Mechanical and Unlubricated Sliding Wear Properties of Nitrile Rubber Reinforced with Micro Glass Flake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment Section
2.1. Materials and Preparation of NBR Specimens
2.2. Experimental Instruments and Measurements
2.2.1. Mechanical Tests
2.2.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.2.3. Dynamic Mechanics Analysis (DMA)
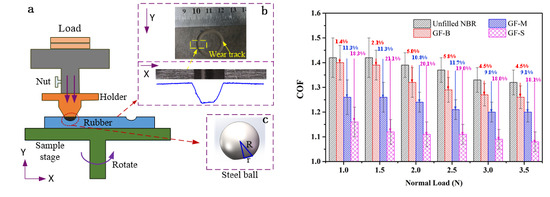
2.2.4. Friction and Wear Tests
2.2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of GF-Filled NBR
3.2. Tribological Properties of NBR Filled with GF
4. Discussions
4.1. Effect of GF Filler on the Friction of NBR
4.2. Effect of GF Filler on the Wear Behavior of NBR
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, S.W. Tribology of Elastomers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.S.; Ha, S.H. Water swelling behaviors of silica-reinforced NBR composites in deionized water and salt solution. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2010, 16, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, T.; Pan, G. Preparation and tribological properties of grapheme oxide/nitrile rubber nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.W.; Liu, H.C.; He, R.Y. Mechanisms of wear of steel by natural rubber in water medium. Wear 2004, 256, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briscoe, B.J.; Sinha, S.K. Wear of Polymers. Proceed. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2002, 216, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorko, G.; Molnár, V.; Živčák, J.; Husáková, N. Failure analysis of textile rubber conveyor belt damaged by dynamic wear. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2013, 28, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Wang, S.; Huo, X. The effect of water content in crude oil on the tribological behavior of screw pump’s stator rubber. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 2868–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Wang, D.; Cong, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Q. Dependence of abrasion behavior on cross-linked heterogeneity in unfilled nitrile rubber. Tribol. Int. 2014, 69, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, J.; Yan, F. Friction and wear behaviors of several polymers sliding against GCr15 and 316 steel under the lubrication of sea water. Tribol. Lett. 2011, 42, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.X.; Dong, F.; Zhang, Z.X.; Meng, X.K.; Peng, X.D. Effect of abrasive size on friction and wear characteristics of nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) in two-body abrasion. Tribol. Int. 2016, 103, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, K.; Ding, X. Tribological properties and morphology of bimodal elastomeric nitrile butadiene rubber networks. Mater. Des. 2013, 52, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, K.; Zhang, Z.; Schlarb, A.K. Effects of various fillers on the sliding wear of polymer composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 2329–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.W. Recent developments of green tribology. Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 2016, 4, 023004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schadler, L.S. Polymer-Based and Polymer-Filled Nanocomposites; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gatos, K.G.; Karger-Kocsis, J. Effect of the aspect ratio of silicate platelets on the mechanical and barrier properties of hydrogenated acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (HNBR)/layered silicate nanocomposites. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malas, A.; Das, C.K.; Das, A.; Heinrich, G. Development of expanded graphite filled natural rubber vulcanizates in presence and absence of carbon black: Mechanical, thermal and morphological properties. Mater. Des. 2012, 39, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laura, D.M.; Keskkula, H.; Barlow, J.W.; Paul, D.R. Effect of rubber particle size and rubber type on the mechanical properties of glass fiber reinforced, rubber-toughened nylon 6. Polymer 2003, 44, 3347–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, C.A.; Bragança, F.C.; Doi, R.T.; Lee, L.T.; Galembeck, F.; Boué, F. Natural rubber-clay nanocomposites: Mechanical and structural properties. Polymer 2010, 51, 3644–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, M.; Liang, W.; Rao, G.; Zhang, L.; Guo, C. Surface modification of fibrillar silicate and its reinforcing mechanism on FS/rubber composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Cao, Z.; Wang, D.; Liu, S. Improving the friction and abrasion properties of nitrile rubber hybrid with hollow glass beads. Tribol. Inter. 2016, 101, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Liu, L.; Meng, F.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, F. The failure behavior of an epoxy glass flake coating/steel system under marine alternating hydrostatic pressure. Corros. Sci. 2014, 86, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiyanarayanan, S.; Azim, S.S.; Venkatachari, G. Corrosion protection coating containing polyaniline glass flake composite for steel. Electrochem. Acta 2008, 53, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yang, J. Influences of glass flakes on fire protection and water resistance of waterborne intumescent fire resistive coating for steel structure. Prog. Org. Coat. 2011, 70, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, P.; Wood, D.J.; Bubb, N.L. Reinforcement of poly(methyl methacrylate) denture base with glass flake. Dent. Mater. 