Antibacterial Films Made of Ionic Complexes of Poly(γ-glutamic acid) and Ethyl Lauroyl Arginate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Measurements
2.3. Complexes Formation and Film Preparation
2.4. Complex Dissociation and Antibacterial Activity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Complexes
3.2. Chemical Characterization
3.3. Thermal Properties and Structure
3.4. Supramolecular Structure and Thermal Transitions
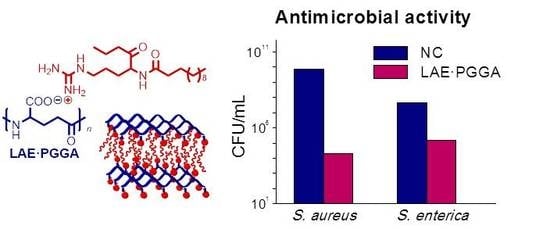
3.5. LAE Release and Antibacterial Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mead, P.S.; Slutsker, L.; Dietz, V.; McCaig, L.F.; Bresee, J.S.; Shapiro, C.; Griffin, P.M.; Tauxe, R.V. Food-related illness and death in the United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1999, 5, 607–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newell, D.G.; Koopmans, M.; Verhoef, L.; Duizer, E.; Aidara-Kane, A.; Sprong, H.; Opsteegh, M.; Langelaar, M.; Threfall, J.; Scheutz, F.; et al. Food-borne diseases. The challenges of 20 years ago still persist while new ones continue to emerge. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 139, S3–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, E.P.C.; Iqbal, Z.; Avis, T.J. Combating Antimicrobial Resistance in Foodborne Microorganisms. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrucka, R. Antimicrobial packaging with natural compounds—A review. LogForum 2016, 12, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Sarkar, P.; Bhunia, A.K.; Yao, Y. Delivery systems of antimicrobial compounds to food. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 54, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appendini, P.; Hotchkiss, J.H. Review of antimicrobial food packaging. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2002, 3, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Bonilla, A.; Fernández-García, M. Polymeric materials with antimicrobial activity. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 281–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, B.; Keshwani, A.; Kharkwal, H. Antimicrobial food packaging: Potential and pitfalls. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, M.C.; Doyle, M.P. The challenges of eliminating or substituting antimicrobial preservatives in foods. Ann. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 371–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, I.; Singhal, R. Poly (glutamic acid)—An emerging biopolymer of commercial interest. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5551–5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Guerra, S.; García-Álvarez, M.; Portilla-Arias, J.A. Chemical modification of microbial poly(γ-glutamic acid). J. Renew. Mater. 2013, 1, 42–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Camero, G.; García-Álvarez, M.; Martínez de Ilarduya, A.; Fernández, C.; Campos, L.; Muñoz-Guerra, S. Comb-like complexes of bacterial poly(γ,d-glutamic acid) and cationic surfactants. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Álvarez, M.; Álvarez, J.; Alla, A.; Martínez de Ilarduya, A.; Herranz, C.; Muñoz-Guerra, S. Comb-like ionic complexes of cationic surfactants with bacterial poly(γ-glutamic acid) of racemic composition. Macromol. Biosci. 2005, 5, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portilla-Arias, J.A.; García-Alvarez, M.; Martínez de Ilarduya, A.; Muñoz-Guerra, S. Ionic complexes of biosynthetic poly(malic acid) and poly(glutamic acid) as prospective drug-delivery systems. Macromol. Biosci. 2007, 7, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamarra, A.; Martínez de Ilarduya, A.; Vives, M.; Morató, J.; Muñoz-Guerra, S. Ionic complexes of poly(γ-glutamic acid) with alkyltrimethylphosphonium surfactants. Polymer 2017, 116, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Go, T.; Lee, S.; Jeong, S.; Park, G.; Hong, C.; Son, H. In vitro evaluation of new functional properties of poly-γ-glutamic acid) produced by Bacillus subtilis D7. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 21, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siracusa, V.; Rocculi, P.; Romani, S.; Marco, D. Biodegradable polymers for food packaging: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerril, R.; Manso, S.; Nerín, C.; Gómez-Lus, R. Antimicrobial activity of Lauroyl Arginate Ethyl (LAE), against selected food-borne bacteria. Food Control 2013, 32, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, V.; Becerril, R.; Santos, J.A.; Rodríguez-Calleja, J.M.; Nerín, C.; García-López, M.L. Evaluation of two antimicrobial packaging films against Escherichia coli O157:H7 strains in vitro and during storage of a Spanish ripened sheep cheese. Food Control 2014, 42, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, E.; Seguer, J.; Rocabayera, X.; Manresa, A. Cellular effects of monohydrochloride of l-arginine, N-α-lauroyl ethyl ester (LAE) on exposure to Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 96, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruckman, S.A.; Rocabayera, X.; Borzelleca, J.F.; Sandusky, C.B. Toxicological and metabolic investigations of the safety of N-α-lauroyl-l-arginine ethyl ester monohydrochloride (LAE). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2004, 42, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, D.R.; Rocabayera, X.; Ruckman, S.; Segret, R.; Shaw, D. Metabolism and pharmacokinetics of ethyl N-α-lauroyl-l-arginate hydrochloride in human volunteers. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 2711–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muriel-Galet, V.; Cran, M.J.; Bigger, S.W.; Hernández-Muñoz, P.; Gavara, R. Antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer films based on the release of oregano essential oil and green tea extract components. J. Food Eng. 2015, 149, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muriel-Galet, V.; López-Carballo, G.; Gavara, R.; Hernández-Muñoz, P. Antimicrobial food packaging film based on the release of LAE from EVOH. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 157, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Jin, T.Z.; Yang, R. Antimicrobial polylactic acid packaging films against Listeria and Salmonella in culture medium and on ready-to-eat meat. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 3293–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, Q. Physical and antimicrobial properties of chitosan films incorporated with lauric arginate, cinnamon oil, and ethylenediaminetetraacetate. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 65, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higueras, L.; López-Carballo, G.; Hernández-Muñoz, P.; Gavara, R.; Rollini, M. Development of a novel antimicrobial film based on chitosan with LAE (ethyl-Nα-dodecanoyl-l-arginate) and its application to fresh chicken. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 165, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattanayaiying, R.; H-Kittikun, A.; Cutter, C.N. Optimization of formulations for pullulan films containing lauric arginate and nisin Z. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiri, M.; Cerisuelo, J.P.; Domínguez, I.; López-Carballo, G.; Hernández-Muñoz, P.; Gavara, R. Novel antimicrobial zein film for controlled release of lauroyl arginate (LAE). Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asker, D.; Weiss, J.; McClements, D.J. Analysis of the Interactions of a Cationic Surfactant (Lauric Arginate) with an anionic biopolymer (Pectin): Isothermal Titration Calorimetry, Light Scattering, and Microelectrophoresis. Langmuir 2009, 25, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asker, D.; Weiss, J.; McClements, D.J. Formation and Stabilization of antimicrobial delivery systems based on electrostatic complexes of cationic-non-ionic mixed micelles and anionic polysaccharides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeffler, M.; McClements, D.J.; McLandsborough, L.; Terjung, N.; Chang, Y.; Weiss, J. Electrostatic interactions of cationic lauric arginate with anionic polysaccharides affect antimicrobial activity against spoilage yeasts. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponomarenko, E.A.; Waddon, A.J.; Tirrell, D.A.; Macknight, W.J. Structure and properties of stoichiometric complexes formed by sodium poly(α,l-glutamate) and oppositely charged surfactants. Langmuir 1996, 12, 2169–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolentino, A.; Alla, A.; Martínez de Ilarduya, A.; Muñoz-Guerra, S. Comb-like ionic complexes of pectinic and alginic acids with alkyltrimethylammonium surfactants. Carbohyd. Polym. 