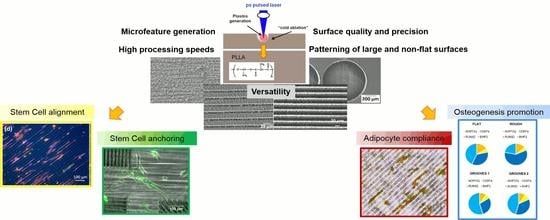
Laser Surface Microstructuring of a Bio-Resorbable Polymer to Anchor Stem Cells, Control Adipocyte Morphology, and Promote Osteogenesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Surface Microstructuring Technique
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Quantitative RT-PCR (qPCR)
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Laser Irradiation on Material Surface Properties and Microstructure
3.2. Effect of Surface Topography on Undifferentiated MSCs
3.3. Effect of Surface Topography on Differentiated Human MSCs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lawall, H.; Bramlage, P.; Amann, B. Treatment of peripheral arterial disease using stem and progenitor cell therapy. J. Vasc. Surg. 2011, 53, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cideciyan, A.V.; Hauswirth, W.W.; Aleman, T.S.; Kaushal, S.; Schwarts, S.; Boye, S.L.; Windsor, E.A.M.; Conlon, T.J.; Sumaroka, A.; Roman, A.J.; et al. Vision 1 year after gene therapy for Leber’s congenital amaurosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 725–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolettis, T.M.; Vilaeti, A.; Dimos, K.; Tsitou, N.; Agathopoulos, S. Tissue engineering for post-myocardial infarction ventricular remodeling. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, V. Where stem cells call home. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peerani, R.; Zandstra, P.W. Enabling stem cell therapies through synthetic stem cell-niche engineering. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prewitz, M.C.; Seib, F.P.; von Bonin, M.; Friedrichs, J.; Stiβel, A.; Niehage, C.; Müller, K.; Anastassiadis, K.; Waskow, C.; Hoflack, B.; et al. Tightly anchored tissue-mimetic matrices as instructive stem cell microenvironment. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilian, K.A.; Bugarija, B.; Lahn, B.T.; Mrksich, M. Geometric cues for directing the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4872–4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kolind, K.; Leong, K.W.; Besenbacher, F.; Foss, M. Guidance of stem cell fate on 2D patterned surfaces. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6626–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.M.; Jiang, Z.; Bastmeyer, M.; Lahann, J. Physical aspects of cell culture substrates: Topography, roughness, and elasticity. Small 2012, 8, 336–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Béduer, A.; Vieu, C.; Arnauduc, F.; Sol, J.C.; Loubinoux, I.; Vaysse, L. Engineering of adult human neural stem cells differentiation through surface micropatterning. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khang, D.; Choi, J.; Im, Y.M.; Kim, Y.J.; Jang, J.H.; Kang, S.S.; Nam, T.H.; Song, J.; Park, J.W. Role of subnano-, nano-, and submicron-surface features on osteoblast differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 5997–6007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Tison, C.K.; Chatterjee, K.; Pine, P.S.; McDaniel, J.H.; Salit, M.L.; Young, M.F.; Simon, C.G., Jr. The determination of stem cell fate by 3D scaffold structures through the control of cell shape. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9188–9196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, S.; Singha, S.; Cho, M.R.; Gordon, R.J. 3D femtosecond laser patterning of collagen for directed cell attachment. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 4597–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeong, W.Y.; Yu, H.; Lim, K.P.; Ng, K.L.G.; Boey, Y.C.F.; Subbu, V.S.; Tan, L.P. Multiscale topological guidance for cell alignment via direct laser writing on biodegradable polymer. Tissue Eng. C Methods 2010, 16, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Lim, Y.C.; Farson, D.F.; Powell, H.M.; Lannutti, J. Vascular Wall Engineering Via Femtosecond Laser Ablation: Scaffolds with Self-Containing Smooth Muscle Cell Populations. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 39, 3031–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li-Ping Lee, B.; Jeon, H.; Wang, A.; Yan, Z.; Yu, J.; Grigoropoulos, C.; Li, S. Femtosecond laser ablation enhances cell infiltration into three-dimensional electrospun scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 2648–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daskalova, A.; Nathala, C.S.R.; Kavatzikidou, P.; Ranella, A.; Szoszkiewicz, R.; Husinsky, W.; Fotakis, C. FS laser processing of bio-polymer thin films for studying cell-to-substrate specific response. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 382, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wen, F.; Wong, Y.S.; Boey, F.Y.; Subbu, V.S.; Tai Leong, D.; Woei Ng, K.; Ka Lai Ng, G.; Tan, L.P. Direct laser machining-induced topographic pattern promotes up-regulation of myogenic markers in human mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wong, Y.S.; Wen, F.; Ng, K.W.; Ng, G.K.; Venkatraman, S.S.; Boey, F.Y.; Tan, L.P. Human Mesenchymal Stem-Cell Behaviour on Direct Laser Micropatterned Electrospun Scaffolds with Hierarchical Structures. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusen, L.; Cazan, M.; Mustaciosu, C.; Filipescu, M.; Sandel, S.; Zamfirescu, M.; Dinca, V.; Dinescu, M. Tailored topography control of biopolymer surfaces by ultrafast lasers for cell-substrate studies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 302, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaliari, E.; Kavatzikidou, P.; Angelaki, D.; Chaniotaki, L.; Manousaki, A.; Siakouli-Galanopoulou, A.; Ranella, A.; Stratakis, E. Engineering cell adhesion and orientation via ultrafast laser fabricated microstructured substrates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlie, S.; Fadeeva, E.; Koroleva, A.; Chichkov, B.N. Laser-engineered topography: Correlation between structure dimensions and cell control. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2012, 23, 2813–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, R.; Moreno-Flores, S.; Quintana, I.; Vivanco, M.d.M.; Sarasua, J.R.; Toca-Herrera, J.L. Ultrafast laser microprocessing of medical polymers for cell engineering applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 37, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacharra, S.; Ortiz, R.; McMahon, S.; Wang, W.; Viebahn, R.; Salber, J.; Quintana, I. Surface patterning of a novel PEG-functionalized Poly-L-lactide polymer to improve its biocompatibility: Applications to Bioresorbable Vascular Stents (BVS). J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koufaki, N.; Ranella, A.; Aifantis, K.E.; Barberoglou, M.; Psycharakis, S.; Fotakis, C.; Stratakis, E. Controlling cell adhesion via replication of laser micro/nano-textured surfaces on polymers. Biofabrication 2011, 3, 045004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuendorf, R.E.; Saiz, E.; Tomsia, A.P.; Ritchie, R.O. Adhesion between biodegradable polymers and hydroxyapatite: Relevance to synthetic bone-like materials and tissue engineering scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, R.; Quintana, I.; Etxarri, J.; Lejardi, A.; Sarasua, J.R. Picosecond laser ablation of poly-L-lactide: Effect of crystallinity on the material response. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 094902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriondo, O.; Rábano, M.; Domenici, G.; Carlevaris, O.; López-Ruiz, J.A.; Zabalza, I.; Berra, E.; Vivanco, M.D. Distinct breast cancer stem/progenitor cell populations require either HIF1α or loss of PHD3 to expand under hypoxic conditions. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 31721–31739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meaurio, E.; Lopez-Rodriguez, N.; Sarasua, J.R. Infrared spectrum of poly(L-lactide): Application to crystallinity studies. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 9291–9301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuchkov, N.K. UV copper ion laser in Ne-Cubr pulse-longitudinal discharge. In Advances in Laser and Optics Research; Arkin, W.T., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Volume 2, pp. 1–34. ISBN 1-59033-398-5. [Google Scholar]
- McBeath, R.; Pirone, D.M.; Nelson, C.M.; Bhadriraju, K.; Chen, C.S. Cell shape, cytoskeletal tension, and RhoA regulate stem cell lineage commitment. Dev. Cell 2004, 6, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paragkumar, N.T.; Edith, D.; Six, J.L. Surface characteristics of PLA and PLGA films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 253, 2758e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepak, B.D.; Antonczak, A.J.; Szustakiewicz, K.; Koziol, P.E.; Abramski, K.M. Degradation of poly(L-lactide) under KrF excimer laser treatment. Polym. Dégrad. Stab. 2014, 110, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Luo, Y.; Yu, J.; Liu, B.; Hu, M.; Chai, L.; Wang, C. Effects of high-repetition-rate femtosecond laser micromachining on the physical and chemical properties of polylactide (PLA). Opt. Express 2015, 23, 26932–26939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, A.; Yada, S.; Terakawa, M. Biodegradability of poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) after femtosecond laser irradiation. Nat. Res. J. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadeeva, E.; Deiwick, A.; Chichkov, B.; Schlie-Wolter, S. Impact of laser-structured biomaterial interfaces on guided cell responses. Interface Focus 2014, 4, 20130048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantawong, F.; Burgess, K.E.V.; Jayawardena, K.; Hart, A.; Riehle, M.O.; Oreffo, R.O.; Dalby, M.J.; Burchmore, R. Effects of a surface topography composite with puerariae radix on human STRO-1-positive stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 3694–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yim, E.K.F.; Darling, E.M.; Kulangara, K.; Guilak, F.; Leong, K.M. Nanotopography-induced changes in focal adhesions, cytoskeletal organization, and mechanical properties of human mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kantawong, F.; Burchmore, R.; Wilkinson, C.D.W.; Oreffo, R.O.C.; Dalby, M.J. Differential in-gel electrophoresis (DIGE) analysis of human bone marrow osteoprogenitor cell contact guidance. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, D.W.; Wong, K.S.; Brunette, D.M. Microfabricated discontinuous-edge surface topographies influence osteoblast adhesion, migration, cytoskeletal organization, and proliferation and enhance matrix and mineral deposition in vitro. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2006, 78, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, A.Y.; Jang, K.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.B.; Suh, K.Y. Effect of nanogroove geometry on adipogenic differentiation. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 494017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.T.; Hochfeld, W.E.; Myburgh, R.; Pepper, M.S. Adipocyte and adipogenesis. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 92, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahceci, M.; Gokalp, D.; Bahceci, S.; Tuzcu, A.; Atmaca, S.; Arikan, S. The correlation between adiposity and adiponectin, tumor necrosis factor –a, interleukin-6 and high sensitivity C-reactive protein. Is adipocyte size associated with inflammation in adults? J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2007, 30, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.K.; Ciaraldi, T.P.; Henry, R.R.; Wittgrove, A.C.; Phillips, S.A. Adipose tissue depot and cell size dependency of adiponectin synthesis and secretion in human obesity. Adipocyte 2013, 2, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carraway, K.L.; Carraway, C.A.C. Membrane-cytoskeleton interaction in animal cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1989, 988, 147–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadei, A.; Epis, R.; Ferroni, L.; Tocco, I.; Gardin, C.; Bressan, E.; Sivolella, S.; Vindigni, V.; Pinton, P.; Mucci, G.; et al. Review article: Adipose tissue regeneration: A state of the art. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 462543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiguera, S.; Gonfiotti, A.; Jaus, M.; Comin, C.E.; Paglierani, M.; Gaudio, C.; Bianco, A.; Ribatti, D.; Macchiarini, P. Development of bioengineered human larynx. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 4433–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Hong, J.M.; Jung, J.W.; Shim, J.H.; Oh, J.H.; Cho, D.W. 3D printing of composite tissue with complex shape applied to ear regeneration. Biofabrication 2014, 6, 024103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, S.A.; Chen, C.S. Emergence of patterned stem cell differentiation within multicellular structures. Stem Cells 2008, 26, 2921–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, R.; Yao, X.; Ding, J. Effect of cell anisotropy on differentiation of stem cells on micropatterned surfaces through the controlled single cell adhesion. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 8048–8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goubko, C.A.; Cao, X. Patterning multiple cell types in co-cultures: A. review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 1855–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Lu, H.; Kawazoe, N.; Chen, G. Adipogenic differentiation of individual mesenchymal stem cell on different geometric micropatterns. Langmuir 2011, 27, 6155–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watari, S.; Hayashi, K.; Wood, J.A.; Russell, P.; Nealey, P.F.; Murphy, C.J.; Genetos, D.C. Modulation of osteogenic differentiation in hMSCs cells by submicron topographically-patterned ridges and grooves. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobbenga, S.; Fratila-Apachitei, L.E.; Zadpoor, A.A. Nanopattern-induced osteogenic differentiation of stem cells—A systematic review. Acta Biomater. 2016, 46, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulshof, F.F.B.; Papenburg, B.; Vasilevich, A.; Hulsman, M.; Zhao, Y.; Levers, M.; Fekete, N.; de Boer, M.; Yuan, H.; Singh, S.; et al. Mining for osteogenic surface topographies: In silico design to in vivo osseo-integration. Biomaterials 2017, 13, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, B.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, H.K.; Tran, H.T.; Kim, S.H.; Jeon, H.; Kim, S.; Sim, J.H.; et al. A specific groove pattern can effectively induce osteoblast differentiation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1703569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abagnale, G.; Steger, M.; Nguyen, V.H.; Hersch, N.; Sechi, A.; Joussen, S.; Denecke, B.; Merkel, R.; Hoffmann, B.; Dreser, A.; et al. Surface topography enhances differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells towards osteogenic and adipogenic lineages. Biomaterials 2015, 61, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Pristine Area | Grooved Area | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C 1s | O 1s | C 1s | O 1s | |
| Position | 285.50 | 532.50 | 286.50 | 533.00 |
| at % | 65.61 | 34.39 | 60.94 | 39.06 |
| C:O | 1.9 | 1.56 | ||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortiz, R.; Aurrekoetxea-Rodríguez, I.; Rommel, M.; Quintana, I.; Vivanco, M.d.; Toca-Herrera, J.L. Laser Surface Microstructuring of a Bio-Resorbable Polymer to Anchor Stem Cells, Control Adipocyte Morphology, and Promote Osteogenesis. Polymers 2018, 10, 1337. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121337
Ortiz R, Aurrekoetxea-Rodríguez I, Rommel M, Quintana I, Vivanco Md, Toca-Herrera JL. Laser Surface Microstructuring of a Bio-Resorbable Polymer to Anchor Stem Cells, Control Adipocyte Morphology, and Promote Osteogenesis. Polymers. 2018; 10(12):1337. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121337
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtiz, Rocio, Iskander Aurrekoetxea-Rodríguez, Mathias Rommel, Iban Quintana, Maria dM Vivanco, and Jose Luis Toca-Herrera. 2018. "Laser Surface Microstructuring of a Bio-Resorbable Polymer to Anchor Stem Cells, Control Adipocyte Morphology, and Promote Osteogenesis" Polymers 10, no. 12: 1337. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121337
APA StyleOrtiz, R., Aurrekoetxea-Rodríguez, I., Rommel, M., Quintana, I., Vivanco, M. d., & Toca-Herrera, J. L. (2018). Laser Surface Microstructuring of a Bio-Resorbable Polymer to Anchor Stem Cells, Control Adipocyte Morphology, and Promote Osteogenesis. Polymers, 10(12), 1337. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121337