ECM Decorated Electrospun Nanofiber for Improving Bone Tissue Regeneration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Electrospinning
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. ECM Decoration on Electrospun Nanofibers
2.4. Cell Attachment and Morphology
2.5. Cell Metabolism
2.6. ALP Activity
2.7. Characterization of Mineralized Tissue Formation
2.8. Mineralization
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
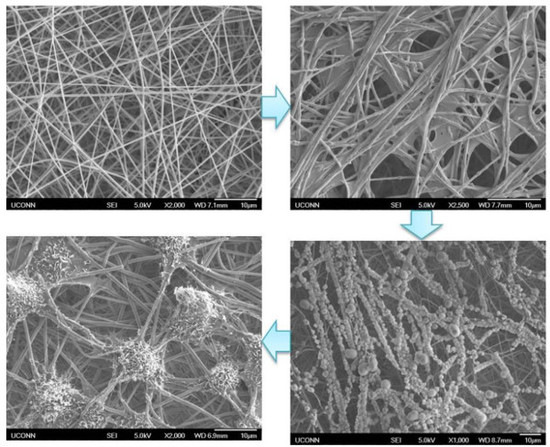
3.1. Generation and Characterization of ECM Decorated PLLA NF
3.2. Cell Attachment and Spread
3.3. Cell Proliferation and Differentiation
3.4. Cell Morphology and Mineral Deposition
3.5. Biomineralization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amini, A.; Laurencin, C.T.; Nukavarapu, S.P. Bone tissue engineering: Recent advances and challenges. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 40, 363–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Tang, X.; Gohil, S. V.; Laurencin, C.T. Biomaterials for Bone Regenerative Engineering. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 1268–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karageorgiou, V.; Kaplan, D. Porosity of 3D biomaterial scaffolds and osteogenesis. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5474–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babensee, J.E.; McIntire, L.V.; Mikos, A.G. Growth factor delivery for tissue engineering. Pharm. Res. 2000, 17, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crane, G.M.; Ishaug, S.L.; Mikos, A.G. Bone Tissue Engineering. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 1322–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, G.B.; Ma, P.X. Macroporous and nanofibrous polymer scaffolds and polymer/bone-like apatite composite scaffolds generated by sugar spheres. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2006, 78, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, W.L.; Dennis, R.G.; Kileny, J.L.; Mooney, D.J. Salt fusion: An approach to improve pore interconnectivity within tissue engineering scaffolds. Tissue Eng. 2002, 8, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Wen, P.; Zhang, Y.; Long, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Xing, F.; Gao, J. Preparation of aligned porous gelatin scaffolds by unidirectional freeze-drying method. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deville, S.; Saiz, E.; Tomsia, A.P. Freeze casting of hydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 5480–5489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheridan, M.H.; Shea, L.D.; Peters, M.C.; Mooney, D.J. Bioabsorbable polymer scaffolds for tissue engineering capable of sustained growth factor delivery. J. Control. Release 2000, 64, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, X.H.; Ma, P.X. Induction of osteoblast differentiation phenotype on poly(l-lactic acid) nanofibrous matrix. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 3815–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner, S.; Traub, W.; Wagner, H.D. Lamellar bone: Structure-function relations. J. Struct. Biol. 1999, 126, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muschler, G.F.; Nakamoto, C.; Griffith, L.G. Engineering principles of clinical cell-based tissue engineering. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2004, 86, 1541–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-J.; Laurencin, C.T.; Caterson, E.J.; Tuan, R.S.; Ko, F.K. Electrospun nanofibrous structure: A novel scaffold for tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 60, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sill, T.J.; von Recum, H.A. Electrospinning: Applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1989–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, H.; Shin, Y.M.; Terai, H.; Vacanti, J.P. A biodegradable nanofiber scaffold by electrospinning and its potential for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 2077–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Li, X.; Xie, C.; Zhuang, H.; Zhou, S.; Weng, J. Hydroxyapatite nucleation and growth mechanism on electrospun fibers functionalized with different chemical groups and their combinations. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4620–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Bashur, C.A.; Goldstein, A.S.; Schmidt, C.E. Polypyrrole-coated electrospun PLGA nanofibers for neural tissue applications. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 4325–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, D.; Chen, X.; Xu, Q.; Lu, F.; Nie, J. Electrospun Water-Soluble Carboxyethyl Chitosan/Poly(vinyl alcohol) Nanofibrous Membrane as Potential Wound Dressing for Skin Regeneration. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, C.-W.; Bai, M.-Y.; Chang, Y.; Chung, M.-F.; Lee, T.-Y.; Wu, C.-T.; Maiti, B.; Liao, Z.X.; Li, R.K.; Sung, H.W. Electrical coupling of isolated cardiomyocyte clusters grown on aligned conductive nanofibrous meshes for their synchronized beating. