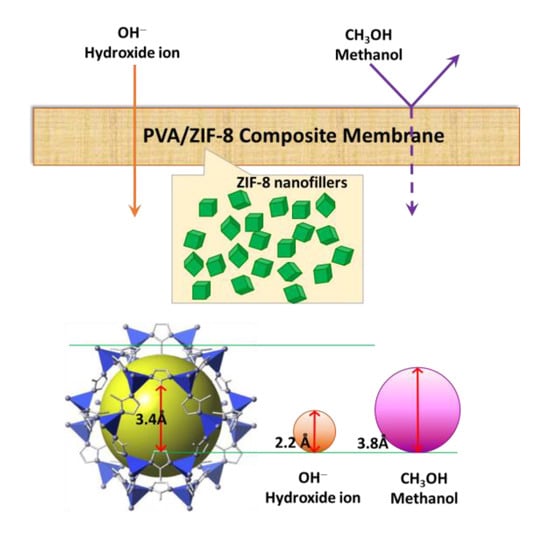
Highly Zeolite-Loaded Polyvinyl Alcohol Composite Membranes for Alkaline Fuel-Cell Electrolytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. ZIF-8 Synthesis and PVA/ZIF-8 Composite Preparation
2.2. Physical–Chemical Properties of ZIF-8 Particles and Membranes
2.3. Electrolyte Conductivity
2.4. Methanol Permeability Measurement
2.5. Cell Performance Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology and Crystallinity of PVA and PVA/ZIF-8 Composites
3.2. Alkali Uptake and Ionic Conductivity of KOH-Doped PVA and PVA/ZIF-8 Composites
3.3. Methanol Permeability through KOH-Doped Membranes
3.4. Effect of ZIF-8 on Fuel-Cell Performance
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pourzare, K.; Mansourpanah, Y.; Farhadi, S. Advanced nanocomposite membranes for fuel cell applications: A comprehensive review. Biofuel Res. J. 2016, 3, 496–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalia, A.; Bella, F.; Lamberti, A.; Bianco, S.; Gerbaldi, C.; Tresso, E.; Pirri, C.F. A flexible and portable powerpack by solid-state supercapacitor and dye-sensitized solar cell integration. J. Power Sources 2017, 359, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanti, R.; Bella, F.; Salim, Y.; Chee, S.; Ramesh, S.; Ramesh, K. Poly (methyl methacrylate-co-butyl acrylate-co-acrylic acid): Physico-chemical characterization and targeted dye sensitized solar cell application. Mater. Des. 2016, 108, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colò, F.; Bella, F.; Nair, J.R.; Gerbaldi, C. Light-cured polymer electrolytes for safe, low-cost and sustainable sodium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2017, 365, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Abdullah, O.G.; Hussein, S.A.; Ahmed, H.M. Effect of PVA blending on structural and ion transport properties of CS: AgNt-based polymer electrolyte membrane. Polymers 2017, 9, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Fu, Y.; Manthiram, A. Novel blend membranes based on acid-base interactions for fuel cells. Polymers 2012, 4, 1627–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolini, E.; Lopes, T.; Gonzalez, E.R. An overview of platinum-based catalysts as methanol-resistant oxygen reduction materials for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 461, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, A.H.P.; Nascimento, M.L.F.; de Oliveira, H.P. Preparation of KOH-doped PVA/PSSA solid polymer electrolyte for DMFC: The influence of TiO2 and PVP on performance of membranes. Fuel Cells 2016, 16, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibino, T.; Shen, Y.; Nishida, M.; Nagao, M. Hydroxide ion conducting antimony (v)-doped tin pyrophosphate electrolyte for intermediate-temperature alkaline fuel cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10786–10790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Cruz, L.; Casado-Coterillo, C.; Iniesta, J.; Montiel, V.; Irabien, Á. Chitosan: Poly (vinyl) alcohol composite alkaline membrane incorporating organic ionomers and layered silicate materials into a PEM electrochemical reactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 498, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tadanaga, K.; Furukawa, Y.; Hayashi, A.; Tatsumisago, M. Direct ethanol fuel cell using hydrotalcite clay as a hydroxide ion conductive electrolyte. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4401–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lue, S.J.; Mahesh, K.P.O.; Wang, W.-T.; Chen, J.-Y.; Yang, C.-C. Permeant transport properties and cell performance of potassium hydroxide doped poly(vinyl alcohol)/fumed silica nanocomposites. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 367, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.-S.; Cheng, M.-Y.; Xie, X.-L.; Rick, J.; Huang, Y.-J.; Chang, F.-C.; Hwang, B.-J. Alkali doped polyvinyl alcohol/graphene electrolyte for direct methanol alkaline fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2013, 239, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Aulich, T. High activity and durability of Pt catalyst toward methanol electrooxidation in intermediate temperature alkaline media. J. Power Sources 2012, 209, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merle, G.; Wessling, M.; Nijmeijer, K. Anion exchange membranes for alkaline fuel cells: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 377, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Yamazaki, Y.; Kim, J.