Tuning Carbon Dots’ Optoelectronic Properties with Polymers
Abstract
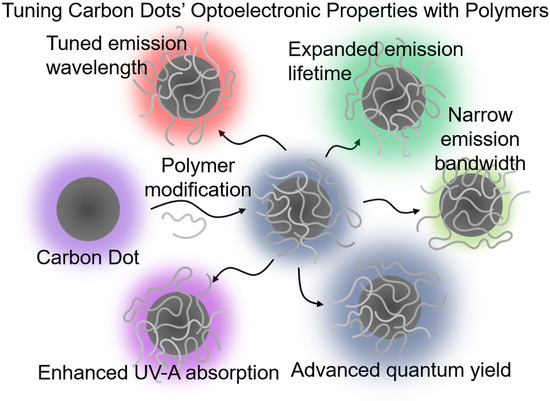
:1. Introduction
2. Enhancing Carbon Dots’ Features Via Passivation
3. Tuning Optical Properties with Polymers
3.1. Expanding Emission Lifetimes
3.2. Advancing Quantum Yields
3.3. Tuning Absorption/Emission Wavelengths
3.3.1. Visible Spectrum
3.3.2. Near Infrared
3.4. Enhancing UV-A Absorption
3.5. Narrowing Emission Bandwidths
4. Perspectives for Polymers in Carbon Dots
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, S.Y.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimos, K. Carbon Quantum Dots: Surface Passivation and Functionalization. Curr. Org. Chem. 2016, 20, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.C.; Yu, K.S.; Han, S.Y.; Kim, J.-J.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, N.S.; Jeong, Y.G.; Kim, D.K. Highly photoluminescent N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAAM) passivated carbon dots for multicolor bioimaging applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 98, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y.; Geng, X.; Hu, Y.; Meng, H.; Ge, J.; Qu, L. Synthesis of Luminescent Carbon Dots with Ultrahigh Quantum Yield and Inherent Folate Receptor-Positive Cancer Cell Targetability. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qu, D.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X.; Haddad, R.E.; Fan, H.; Sun, Z. Formation mechanism and optimization of highly luminescent N-doped graphene quantum dots. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, S.; Choudhary, R.; Roy, E.; Madhuri, R.; Sharma, P.K. Triple signalling mode carbon dots-based biodegradable molecularly imprinted polymer as a multi-tasking visual sensor for rapid and “on-site” monitoring of silver ions. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 11965–11976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, C. Graphene quantum dots: Emergent nanolights for bioimaging, sensors, catalysis and photovoltaic devices. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 3686–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Zhu, A.; Tian, Y. Functional Surface Engineering of C-Dots for Fluorescent Biosensing and in Vivo Bioimaging. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, A.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, C.; Gao, N.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Recent advances in bioapplications of C-dots. Carbon 2015, 85, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Xia, Y. Synthesis-Modification Integration: One-Step Fabrication of Boronic Acid Functionalized Carbon Dots for Fluorescent Blood Sugar Sensing. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5323–5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Sun, Y.; Yang, J.; Hu, Y.; Yang, R.; Li, Z.; Qu, L.; Lin, Y. High performance fluorescence biosensing of cysteine in human serum with superior specificity based on carbon dots and cobalt-derived recognition. Sens. Actuators B 2019, 280, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.-Y.; Li, J.; Ge, J.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.-L.; Li, Z.-H.; Qu, L.-B. A rapid fluorescence “switch-on” assay for glutathione detection by using carbon dots–MnO2 nanocomposites. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 72, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Yan, X.; Li, Z.; Qu, L.; Zhu, C.; Ye, R.; Li, S.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Highly photoluminescent carbon dots derived from linseed and their applications in cellular imaging and sensing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 3181–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ray, R.; Gu, Y.; Ploehn, H.J.; Gearheart, L.; Raker, K.; Scrivens, W.A. Electrophoretic Analysis and Purification of Fluorescent Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12736–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.-P.; Zhou, B.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W.; Fernando, K.A.S.; Pathak, P.; Meziani, M.J.; Harruff, B.A.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Quantum-Sized Carbon Dots for Bright and Colorful Photoluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7756–7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Sharma, S.K.; Peng, Z.; Leblanc, R.M. Polymers in Carbon Dots: A Review. Polymers 2017, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, V.; Margraf, J.T.; Dolle, C.; Butz, B.; Nacken, T.J.; Walter, J.; Bauer, W.; Peukert, W.; Spiecker, E.; Clark, T.; et al. Carbon Nanodots: Toward a Comprehensive Understanding of Their Photoluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 17308–17316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimos, K.; Arcudi, F.; Kouloumpis, A.; Koutselas, I.B.; Rudolf, P.; Gournis, D.; Prato, M. Top-down and bottom-up approaches to transparent, flexible and luminescent nitrogen-doped carbon nanodot-clay hybrid films. