Decreasing the Residual DC Voltage by Neutralizing the Charged Mobile Ions in Liquid Crystals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
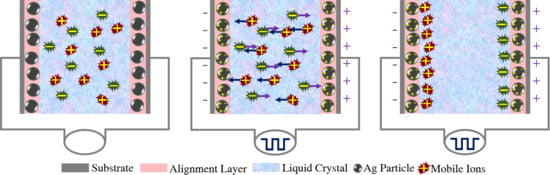
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mizusaki, M.; Miyashita, T.; Uchida, T. Generation mechanism of residual direct current voltage in a liquid crystal display and its evaluation parameters related to liquid crystal and alignment layer materials. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102, 014904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizusaki, M.; Miyashita, T.; Uchida, T. Behavior of ion affecting image sticking on liquid crystal displays under application of direct current voltage. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 104903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizusaki, M.; Miyashita, T.; Uchida, T. Kinetic analysis of image sticking with adsorption and desorption of ions to a surface of an alignment layer. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 044510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Peng, F.; Chen, H.; Yuan, J.; Wu, S.-T.; Li, M.-C.; Lee, S.-L.; Tsai, W.-C. Image sticking in liquid crystal displays with lateral electric fields. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 193102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kwon, Y.R.; Ahn, S.H.; Srivastava, A.K.; Lee, S.H. Investigation on ion movement in the fringe-field switching mode depending on resistivity of alignment layer and dielectric anisotropic sign of liquid crystal. Liq. Cryst. 2015, 42, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-A.; Yang, K.-H. Ionic effects on electro-optics and residual direct current voltages of twisted nematic liquid crystal cells. Liq. Cryst. 2018, 45, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seen, S.M.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, S.H. Image Sticking Resistant Liquid Crystal Display Driven by Fringe Electric Field for Mobile Applications. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 49, 050208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, N.; Jung, J.; Cheong, B.; Yoon, H.; Hong, M. Reduction of residual DC voltage via RC matching in LCD. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 126305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Dai, Y.; Li, T.; Tang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Li, Z.; Meng, X.; He, Z.; Li, J.; Cai, M.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Xing, H.; Ye, W. Enhancement of Image Quality in LCD by Doping γ-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles and Reducing Friction Torque Difference. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, D.; Miyake, T.; Sugimoto, M. A mechanism of short-term image-sticking phenomenon caused by flexoelectric effect in IPS LCD. IEICE T. Electr. 2018, E101-C, 846–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, C.; Kim, T.; Kang, H. Liquid crystal alignment behaviors on capsaicin substituted polystyrene films. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 41376–41383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizusaki, M.; Enomoto, S.; Hara, Y. Generation mechanism of residual direct current voltage for liquid crystal cells with polymer layers produced from monomers. Liq. Cryst. 2017, 44, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-T.; Chen, P.-S.; Chao, C.-Y. Effect of doped insulating nanoparticles on the electro-optical characteristics of nematic liquid crystals. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 48, 015006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.M.; Chung, H.-K.; Park, H.-G.; Jeong, H.-C.; Han, J.-J.; Cho, M.-J.; Lee, J.-W.; Seo, D.-S. Residual DC voltage-free behaviour of liquid crystal system with nickel nanoparticle dispersion. Liq. Cryst. 2014, 41, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Seo, D.-S.; Li, X.-D. Ion-beam-spurted dimethyl-sulfate-doped PEDOT: PSS composite-layer-aligning liquid crystal with low residual direct-current voltage. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 101901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Oh, B.-Y.; Seo, D.-S.; Li, X.-D. Super-fast switching of liquid crystals sandwiched between highly conductive graphene oxide/dimethyl sulfate doped PEDOT: PSS composite layers. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 194505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Park, H.-G.; Lee, J.H.; Seo, D.-S.; Kim, E.-M.; Heo, G.-S. Electro-optical switching of liquid crystals sandwiched between ion-beam-spurted graphene quantum dots-doped PEDOT: PSS composite layers. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 34071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.R.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Jun, M.C.; Baik, H.K. Investigation on newly designed low resistivity polyimide-type alignment layer for reducing DC image sticking of in-plane switching liquid crystal display. Liq. Cryst. 2017, 44, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, Y.; Hanaoka, K.; Shibasaki, M.; Okamoto, K. Relation between monomer structure and image sticking phenomenon of polymer-sustained-alignment liquid crystal displays. Jpn.J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 50, 051702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.J.; Jeong, I.H.; Kang, H.-S.; Kundu, S.; Lee, M.-H.; Lee, S.H. Reduction of the residual DC in the photoaligned twisted nematic liquid crystal display using polymerized reactive mesogen. Appl. Phys. Express 2012, 5, 081701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.-C.; Yaroshchuk, O.; Bidna, T.; Srivastava, A.K.; Chigrinov, V.; Kwok, H.-S. Strengthening of liquid crystal photoalignment on azo dye films: passivation by reactive mesogens. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 48181–48188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.-J.; Hwang, J.-Y.; Seo, D.-S.; Kim, H.-Y. Voltage holding ratio and residual DC property of the IPS-LCD on rubbed polymer layers by voltage-transmittance hysteresis method. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2004, 410, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Seo, D.-S. Ion beam fabrication of aluminum-doped zinc oxide layer for high-performance liquid crystals alignment. Optic. Express 2016, 24, 17424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Ag-s-PI | Ag-s-rPI | Ag-d-PI | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vrdc+ | Vrdc− | Vrdc | Vrdc+ | Vrdc− | Vrdc | Vrdc+ | Vrdc− | Vrdc | |
| 0.2 | 0.6735 | 0.5899 | 0.6317 | 0.7455 | 0.8417 | 0.7936 | 0.4915 | 0.5107 | 0.5011 |
| 0.5 | 0.6371 | 0.6685 | 0.6528 | 0.8900 | 0.8608 | 0.8754 | 0.3234 | 0.3518 | 0.3376 |
| 1.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.2121 | 0.2049 | 0.2085 |
| 2.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.1091 | 0.1173 | 0.1132 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Sang, J.; Liu, H.; Xu, H.; Zhao, S.; Sun, J.; Lee, J.H.; Jeong, H.-C.; Seo, D.-S. Decreasing the Residual DC Voltage by Neutralizing the Charged Mobile Ions in Liquid Crystals. Crystals 2019, 9, 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9040181
Liu Y, Sang J, Liu H, Xu H, Zhao S, Sun J, Lee JH, Jeong H-C, Seo D-S. Decreasing the Residual DC Voltage by Neutralizing the Charged Mobile Ions in Liquid Crystals. Crystals. 2019; 9(4):181. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9040181
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yang, Jingxin Sang, Hao Liu, Haiqin Xu, Shuguang Zhao, Jiatong Sun, Ju Hwan Lee, Hae-Chang Jeong, and Dae-Shik Seo. 2019. "Decreasing the Residual DC Voltage by Neutralizing the Charged Mobile Ions in Liquid Crystals" Crystals 9, no. 4: 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9040181
APA StyleLiu, Y., Sang, J., Liu, H., Xu, H., Zhao, S., Sun, J., Lee, J. H., Jeong, H. -C., & Seo, D. -S. (2019). Decreasing the Residual DC Voltage by Neutralizing the Charged Mobile Ions in Liquid Crystals. Crystals, 9(4), 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst9040181