-D.; Kudo, T.; Honma, I. High ionic conductivity of Mg–Al layered double hydroxides at intermediate temperature (100–200 °C) under saturated humidity condition (100% RH). Solid State Ion. 2010, 181, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh Kumar, S.; Ma, W.-T.; Lu, H.-C.; Teng, L.-W.; Hsu, H.-C.; Shih, C.-M.; Yang, C.-C.; Lue, S.J. Surfactant-Assisted Perovskite Nanofillers Incorporated in Quaternized Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) Composite Membrane as an Effective Hydroxide-Conducting Electrolyte. Energies 2017, 10, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Hu, C.; Jiang, Z. Novel ploy(vinyl alcohol)/carbon nanotube hybrid membranes for pervaporation separation of benzene/cyclohexane mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 297, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D. Preparation and characterization of crosslinked PVA/SiO2 hybrid membranes containing sulfonic acid groups for direct methanol fuel cell applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 240, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Shi, J.; Zou, X.; Wang, S.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Zhang, W.; Holmes, M. Novel colorimetric films based on starch/polyvinyl alcohol incorporated with roselle anthocyanins for fish freshness monitoring. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 69, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praptowidodo, V.S. Influence of swelling on water transport through PVA-based membrane. J. Mol. Struct. 2005, 739, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sairam, M.; Patil, M.; Veerapur, R.; Patil, S.; Aminabhavi, T. Novel dense poly(vinyl alcohol)–TiO2 mixed matrix membranes for pervaporation separation of water–isopropanol mixtures at 30 °C. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lue, S.J.; Chen, J.-Y.; Yang, J.M. Crystallinity and Stability of Poly(vinyl alcohol)-Fumed Silica Mixed Matrix Membranes. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2008, 47, 39–51. [Google Scholar]
- Lue, S.; Lee, D.; Chen, J.; Chiu, C.; Hu, C.; Jean, Y.; Lai, J. Diffusivity enhancement of water vapor in poly(vinyl alcohol)–fumed silica nano-composite membranes: Correlation with polymer crystallinity and free-volume properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.-H.; Lue, S.J.; Chang, C.-M.; Liu, Y.-L. Alkali doped polyvinyl alcohol/multi-walled carbon nano-tube electrolyte for direct methanol alkaline fuel cell. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 376, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lue, S.J.; Wang, W.-T.; Mahesh, K.P.O.; Yang, C.-C. Enhanced performance of a direct methanol alkaline fuel cell (DMAFC) using a polyvinyl alcohol/fumed silica/KOH electrolyte. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 7991–7999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Qiao, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, J.; Okada, T. Alkali doped poly(vinyl alcohol) for potential fuel cell applications. Synth. Met. 2010, 160, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-F.; Lo, C.-F.; Li, L.-Y.; Li, H.-Y.; Chang, C.-M.; Liao, K.-S.; Hu, C.-C.; Liu, Y.-L.; Lue, S.J. Thermally stable polybenzimidazole/carbon nano-tube composites for alkaline direct methanol fuel cell applications. J. Power Sources 2014, 246, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Chung, W.-J.; Pinnau, I.; Song, J.; Du, N.; Robertson, G.P.; Guiver, M.D. Gas transport behavior of mixed-matrix membranes composed of silica nanoparticles in a polymer of intrinsic microporosity (PIM-1). J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 346, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, Y.H.; Chen, J.T.; Chang, C.H.; Liao, K.S.; Tung, K.L.; Price, W.E.; Yamauchi, Y.; Wu, K.C. A Drying-Free, Water-Based Process for Fabricating Mixed-Matrix Membranes with Outstanding Pervaporation Performance. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 12793–12796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venna, S.R.; Carreon, M.A. Highly Permeable Zeolite Imidazolate Framework-8 Membranes for CO2/CH4 Separation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, A.; Doonan, C.J.; Uribe-Romo, F.J.; Knobler, C.B.