2011, 86, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolentino, A.; Alla, A.; Martínez de Ilarduya, A.; Muñoz-Guerra, S. Comb-like ionic complexes of hyaluronic acid with alkyltrimethylammonium surfactants. Carbohyd. Polym. 2013, 92, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán, N.; Marcato, P.D.; De Souza, G.I.H.; Alves, O.L.; Espósito, E. Antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles produced by fungal process on textile fabrics and their effluent treatment. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2007, 3, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portilla-Arias, J.A.; García-Álvarez, M.; Martínez de Ilarduya, A.; Muñoz-Guerra, S. Thermal decomposition of microbial poly(γ-glutamic acid) and poly(γ-glutamate)s. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 1916–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolentino, A.; Leon, S.; Alla, A.; Martínez de Ilarduya, A.; Muñoz-Guerra, S. Comblike ionic complexes of poly(γ-glutamic acid) and alkanoylcholines derived from fatty acids. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 1607–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, H.; Nambu, Y.; Endo, T. Alkaline hydrolysis of poly(γ-glutamic acid) produced by microorganism. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1996, 34, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Davidson, P.M.; Zhong, Q. Antimicrobial properties of lauric arginate alone or in combination with essential oils in tryptic soy broth and 2% reduced fat milk. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 166, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaara, M. Agents that increase the permeability of the outer membrane. Microbiol. Rev. 1992, 56, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oliver, J.D. The viable but nonculturable state in bacteria. J. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]









| Complex | LAE:PGGA a | Mixing Conditions | Yield (%) | Color | Composition d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c (M) b | T (°C) c | |||||
| LAE·PGGA-1 | 1.0:1.0 | 0.01 | 35 | 70 | white | 0.9:1.0 |
| LAE·PGGA-0.5 | 0.5:1.0 | 0.01 | 35 | 57 | white | 0.5:1.0 |
| Sample | °Td a (°C) | maxTd a (°C) | W a (%) | Tm (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LAE | 245 | 275/311 | 27/10 | 62 |
| LAE·PGGA-1 | 255 | 280/349 | 68/15 | - |
| LAE·PGGA-0.5 | 253 | 273/342 | 63/16 | - |
| Sample | SAXS | WAXS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L010 °C | L0120 °C | L010 °C | d10 °C | d120 °C | d10 °C | |
| LAE | 3.0 | - | - | Multiple | - | - |
| LAE·PGGA-1 | 3.8 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 |
| LAE·PGGA-0.5 | 3.8 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 |
| S. enterica | E. coli | L. monocytogenes | S. aureus | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 7 d | 24 h | 7 d | 24 h | 7 d | 24 h | 7 d | ||
| PGGA | Log(CFU) a | 7.6 | 10.6 | 8.6 | 11.3 | 11.2 | 10.30 | 9.8 | 8.0 |
| LAE·PGGA-1 | Log(CFU) | 5.2 | 8.4 | 6.3 | 6.7 | 3.9 | total | 4.3 | 0.3 |
| LRV b | 2.4 | 2.5 | 2.3 | 4.6 | 7.3 | 5.5 | 7.7 | ||
| PR (%) c | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.5 | >99.9 | >99.9 | 100 | >99.9 | >99.9 | |
| LAE·PGGA-0.5 | Log(CFU) | 7.6 | 10.4 | 5.3 | 10.6 | 4.2 | total | 4.5 | total |
| LRV | 0.01 | 0.5 | 3.3 | 0.6 | 7.0 | 5.4 | |||
| PR (%) | 2.3 | 70.9 | 99.9 | 76.8 | >99.9 | 100 | >99.9 | 100 | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gamarra-Montes, A.; Missagia, B.; Morató, J.; Muñoz-Guerra, S. Antibacterial Films Made of Ionic Complexes of Poly(γ-glutamic acid) and Ethyl Lauroyl Arginate. Polymers 2018, 10, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010021
Gamarra-Montes A, Missagia B, Morató J, Muñoz-Guerra S. Antibacterial Films Made of Ionic Complexes of Poly(γ-glutamic acid) and Ethyl Lauroyl Arginate. Polymers. 2018; 10(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleGamarra-Montes, Ana, Beatriz Missagia, Jordi Morató, and Sebastián Muñoz-Guerra. 2018. "Antibacterial Films Made of Ionic Complexes of Poly(γ-glutamic acid) and Ethyl Lauroyl Arginate" Polymers 10, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010021
APA StyleGamarra-Montes, A., Missagia, B., Morató, J., & Muñoz-Guerra, S. (2018). Antibacterial Films Made of Ionic Complexes of Poly(γ-glutamic acid) and Ethyl Lauroyl Arginate. Polymers, 10(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10010021