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.H.; Castano, O.; Kim, H.W. Electrospun materials as potential platforms for bone tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1065–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Vepari, C.; Jin, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kaplan, D.L. Electrospun silk-BMP-2 scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 3115–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Venugopal, J.R.; El-Turki, A.; Ramakrishna, S.; Su, B.; Lim, C.T. Electrospun biomimetic nanocomposite nanofibers of hydroxyapatite/chitosan for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4314–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xie, J.; Yuan, X.; Xia, Y. Coating Electrospun Poly(ε-caprolactone) Fibers with Gelatin and Calcium Phosphate and Their Use as Biomimetic Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. Langmuir 2008, 24, 14145–14150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, L.S.; Laurencin, C.T. Biodegradable polymers as biomaterials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 762–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, G.; Vernekar, V.N.; Kuyinu, E.L.; Laurencin, C.T. Poly (lactic acid)-based biomaterials for orthopaedic regenerative engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 247–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Wei, D.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; He, D.; Zhong, J. Novel biodegradable electrospun nanofibrous P(DLLA-CL) balloons for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures. Nanomedicine 2013, 9, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, G.; Bhattacharjee, M.; Nair, L.S.; Laurencin, C.T. Musculoskeletal Tissue Regeneration: The Role of the Stem Cells. Regen. Eng. Transl. Med. 2017, 3, 133–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peach, M.S.; Ramos, D.M.; James, R.; Morozowich, N.L.; Mazzocca, A.D.; Doty, S.B.; Allcock, H.R.; Kumbar, S.G.; Laurencin, C.T. Engineered stem cell niche matrices for rotator cuff tendon regenerative engineering. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Wolke, J.G.C.; Jansen, J.A. Biomimetic calcium phosphate coating on electrospun poly([var epsilon]-caprolactone) scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 137, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Kumbar, S.G.; Khan, Y.M.; Nair, L.S.; Singh, A.; Krogman, N.R.; Brown, P.W.; Allcock, H.R.; Laurencin, C.T. Biodegradable polyphosphazene-nanohydroxyapatite composite nanofibers: Scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2009, 5, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutolf, M.P.; Weber, F.E.; Schmoekel, H.G.; Schense, J.C.; Kohler, T.; Muller, R.; Hubbell, J.A. Repair of bone defects using synthetic mimetics of collagenous extracellular matrices. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badylak, S.F. The extracellular matrix as a biologic scaffold material. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 3587–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badylak, S.F.; Freytes, D.O.; Gilbert, T.W. Extracellular matrix as a biological scaffold material: Structure and function. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, G.; Nair, L.S.; Laurencin, C.T. Regenerative Engineering of the Rotator Cuff of the Shoulder. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, L.E.; McDevitt, T.C. Cell-derived matrices for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications. Biomater. Sci. 2015, 3, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutolf, M.P.; Hubbell, J.A. Synthetic biomaterials as instructive extracellular microenvironments for morphogenesis in tissue engineering. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.H.; Cooper, J.A., Jr.; Manuel, S.; Freeman, J.W.; Attawia, M.A.; Ko, F.K.; Laurencin, C.T. Anterior cruciate ligament regeneration using braided biodegradable scaffolds: In vitro optimization studies. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 4805–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutha, K.; Schwartz, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hyzy, S.; Boyan, B.D.; McDevitt, T.C. Osteogenic Embryoid Body-Derived Material Induces Bone Formation In Vivo. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faghihi, S.; Azari, F.; Zhilyaev, A.P.; Szpunar, J.A.; Vali, H.; Tabrizian, M. Cellular and molecular interactions between MC3T3-E1 pre-osteoblasts and nanostructured titanium produced by high-pressure torsion. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 3887–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokubo, T.; Takadama, H. How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2907–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Y.; Liu, L.; Cheng, R.; Cui, W. ECM Decorated Electrospun Nanofiber for Improving Bone Tissue Regeneration. Polymers 2018, 10, 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030272
Fu Y, Liu L, Cheng R, Cui W. ECM Decorated Electrospun Nanofiber for Improving Bone Tissue Regeneration. Polymers. 2018; 10(3):272. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030272
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Yong, Lili Liu, Ruoyu Cheng, and Wenguo Cui. 2018. "ECM Decorated Electrospun Nanofiber for Improving Bone Tissue Regeneration" Polymers 10, no. 3: 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030272
APA StyleFu, Y., Liu, L., Cheng, R., & Cui, W. (2018). ECM Decorated Electrospun Nanofiber for Improving Bone Tissue Regeneration. Polymers, 10(3), 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030272