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Synthesis, structure, and carbon dioxide capture properties of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Xia, Y. Zeolitic imidazolate framework materials: Recent progress in synthesis and applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 16811–16831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Wang, H. Zeolitic imidazolate framework composite membranes and thin films: Synthesis and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 4470–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allendorf, M.D.; Schwartzberg, A.; Stavila, V.; Talin, A.A. A roadmap to implementing metal-organic frameworks in electronic devices: Challenges and critical directions. Chemistry 2011, 17, 11372–11388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.S.; Liang, F.Y.; Bux, H.; Feldhoff, A.; Yang, W.S.; Caro, J. Molecular sieve membrane: Supported metal-organic framework with high hydrogen selectivity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liang, F.; Bux, H.; Yang, W.; Caro, J. Zeolitic imidazolate framework ZIF-7 based molecular sieve membrane for hydrogen separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 354, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.L.; Le, K.K.A.; Phan, N.T.S. A zeolite imidazolate framework ZIF-8 catalyst for friedel-crafts acylation. Chin. J. Catal. 2012, 33, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Shui, J.-L.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Reprogle, B.M.; Wang, D.; Liu, D.-J. Iron imidazolate framework as precursor for electrocatalysts in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 3200–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larouche, N.; Chenitz, R.; Lefèvre, M.; Proietti, E.; Dodelet, J.-P. Activity and stability in proton exchange membrane fuel cells of iron-based cathode catalysts synthesized with addition of carbon fibers. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 115, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.S.; Ni, Z.; Côté, A.P.; Choi, J.Y.; Huang, R.; Uribe-Romo, F.J.; Chae, H.K.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Exceptional chemical and thermal stability of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10186–10191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, G.; Li, H.; Chen, V. Challenges and opportunities for mixed-matrix membranes for gas separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 4610–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, T.C.; Noble, R.D.; Falconer, J.L. Fundamentals and applications of pervaporation through zeolite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 245, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, Y. Volumes of aqueous hydrogen and hydroxide ions at 0 to 200 °C. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 137, 154501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, B.; Smyrl, W.H.; Cussler, E.L. Polymer-zeolite composite membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. AIChE J. 2003, 49, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.-M.; Yang, C.-C.; Hu, C.-C.; Pai, Y.-L.; Lue, S.J. Novel quaternized polyvinyl alcohol/quaternized chitosan nano-composite as an effective hydroxide-conducting electrolyte. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 485, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salavagione, H.J.; Martínez, G.; Gómez, M.A. Synthesis of poly(vinyl alcohol)/reduced graphite oxide nanocomposites with improved thermal and electrical properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soboleva, T.; Xie, Z.; Shi, Z.; Tsang, E.; Navessin, T.; Holdcroft, S. Investigation of the through-plane impedance technique for evaluation of anisotropy of proton conducting polymer membranes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2008, 622, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahan, B.; Wainright, J. AC impedance investigations of proton conduction in NafionTM. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1993, 140, L185–L186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.-F.; Wu, J.-F.; Li, H.-Y.; Hung, W.-S.; Shih, C.-M.; Hu, C.-C.; Liu, Y.-L.; Lue, S.J. Novel polyvinyl alcohol nanocomposites containing carbon nano-tubes with Fe3O4 pendants for alkaline fuel cell applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 444, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidan, H.M. Structural properties of CrF3- and MnCl2-filled poly(vinyl alcohol) films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 88, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, P.-D.; Chen, J.-H.; Wu, H.-L. Solvent effect on structural change of poly(vinyl alcohol) physical gels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 69, 2477–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasekara, R.; Harding, I.; Bowater, I.; Christie, G.B.Y.; Lonergan, G.T. Preparation, surface modification and characterisation of solution cast starch PVA blended films. Polym. Test. 2004, 23, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Lu, L.; Peng, F.