A Study of the Structural Organization of Water and Aqueous Solutions by Means of Optical Microscopy
Abstract
:“…a scientist must also be absolutely like a child. If he sees a thing, he must say that he sees it, whether it was what he thought he was going to see or not. See first, think later, then test. But always see first. Otherwise you will only see what you were expecting. Most scientists forget that. I’ll show you something to demonstrate that later. … You can’t possibly be a scientist if you mind people thinking that you’re a fool.”Douglas Adams.“So long, and thanks for all the fish” (“The Hitch Hiker’s Guide to the Galaxy” #4)
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. The Essence of the Phenomenon
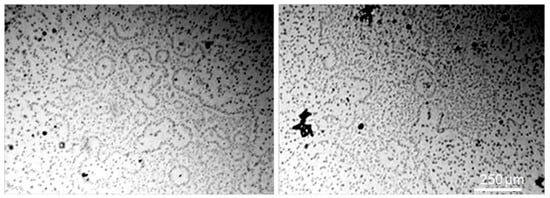
3.2. Glass Surface under Optical Microscope
3.3. Coacervation of the Dispersed Water System. Formation of a New Phase
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malenkov, G.G. Structure and dynamics of liquid water. J. Struct. Chem. 2006, 47, S5–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkisov, G.N. Structural models of water. Phys. Usp. 2006, 49, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, S.D.; Mosyagina, I.V. Cluster Structure of Water (Review). Available online: preprints.lebedev.ru/wp-content/uploads/2011/12/35_11_pr.pdf (accessed on 11 December 2011). (In Russian).
- Zakharov, S.D.; Zyuzin, M.V.; Mosyagina, I.V. Water: Microstructure and Fluctuations. Available online: http://www.biophys.ru/archive/h2o-00027.pdf (accessed on 27 January 2012). (In Russian).
- Nilsson, A.; Pettersson, L.G.M. Perspective on the structure of liquid water. Chem. Phys. 2011, 389, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mel’nichenko, N.A. Structure and dynamical properties of liquid water. Vestn. Far East Branch Russ. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1, 65–74. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Tsivadze, A.Y. (Ed.) Structural Self-Organization in Solutions and at the Interface of Phases; Editorial URSS: Moscow, Russia, 2008; 544p, ISBN 978-5-382-00796-0. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Wikfeldt, K.T.; Tokushima, T.; Nordlund, D.; Harada, Y.; Bergmann, U.; Niebuhr, M.; Weiss, T.M.; Horikawa, Y.; Leetmaa, M.; et al. The inhomogeneous structure of water at ambient conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 15214–15218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Speedy, R.J.; Angell, C.A. Isothermal compressibility of supercooled water and evidence for a thermodynamic singularity at −45 °C. J. Chem. Phys. 1976, 65, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pool, P.H.; Sciortino, F.; Essmann, U.; Stanley, H.E. Phase behavior of metastable water. Nature 1992, 360, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angell, C.A. Insights into phases of liquid water from study of its unusual glass-forming properties. Science 2008, 319, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, O.; Stanley, H.E. The relationship between liquid, supercooled and glassy water. Nature 1998, 396, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striolo, A. From interfacial water to macroscopic observables: A review. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2011, 29, 211–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Skinner, J.L. Evidence for a liquid-liquid critical point in supercooled water within the E3B3 model and a possible interpretation of the kink in the homogeneous nucleation line. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 144, 214501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ito, K.; Yoshida, H.; Ise, N. Void Structure in colloidal dispersions. Science 1994, 263, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ise, N. When, why, and how does like like like. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2007, 83, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ise, N.; Matsuoka, H.; Ito, K.; Yoshida, H.; Yamanaka, J. Ordering of latex particles and ionic polymers in solutions. Langmuir 1990, 6, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ise, N. Like likes like: Counterion-mediated attraction in macroionic and colloidal interaction. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 10279–10287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, H.; Ise, N.; Hashimoto, T. Restricted motion of a particle trapped inside a void in a colloidal dispertion. Langmuir 1995, 11, 2853–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhno, T.A.; Yakhno, V.G. The coffee-drop phenomenon and its time fluctuations: Self-sustained oscillations in colloidal liquids. Tech. Phys. 2017, 62, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhno, T.A.; Yakhno, V.G. Water-induced self-oscillatory processes in colloidal systems by the example of instant coffee. J. Basic Appl. Res. Int. 2017, 20, 70–83. [Google Scholar]
- Bunkin, N.F.; Bunkin, F.V. Bubbstons: Stable microscopic gas bubbles in very dilute electrolytic solutions. Sov. Phys. JETP 1992, 74, 271–278. [Google Scholar]