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 10256–10262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Wang, Y.; Cai, C.; Lin, H. Activating Room Temperature Long Afterglow of Carbon Dots via Covalent Fixation. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 4866–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Zhang, L.; Lu, J.; Xu, C.; Cai, C.; Lin, H. Triple-Mode Emission of Carbon Dots: Applications for Advanced Anti-Counterfeiting. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 7231–7235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Zou, R.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Yue, D. Large-scale synthesis of N-doped carbon quantum dots and their phosphorescence properties in a polyurethane matrix. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 4742–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardekani, S.M.; Dehghani, A.; Hassan, M.; Kianinia, M.; Aharonovich, I.; Gomes, V.G. Two-photon excitation triggers combined chemo-photothermal therapy via doped carbon nanohybrid dots for effective breast cancer treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Souza, D.R.; Caminhas, L.D.; de Mesquita, J.P.; Pereira, F.V. Luminescent carbon dots obtained from cellulose. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 203, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jiang, W.; Qiu, L.; Jiang, X.; Zuo, D.; Wang, D.; Yang, L. One pot synthesis of highly luminescent polyethylene glycol anchored carbon dots functionalized with a nuclear localization signal peptide for cell nucleus imaging. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 6104–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, W.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X. One-Pot to Synthesize Multifunctional Carbon Dots for Near Infrared Fluorescence Imaging and Photothermal Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 23533–23541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Di, J.; Sun, Y.; Fu, J.; Wei, Z.; Matsui, H.; del C. Alonso, A.; Zhou, S. Biocompatible PEG-Chitosan@Carbon Dots Hybrid Nanogels for Two-Photon Fluorescence Imaging, Near-Infrared Light/pH Dual-Responsive Drug Carrier, and Synergistic Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 5537–5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momper, R.; Steinbrecher, J.; Dorn, M.; Rörich, I.; Bretschneider, S.; Tonigold, M.; Ramanan, C.; Ritz, S.; Mailänder, V.; Landfester, K.; et al. Enhanced photoluminescence properties of a carbon dot system through surface interaction with polymeric nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 518, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Hu, Y.; Wang, P.; Yang, L.; Al Awak, M.M.; Tang, Y.; Twara, F.K.; Qian, H.; Sun, Y.-P. Modified facile synthesis for quantitatively fluorescent carbon dots. Carbon 2017, 122, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Duan, J.; Xiao, Y.; Tang, G.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xue, W. Microenvironment-Driven Cascaded Responsive Hybrid Carbon Dots as a Multifunctional Theranostic Nanoplatform for Imaging-Traceable Gene Precise Delivery. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 3438–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, C. Polyethyleneimine-Functionalized Fluorescent Carbon Dots: Water Stability, pH Sensing, and Cellular Imaging. ChemNanoMat 2015, 1, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Trinchi, A.; Atkin, P.; Cole, I. Tunable Photoluminescence Across the Entire Visible Spectrum from Carbon Dots Excited by White Light. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 2970–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, A.; Lee, J.; Park, B.; Ray, C.; Sankar, K.V.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, I.-J.; Jun, S.C. Facile approach to synthesize highly fluorescent multicolor emissive carbon dots via surface functionalization for cellular imaging. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 513, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, M.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, L.; Guo, L.; Niu, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, P.; et al. Two-photon-excited near-infrared emissive carbon dots as multifunctional agents for fluorescence imaging and photothermal therapy. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 3113–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Ge, J.; Liu, W.; Niu, G.; Jia, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, P. Tunable multicolor carbon dots prepared from well-defined polythiophene derivatives and their emission mechanism. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Jia, Q.; Liu, W.; Lan, M.; Zhou, B.; Guo, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Gu, Y.; et al. Carbon Dots with Intrinsic Theranostic Properties for Bioimaging, Red-Light-Triggered Photodynamic/Photothermal Simultaneous Therapy In Vitro and In Vivo. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Jia, Q.; Liu, W.; Guo, L.; Liu, Q.; Lan, M.; Zhang, H.; Meng, X.; Wang, P. Red-Emissive Carbon Dots for Fluorescent, Photoacoustic, and Thermal Theranostics in Living Mice. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4169–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virca, C.N.; Winter, H.M.; Goforth, A.M.; Mackiewicz, M.R.; McCormick, T.M. Photocatalytic water reduction using a polymer coated carbon quantum dot sensitizer and a nickel nanoparticle catalyst. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 195402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Jing, P.; Sun, L.; An, Y.; Shan, X.; Lu, X.; Zhou, D.; Han, D.; Shen, D.; Zhai, Y.; et al. Near-Infrared Excitation/Emission and Multiphoton-Induced Fluorescence of Carbon Dots. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, X.; Hu, R.; Chen, H.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Lv, F.; Liang, X.-J.; et al. Near-Infrared (NIR)-Absorbing Conjugated Polymer Dots as Highly Effective Photothermal Materials for In Vivo Cancer Therapy. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 8669–8675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, S.C.; Permatasari, F.A.; Fukazawa, H.; Schneider, E.M.; Balgis, R.; Ogi, T.; Okuyama, K.; Stark, W.J. Direct synthesis of carbon quantum dots in aqueous polymer solution: One-pot reaction and preparation of transparent UV-blocking films. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 5187–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.-S.; Fang, C.-C.; Yan, J.-Y.; Tseng, P.-J.; Pyle, J.R.; Chen, C.-P.; Lin, S.-Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Chan, Y.-H. Molecular Engineering and Design of Semiconducting Polymer Dots with Narrow-Band, Near-Infrared Emission for in Vivo Biological Imaging. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3166–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Deng, S.; Qian, G.; Wang, M.; Hu, A. Preparation of carbon nanodots from single chain polymeric nanoparticles and theoretical investigation of the photoluminescence mechanism. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, L.; Li, B.; Song, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, S.; Lu, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; et al. Investigation of photoluminescence mechanism of graphene quantum dots and evaluation of their assembly into polymer dots. Carbon 2014, 77, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Yu, S.-B.; Wei, J.-S.; Xiong, H.-M. Full-Color Light-Emitting Carbon Dots with a Surface-State-Controlled Luminescence Mechanism. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Yang, S.; Wang, Z.; Shen, H.; Xu, T.; Sun, L.; Li, H.; Chen, W.; Jiang, X.; Ding, G.; et al. Ultra-High Quantum Yield of Graphene Quantum Dots: Aromatic-Nitrogen Doping and Photoluminescence Mechanism. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2015, 32, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eda, G.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Mattevi, C.; Yamaguchi, H.; Chen, H.-A.; Chen, I.S.; Chen, C.-W.; Chhowalla, M. Blue Photoluminescence from Chemically Derived Graphene Oxide. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, L.; Zhou, N.; Zhao, X.; Song, Y.; Maharjan, S.; Zhang, J.; Lu, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, B. The crosslink enhanced emission (CEE) in non-conjugated polymer dots: From the photoluminescence mechanism to the cellular uptake mechanism and internalization. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 13845–13848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Pang, D.-W. Photoluminescence-Tunable Carbon Nanodots: Surface-State Energy-Gap Tuning. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Y.; Wu, A.; Cai, C.; Lin, H. Red, Green, and Blue Luminescence by Carbon Dots: Full-Color Emission Tuning and Multicolor Cellular Imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 5360–5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Song, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shao, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B. The photoluminescence mechanism in carbon dots (graphene quantum dots, carbon nanodots, and polymer dots): Current state and future perspective. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 355–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhou, M.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Q.; Shi, J.; Gong, A.; Yang, M. Efficient Room-Temperature Phosphorescence from Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots in Composite Matrices. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 8221–8227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; An, X.; Gong, J. Novel pH sensitive N-doped carbon dots with both long fluorescence lifetime and high quantum yield. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 32319–32322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Wei, L.; Su, Y.; Li, Z.; Geng, H.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Y. Efficient long lifetime room temperature phosphorescence of carbon dots in a potash alum matrix. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 2798–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhao, D.; Chen, X.; Wang, F.; Song, H.; Shen, D. Long lifetime pure organic phosphorescence based on water soluble carbon dots. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 5751–5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golden, J.H.; Deng, H.; DiSalvoa, F.J.; Fréchet, J.M.J.; Thompson, P.M. Monodisperse Metal Clusters 10 Angstroms in Diameter in a Polymeric Host: The “Monomer as Solvent” Approach. Science 1995, 268, 1463–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.M.; Mancini, M.C.; Nie, S. Second window for in vivo imaging. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 710–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wei, J.-S.; Zhang, P.; Niu, X.-Q.; Zhao, W.; Zhu, Z.-Y.; Ding, H.; Xiong, H.-M. Red-Emissive Carbon Dots for Fingerprints Detection by Spray Method: Coffee Ring Effect and Unquenched Fluorescence in Drying Process. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 18429–18433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, X.; Qu, D.; Yang, D.; Nie, B.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, H.; Sun, Z. Synthesis of Carbon Dots with Multiple Color Emission by Controlled Graphitization and Surface Functionalization. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, K.; Lin, H. Near-infrared emissive carbon dots for two-photon fluorescence bioimaging. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 17350–17356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghamsari, M.S.; Bidzard, A.M.; Han, W.; Park, H.-H. Wavelength-tunable visible to near-infrared photoluminescence of carbon dots: The role of quantum confinement and surface states. J. Nanophotonics 2016, 10, 026028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, K.; Wu, A.; Lin, H. Toward High-Efficient Red Emissive Carbon Dots: Facile Preparation, Unique Properties, and Applications as Multifunctional Theranostic Agents. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 8659–8668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.-P.; Zhou, B.; Shen, X.-C.; Yu, Y.-X.; Ji, S.-C.; Wen, C.-C.; Liang, H. Selective Probing of Gaseous Ammonia Using Red-Emitting Carbon Dots Based on an Interfacial Response Mechanism. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 18993–18999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, K.; Reckmeier, C.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Wu, C.; Yu, W.W.; Rogach, A.L. Combination of carbon dot and polymer dot phosphors for white light-emitting diodes. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 12045–12050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yuan, F.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Zhong, H.; Fan, L.; Yang, S. 53% Efficient Red Emissive Carbon Quantum Dots for High Color Rendering and Stable Warm White-Light-Emitting Diodes. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1702910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Sui, L.; Liu, J.; Zhu, S.; Chen, A.; Jin, M.; Yang, B. Near-Infrared Photoluminescent Polymer-Carbon Nanodots with Two-Photon Fluorescence. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Tan, Z.A.; Fan, L.; Yang, S. Bright Multicolor Bandgap Fluorescent Carbon Quantum Dots for Electroluminescent Light-Emitting Diodes. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.-Y.; Gong, X.-J.; Liu, Y.; Lu, W.-J.; Gao, Y.-F.; Xian, M.; Shuang, S.-M.; Dong, C. Facile preparation of bright orange fluorescent carbon dots and the constructed biosensing platform for the detection of pH in living cells. Talanta 2018, 189, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Sun, S.; Zhang, A.; Jiang, K.; Zhang, L.; Dong, C.; Huang, Q.; Wu, A.; Lin, H. Truly Fluorescent Excitation-Dependent Carbon Dots and Their Applications in Multicolor Cellular Imaging and Multidimensional Sensing. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7782–7787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, S.; Zhou, D.; Li, D.; Ji, W.; Jing, P.; Han, D.; Liu, L.; Zeng, H.; Shen, D. Toward Efficient Orange Emissive Carbon Nanodots through Conjugated sp2-Domain Controlling and Surface Charges Engineering. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3516–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, T.-F.; Huang, W.-L.; Chung, C.-J.; Chiang, I.T.; Chen, L.-C.; Chang, H.-Y.; Su, W.-C.; Cheng, C.; Chen, S.-J.; Teng, H. Elucidating Quantum Confinement in Graphene Oxide Dots Based on Excitation-Wavelength-Independent Photoluminescence. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 2087–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konwar, A.; Gogoi, N.; Majumdar, G.; Chowdhury, D. Green chitosan–carbon dots nanocomposite hydrogel film with superior properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutsioukis, A.; Akouros, A.; Zboril, R.; Georgakilas, V. Solid phase extraction for the purification of violet, blue, green and yellow emitting carbon dots. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 11293–11296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alas, M.O.; Genc, R. An investigation into the role of macromolecules of different polarity as passivating agent on the physical, chemical and structural properties of fluorescent carbon nanodots. J. Nanopart. Res. 2017, 19, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhu, S.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, C.; Sun, L.; Tang, W.; Liu, R.; Sun, Y.; Yu, M. Nitrogen-doped carbon dots with excitation-independent long-wavelength emission produced by a room-temperature reaction. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 11912–11914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourlinos, A.B.; Trivizas, G.; Karakassides, M.A.; Baikousi, M.; Kouloumpis, A.; Gournis, D.; Bakandritsos, A.; Hola, K.; Kozak, O.; Zboril, R.; et al. Green and simple route toward boron doped carbon dots with significantly enhanced non-linear optical properties. Carbon 2015, 83, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Xiang, W.; Gao, H.; Wang, J.; Ni, Y.; Liang, X. Facile synthesis of tunable fluorescent carbon dots and their third-order nonlinear optical properties. Dyes Pigments 2016, 128, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannouli, I.; Bourlinos, A.B.; Bakandritsos, A.; Couris, S. Nonlinear optical properties of colloidal carbon nanoparticles: Nanodiamonds and carbon dots. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 40152–40160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Feng, M.; Li, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhan, H. Enhanced nonlinear optical properties of nonzero-bandgap graphene materials in glass matrices. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 4121–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloukos, P.; Papagiannouli, I.; Bourlinos, A.B.; Zboril, R.; Couris, S. Third-order nonlinear optical response and optical limiting of colloidal carbon dots. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 12013–12027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.; Yamada, Y.; Zhou, S.; Shimotsuma, Y.; Miura, K.; Qiu, J. Carbon nanodots with strong nonlinear optical response. Carbon 2014, 69, 638–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamijala, S.S.R.K.C.; Mukhopadhyay, M.; Pati, S.K. Linear and Nonlinear Optical Properties of Graphene Quantum Dots: A Computational Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 12079–12087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Polymers | Notes/Specific Applications | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| PEG and PVA | Expanded emission lifetime-Phosphorescence-Data encryption [19] | [19,20] |
| PU 1 | PU suppresses nonradiative transitions-Phosphorescence | [21] |
| PEG | Advancing quantum yield (QY) [22,23,24], Tuning emission [25,26] | [22,23,24,25,26] |
| Chitosan and PS 2 | Advancing QY by attaching carbon dots on PS | [27] |
| PEI | Advancing QY [28,29,30], Tune emission across visible [31,32] | [28,29,30,31,32] |
| PT 3 | Tune emission to visible and/or near-IR | [33,34,35,36] |
| PVP 4 | Advancing QY [37], Tune emission to near-IR [38] | [37,38] |
| PSMA 5 | Tune absorption to near-IR-Photothermal therapy | [39] |
| b-PEI and PVA | Enhancing UV-A absorption | [40] |
| Various | Narrowing emission bandwidth | [41] |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dimos, K. Tuning Carbon Dots’ Optoelectronic Properties with Polymers. Polymers 2018, 10, 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121312
Dimos K. Tuning Carbon Dots’ Optoelectronic Properties with Polymers. Polymers. 2018; 10(12):1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121312
Chicago/Turabian StyleDimos, Konstantinos. 2018. "Tuning Carbon Dots’ Optoelectronic Properties with Polymers" Polymers 10, no. 12: 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121312
APA StyleDimos, K. (2018). Tuning Carbon Dots’ Optoelectronic Properties with Polymers. Polymers, 10(12), 1312. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121312