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z. Pervaporation of benzene/cyclohexane mixtures through CMS-filled poly(vinyl alcohol) membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 52, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirilargani, M.; Sadatnia, B. Poly(vinyl alcohol)/zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIF-8) mixed matrix membranes for pervaporation dehydration of isopropanol. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 469, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Alexandridis, P. Composite polymer electrolytes: Nanoparticles affect structure and properties. Polymers 2016, 8, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merle, G.; Hosseiny, S.S.; Wessling, M.; Nijmeijer, K. New cross-linked PVA based polymer electrolyte membranes for alkaline fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 409–410, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Li, L.; Su, L.; Zhang, Y. Supercritical carbon dioxide treated Nafion 212 commercial membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. Electrochem. Commun. 2012, 14, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.-S.; Jiang, L.Y.; Li, Y.; Kulprathipanja, S. Mixed matrix membranes (MMMs) comprising organic polymers with dispersed inorganic fillers for gas separation. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 483–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, T.H.; Liu, J.; Lee, J.S.; Koros, W.J.; Jones, C.W.; Nair, S. Facile high-yield solvothermal deposition of inorganic nanostructures on zeolite crystals for mixed matrix membrane fabrication. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 14662–14663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdi, E.M.; Tan, J.-C. Mixed-matrix membranes of zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF-8)/Matrimid nanocomposite: Thermo-mechanical stability and viscoelasticity underpinning membrane separation performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 498, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.-C.; Liao, G.M.; Kumar, S.R.; Shih, C.-M.; Yang, C.-C.; Wang, D.-M.; Lue, S.J. Fabrication and Characterization of Chitosan Nanoparticle-Incorporated Quaternized Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Composite Membranes as Solid Electrolytes for Direct Methanol Alkaline Fuel Cells. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 187, 616–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.-Y.; Lin, H.-K.; Liu, N.-Y.; Mahesh, K.P.O.; Lue, S.J. Cell performance modeling of direct methanol fuel cells using proton-exchange solid electrolytes: Effective reactant diffusion coefficients in porous diffusion layers. J. Power Sources 2013, 227, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Cao, Y.; Scott, K. A composite membrane of caesium salt of heteropolyacids/quaternary diazabicyclo-octane polysulfone with poly (tetrafluoroethylene) for intermediate temperature fuel cells. Membranes 2012, 2, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brueckner, T.M.; Pickup, P.G. Kinetics and Stoichiometry of Methanol and Ethanol Oxidation in Multi-Anode Proton Exchange Membrane Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, F1172–F1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, N.; Takeichi, M.; Itagaki, M.; Uchida, H.; Watanabe, M. Temperature-dependence of oxygen reduction activity at a platinum electrode in an acidic electrolyte solution investigated with a channel flow double electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2005, 574, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Roberts, E.P.L.; Holmes, S.M. Evaluation of composite membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2006, 154, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lue, S.J.; Pan, W.-H.; Chang, C.-M.; Liu, Y.-L. High-performance direct methanol alkaline fuel cells using potassium hydroxide-impregnated polyvinyl alcohol/carbon nano-tube electrolytes. J. Power Sources 2012, 202, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-C. Synthesis and characterization of the cross-linked PVA/TiO2 composite polymer membrane for alkaline DMFC. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 288, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.-M.; Li, P.-C.; Lin, J.-S.; Ma, W.-T.; Yu, B.-C.; Li, H.-Y.; Liu, Y.-L.; Yang, C.-C.; Shih, C.