- Bunkin, N.F.; Bunkin, F.V. Bubston structure of water and electrolyte water solutions. Phys. Usp. 2016, 59, 846–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunkin, N.F.; Shkirin, A.V.; Kozlov, V.A.; Starosvetskij, A.V. Laser scattering in water and aqueous solutions of salts. Proc. SPIE 2010, 7376, 73761D. [Google Scholar]
- Bunkin, N.F.; Ninham, B.W.; Ignatiev, P.S.; Kozlov, V.A.; Shkirin, A.V.; Starosvetskij, A.V. Long-living nanobubbles of dissolved gas in aqueous solutions of salts and erythrocyte suspensions. J. Biophotonics 2011, 4, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunkin, N.F.; Shkirin, A.V.; Suyazov, N.V.; Yurchenko, S.O. Structure of the nanobubble clusters of dissolved air in liquid media. J. Biol. Phys. 2012, 38, 121–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunkin, N.F.; Shkirin, A.V.; Suyazov, N.V.; Starosvetskij, A.V. Calculations of light scattering matrices for stochastic ensembles of nanosphere clusters. J. Quant. Spectr. Rad. Trans. 2013, 123, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunkin, N.F.; Bunkin, F.V. Bubston structure of water and aqueous solutions of electrolytes. Phys. Wave Phenom. 2013, 21, 81–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunkin, N.F.; Shkirin, A.V.; Kozlov, V.A.; Starosvetsky, A.V.; Ignatiev, P.S. Quasistable clusters of nanobubbles of dissolved gas in water and aqueous solutions of electrolytes. Nanosyst. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2011, 9, 499–504. [Google Scholar]
- Bukaty, V.I.; Nesteruk, P.I. Investigation of optical inhomogeneities (clusters) in bidistilled water by the optical method of small angles. Polzunovskiy Vestn. 2011, 3, 106–108. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Bukaty, V.I.; Nesteruk, P.I. Development of a measuring and computing complex and a method of small scattering angles to control optical inhomogeneities (clusters) in bidistilled water after the action of a magnetic field. Electron. Phys. Technol. J. 2012, 7, 1–10. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Fesenko, E.E.; Terpugov, E.L. On the unusual spectral properties of water in a thin layer. Biofizika 1999, 44, 5–9. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Smirnov, A.N.; Lapshin, V.B.; Balyshev, A.V.; Lebedev, I.M.; Syroeoshkin, A.V. Supranadmolecular Complexes of Water. Electron. J. Investig. Russia 2014, 413–421. Available online: http://zhurnal.ape.relarn.ru/articles/2004/038.pdf (accessed on 13 May 2004). (In Russian).
- Goncharuk, V.V.; Smirnov, V.N.; Syroeshkin, A.V.; Malyarenko, V.V. Clusters and giant heterophase clusters of water. Chem. Technol. Water 2007, 29, 3–17. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Sedlák, M. Large-scale supramolecular structure in solutions of low molar mass compounds and mixtures of liquids: I. Light scattering characterization. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 4329–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laptev, B.I.; Sidorenko, G.N.; Gorlenko, N.P.; Kulchenko, A.K.; Sarkisov, Y.S.; Antoshkin, L.V. Evaluation of the structure of water and aqueous solutions of sodium chloride using dielectrometry and resonance method. Vestn. TSUAB 2013, 2, 235–244. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Maestro, L.M.; Marqués, M.I.; Camarillo, E.; Jaque, D.; García Solé, J.; Gonzalo, J.A.; Jaque, F.; del Valle, J.C.; Mallamace, F.; Stanley, H.E. On the existence of two states in liquid water: Impact on biological and nanoscopic systems. Int. J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 13, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, P.; Amann-Winkel, K.; Angell, C.A.; Anisimov, M.A.; Caupin, F.; Chakravarty, C.; Lascaris, E.; Loerting, T.; Panagiotopoulos, A.Z.; Russo, J.; et al. Water: A Tale of Two Liquids. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 7463–7500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakhno, T.A.; Yakhno, V.G.; Zanozina, V.F. Phase transitions of water as a source of slow oscillatory processes in liquid media. In Proceedings of the XII International Science-Technical Conference “Modern Trends in Biological Physics and Chemisitry”, Sevastopol, Russia, 2–6 October 2017; pp. 23–27. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott, E.R.; Stromberg, R.R.; Grant, W.H.; Cessac, G.L. Polywater. Science 1969, 164, 1482–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deryagin, B.V. New Data on Superdense Water. Phys. Usp. 1970, 13, 305–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.E.; Rousseau, D.L.; Board, R.D. “Polywater”: Evidence from electron microscopy for chemical analysis (ESCA) of a complex salt mixture. Science 1971, 171, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, D.L.; Porto, S.P. Polywater: Polymer or artifact? Science 1970, 167, 1715–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, D.L. “Polywater” and sweat: Similarities between the infrared spectra. Science 1971, 171, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakhno, T.A.; Drozdov, M.N.; Yakhno, V.G. Giant Water Clusters: Where Are They From? 2018. Available online: https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1810/1810.05452.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2018).
