distance | lbl. | freq. | CN | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ba(1) | –Pb(1) | 361.7(2) | 3× | Pb(1) | –Pb(1) | 315.0(2) | a | 2× | ||
| –Pb(2) | 365.6(2) | 3× | –Pb(1) | 346.4(2) | b | 2× | ||||
| –Pb(1) | 366.2(1) | 6× | 12 | –Pb(2) | 346.6(1) | c | 2× | |||
| –Ba(2) | 361.6(2) | |||||||||
| Ba(2) | –Pb(1) | 361.6(2) | 3× | –Ba(1) | 361.7(2) | |||||
| –Pb(2) | 364.6(1) | 6× | –Ba(1) | 366.2(1) | 2× | 6 + 4 | ||||
| –Pb(2) | 365.0(2) | 3× | 12 | |||||||
| Pb(2) | –Pb(1) | 346.6(1) | c | 2× | ||||||
| –Pb(2) | 347.8(2) | d | 2× | |||||||
| –Pb(2) | 350.7(2) | e | 2× | |||||||
| –Ba(2) | 364.6(1) | 2× | ||||||||
| –Ba(2) | 365.0(2) | |||||||||
| –Ba(1) | 365.6(2) | |||||||||
| –Pb(2) | 378.0(2) | f | 2× | 6 + 4 + 2 | ||||||
| Atoms | Distance | freq. | CN | Atoms | Distance | lbl. | freq. | CN | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sr(1) | –M(2) | 348.4(2) | 6× | Sn(1) | –Sn(1) | 302.9(8) | a | 2× | ||
| –Sn(1) | 349.5(1) | 6× | 12 | –M(2) | 339.9(2) | b | 4× | |||
| –Sr(2) | 347.8(6) | 2× | ||||||||
| Sr(2) | –Sn(1) | 347.8(6) | 3× | –Sr(1) | 349.5(1) | 2× | 6 + 4 | |||
| –M(2) | 349.1(1) | 6× | –Sn(1) | 394.1(8) | 2× | |||||
| –M(2) | 353.2(7) | 3× | 12 | |||||||
| M(2) | –M(2) | 339.3(4) | c | 2× | ||||||
| –Sn(1) | 339.9(2) | b | 2× | |||||||
| –M(2) | 345.0(4) | d | 2× | |||||||
| –Sr(1) | 348.4(2) | |||||||||
| –Sr(2) | 349.1(1) | 2× | ||||||||
| –M(2) | 352.0(4) | e | 2× | |||||||
| –Sr(2) | 353.2(7) | 8 + 4 | ||||||||
| Atoms | Distance | freq. | CN | Atoms | Distance | lbl. | freq. | CN | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sr | –M | 350.3(1) | 12× | 12 | M | –M | 350.3(1) | a | 6× | |
| –Sr | 350.3(1) | 6× | 6 + 6 | |||||||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Langenmaier, M.; Jehle, M.; Röhr, C. Mixed Sr and Ba Tri-Stannides/Plumbides AII(Sn1−xPbx)3. Crystals 2018, 8, 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8050204
Langenmaier M, Jehle M, Röhr C. Mixed Sr and Ba Tri-Stannides/Plumbides AII(Sn1−xPbx)3. Crystals. 2018; 8(5):204. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8050204
Chicago/Turabian StyleLangenmaier, Michael, Michael Jehle, and Caroline Röhr. 2018. "Mixed Sr and Ba Tri-Stannides/Plumbides AII(Sn1−xPbx)3" Crystals 8, no. 5: 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8050204
APA StyleLangenmaier, M., Jehle, M., & Röhr, C. (2018). Mixed Sr and Ba Tri-Stannides/Plumbides AII(Sn1−xPbx)3. Crystals, 8(5), 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8050204