-M.; Lue, S.J. Highly conductive quasi-coaxial electrospun quaternized polyvinyl alcohol nanofibers and composite as high-performance solid electrolytes. J. Power Sources 2016, 304, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh Kumar, S.; Juan, C.-H.; Liao, G.-M.; Lin, J.-S.; Yang, C.-C.; Ma, W.-T.; You, J.-H.; Jessie Lue, S. Fumed Silica Nanoparticles Incorporated in Quaternized Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Nanocomposite Membrane for Enhanced Power Densities in Direct Alcohol Alkaline Fuel Cells. Energies 2016, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-C.; Chiu, S.-S.; Kuo, S.-C.; Liou, T.-H. Fabrication of anion-exchange composite membranes for alkaline direct methanol fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2012, 199, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, G.K.S.; Krause, F.C.; Viva, F.A.; Narayanan, S.R.; Olah, G.A. Study of operating conditions and cell design on the performance of alkaline anion exchange membrane based direct methanol fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 7967–7972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-S.; Ma, W.-T.; Shih, C.-M.; Yu, B.-C.; Teng, L.-W.; Wang, Y.-C.; Cheng, K.-W.; Chiu, F.-C.; Lue, S.J. Reorientation of magnetic graphene oxide nanosheets in crosslinked quaternized polyvinyl alcohol as effective solid electrolyte. Energies 2016, 9, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-S.; Kumar, S.R.; Ma, W.-T.; Shih, C.-M.; Teng, L.-W.; Yang, C.-C.; Lue, S.J. Gradiently distributed iron oxide@graphene oxide nanofillers in quaternized polyvinyl alcohol composite to enhance alkaline fuel cell power density. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 543, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Properties | PVA | PVA/25.40% ZIF-8 | PVA/40.50% ZIF-8 | PVA/45.40% ZIF-8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer crystallinity (%) | 38.09 | 34.18 | 31.87 | 31.33 |
| KOH uptake (g g−1) | 0.92 | 1.07 | 1.072 | 0.998 |
| Conductivity 1 30 °C (S cm−1) | 0.0055 | 0.0158 | 0.0188 | 0.0147 |
| 60 °C (S cm−1) | 0.0075 | 0.0174 | 0.0204 | 0.0156 |
| Permeability 2 (10−6 cm2 s−1) | 4.28 | 1.48 | 1.05 | 2.40 |
| Selectivity 3 30 °C | 1292 | 10,533 | 17905 | 6125 |
| Electrolyte Membrane | Anode Catalyst (Loading in mg cm−2) | Cathode Catalyst (Loading in mg cm−2) | Peak Power Density (mW cm−2) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVA | Pt/C (1) | Pt/C (1) | 6 | Fu et al. [27] |
| PVA/TiO2 | Pt–Ru/C (4) | Pt/C (4) | 8 | Yang et al. [69] |
| PVA/fumed silica | Pt–Ru/C (5) | Pt/C (5) | 39 | Lue et al. [26] |
| PVA/multiwalled carbon nanotubes | Pt–Ru/C (5) | Pt/C (5) | 39 | Pan et al. [25] |
| PVA/graphene | Pt/C (5) | Pt/C (5) | 46 | Ye et al. [13] |
| PVA/carbon nanotubes (CNTs) | Pt–Ru/C (5) | Pt/C (5) | 68 | Lue et al. [68] |
| PVA/Fe3O4-CNTs | Pt–Ru/C (6) | Pt/C (5) | 88 | Lo et al. [50] |
| Tokuyama | Pt–Ru/C (8) | Pt/C (8) | 55 | Prakash et al. [73] |
| QPVA/Q-SiO2 | Pt–Ru/C (4) | MnO2/C (4) | 35 | Yang et al. [72] |
| QPVA/chitosan | Pt–Ru/C (6) | Pt/C (5) | 51 | Li et al. [62] |
| Electrospun QPVA | Pt–Ru/C (6) | Pt/C (5) | 54 | Liao et al. [70] |
| CL-QPVA/GO-Fe3O4 | Pt–Ru/C (6) | Pt/C (5) | 55 | Lin et al. [74] |
| Q-PVA/Q-chitosan | Pt–Ru/C (5) | Pt/C (5) | 73 | Liao et al. [46] |
| QPVA/fumed silica | Pt–Ru/C (5) | Pt/C (5) | 88 | Kumar et al. [71] |
| QPVA/GO-Fe3O4 | Pt–Ru/C (6) | Pt/C (5) | 200 | Lin et al. [75] |
| PVA/40.5% ZIF-8 | Pt–Ru/C (2) | Pt/C (1) | 174 | This work |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, P.-Y.; Hu, T.-Y.; Kumar, S.R.; Chang, C.-H.; Wu, K.C.-W.; Tung, K.-L.; Lue, S.J. Highly Zeolite-Loaded Polyvinyl Alcohol Composite Membranes for Alkaline Fuel-Cell Electrolytes. Polymers 2018, 10, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010102
Hsu P-Y, Hu T-Y, Kumar SR, Chang C-H, Wu KC-W, Tung K-L, Lue SJ. Highly Zeolite-Loaded Polyvinyl Alcohol Composite Membranes for Alkaline Fuel-Cell Electrolytes. Polymers. 2018; 10(1):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010102
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Po-Ya, Ting-Yu Hu, Selvaraj Rajesh Kumar, Chia-Hao Chang, Kevin C.-W. Wu, Kuo-Lun Tung, and Shingjiang Jessie Lue. 2018. "Highly Zeolite-Loaded Polyvinyl Alcohol Composite Membranes for Alkaline Fuel-Cell Electrolytes" Polymers 10, no. 1: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010102
APA StyleHsu, P. -Y., Hu, T. -Y., Kumar, S. R., Chang, C. -H., Wu, K. C. -W., Tung, K. -L., & Lue, S. J. (2018). Highly Zeolite-Loaded Polyvinyl Alcohol Composite Membranes for Alkaline Fuel-Cell Electrolytes. Polymers, 10(1), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010102