- Internet Resource. Available online: http://www.vegasd.ru/whats_glass_surface (accessed on 21 March 2011).
- Ewing, G.E. Ambient thing film water on insulator surfaces. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 1511–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spagnoly, C.; Loos, K.; Ulman, A.; Cowman, M.K. Imaging structured water and bound polysaccharide on mica surface at ambient temperature. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 7124–7128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aarts, I.M.P.; Pipino, A.C.R.; Hoefnagels, J.P.M.; Kessels, W.M.M.; van de Sanden, M.C.M. Quasi-ice monolayer on atomically smooth amorphous SiO2 at room temperature observed with a high-finesse optical resonator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 166104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asay, D.B.; Kim, S.H. Evolution of the adsorbed water layer structure on silicon oxide at room temperature. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 16760–16763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teschke, O. Imaging ice-like structures formed on HOPG at room temperature. Langmuir 2010, 26, 16986–16990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutskov, A.P. A Short Course of Colloid Chemistry; Goskhimizdat: Moscow, Russia, 1958; p. 133. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, R.; Stokes, R. Solutions of Electrolytes. Translation from English; Frumkin, A.N., Ed.; Foreign Literature: Moscow, Russia, 1963; 647p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- IPCC Third Assessment Report: Climate Change 2001 (TAR). Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/ipccreports/tar/wg1/pdf/WGI_TAR_full_report.pdf (accessed on 16 September 2001).
- Warneck, P. Chemistry of the Natural Atmosphere; Academic: San Diego, CA, USA, 1988; 753p, ISBN 9780080529066. [Google Scholar]
- Akhverdov, I.N. Fundamentals of Concrete Physics; Stroiizdat: Moscow, Russia, 1981; 462p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dumansky, A.V. Lyophilicity of Disperse Systems; VSU: Voronezh, Russia, 1940; 153p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, M. Mechanical Properties of Soils; Stroiizdat: Moscow, Russia, 1971; 368p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsova, T.V.; Kudryashov, I.V.; Timashev, V.V. Physical Chemistry of Astringent Materials; Higher School: Moscow, Russia, 1989; 384p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Colten, H.; Antonietti, M. Mesocrystals: Inorganic superstructures made by highly parallel crystallization and controlled alignment. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 5576–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, E.V.; Colfen, H. Mesocrystals: Past, presence, future. Crystals 2007, 7, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, Y.; Tokuyama, M. Novel liquid- and crystal-droplet phases on highly charged colloidal suspensions. Phys. A 2004, 334, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Internet Resource. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Purified_water#Distillation (accessed on 23 September 2015).
- Calvin, M. Chemical Evolution; Molecular Evolution towards the Origin of Living Systems on the Earth and Elsewhere; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1969; 278p. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, S.W. Simulated Natural Experiments in Spontaneous Organization of Morphological Units from Proteinoid. The Origin of Prebiological Systems and of Their Molecular Matrices; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1965; pp. 361–373. [Google Scholar]
- Oparin, A.I. The origin of life on the Earth; Dovel Publication, Inc.: Mineola, NY, USA, 1953; 270p. [Google Scholar]
- Nasonov, D.N.; Alexandrov, V.Y. The Reaction of Living Matter to External Influences; USSR Academy of Sciences: Moscow, Russia, 1940; 261p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ling, G. The Physical Theory of a Living Cell. Unnoticed Revolution; Nauka: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2008; 376p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Bul’enkov, N.A. On the possible role of hydration as the leading integration factor in the organization of biosystems at different levels of their hierarchy. Biofizika 1991, 36, 181–242. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]


















| Contaminant | Parameter | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ions | Resistivity at 25 °C [MΩ·cm] | 10 | 1 | 0.2 |
| Conductivity at 25 °C [μS·cm−1] | 0.1 | 1.0 | 5.0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yakhno, T.; Yakhno, V. A Study of the Structural Organization of Water and Aqueous Solutions by Means of Optical Microscopy. Crystals 2019, 9, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9010052
Yakhno T, Yakhno V. A Study of the Structural Organization of Water and Aqueous Solutions by Means of Optical Microscopy. Crystals. 2019; 9(1):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9010052
Chicago/Turabian StyleYakhno, Tatiana, and Vladimir Yakhno. 2019. "A Study of the Structural Organization of Water and Aqueous Solutions by Means of Optical Microscopy" Crystals 9, no. 1: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9010052
APA StyleYakhno, T., & Yakhno, V. (2019). A Study of the Structural Organization of Water and Aqueous Solutions by Means of Optical Microscopy. Crystals, 9(1), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9010052