2005, 21, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu-Khanh, T.; Fisa, B. Impact fracture of glass flake reinforced polypropylene. Polym. Compos. 1986, 7, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaas, N.V.; Marcus, K.; Kellock, C. The tribological behavior of glass filled polytetrafluoroethylene. Tribol. Int. 2005, 38, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Lee, D. Effect of molecular weight between cross-links on the abrasion behavior of rubber by a blade abrader. Polymer 2000, 41, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, L.; Friedrich, K. Synergistic effects of nanoparticles and traditional tribo-fillers on sliding wear of polymeric hybrid composites. Tribol. Interf. Eng. Ser. 2008, 55, 35–61. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, S. Tribological behavior of in situ Ag nanoparticles/polyelectrolyte composite molecular deposition films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 1714–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Lockette, P.R. Examination of the effects of computationally determined network topology on an analytical constitutive model for bimodal elastomers. Polymer 2008, 49, 5158–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varughese, K.T.; Nando, G.B.; De, P.P.; Sanyal, S.K. Miscible blends from rigid poly(vinyl chloride) and epoxidized natural rubber. J. Mater. Sci. 1988, 23, 3903–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, M.F.; Abulawi, J.; Kong, H.S. Temperature maps for frictional heating in dry sliding. Tribol. Trans. 1991, 34, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, W.; Andreas, A.P. A phenomenological elevated temperature friction model for viscoelastic polymer coatings based on nanoindentation. Tribol. Int. 2018, 119, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharoni, S.M. Wear of polymer by roll-formation. Wear 1973, 25, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukahori, Y.; Yamazaki, H. Mechanism of rubber abrasion. Part I: Abrasion pattern formation in natural rubber vulcanizate. Wear 1994, 171, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barquins, M. Adherence, friction and wear of rubber-like materials. Wear 1992, 158, 87–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatos, K.G.; Kameo, K.; Karger-Kocsis, J. On the friction and sliding wear of rubber/layered silicate nanocomposites. Express Polym. Lett. 2007, 1, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felhös, D.; Karger-Kocsis, J. Tribological testing of peroxide-cured EPDM rubbers with different carbon black contents under dry sliding conditions against steel. Tribol. Int. 2008, 41, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karger-Kocsis, J.; Felhos, D.; Xu, D.; Schlarb, A.K. Unlubri-cated sliding and rolling wear of thermoplastic dynamic vulcanizates (Santoprene®) against steel. Wear 2008, 265, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukahori, Y.; Yamazaki, H. Mechanism of rubber abrasion Part 3: How is friction linked to fracture in rubber abrasion? Wear 1995, 188, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gent, A.N.; Pulford, C.T.R. Mechanisms of rubber abrasion. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1983, 28, 943–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.M.L.; Ferreira, A.J.M. A contribution to the study of the fracture energy of polymer concrete and fibre reinforced polymer concrete. Polym. Test. 2004, 23, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, M.; Takeno, A.; Hara, K.; Watanabe, A. Volume fraction and temperature dependence of mechanical properties of silicone rubber particulate/epoxy blends. Compos. Part A 1995, 26, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, O.; Keskkula, H.; Paul, D.R. Fracture toughness of nylon 6 blends with maleated ethylene/propylene rubbers. Polymer 2000, 41, 8061–8074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.A.M.; Capela, C.; Costa, J.D. A study of the mechanical behavioue on fibre reinforced hollow microspheres hybrid composites. Compos. Part A 2010, 41, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pukánszky, B. Influence of interface interaction on the ultimate tensile properties of polymer composites. Compos. Part A 1990, 21, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| SiO2 | K2O | B2O3 | ZnO | Na2O | MgO | CaO | Al2O3 | TiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 64–70% | 0–3% | 3–8% | 0–5% | 11–18% | 1–4% | 3–7% | 0–5% | 0–3% |
| Ingredient | NBR | Stearic Acid | ZnO | CBS | TMTD | Sulfur | GF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PHR | 100 | 1 | 5 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 1.7 | 15 |
| Specimens | Unfilled NBR | GF-B | GF-M | GF-S |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elastic modulus (MPa) | 0.63 ± 0.01 | 0.63 ± 0.01 | 0.65 ± 0.01 | 0.66 ± 0.02 |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 6.24 ± 0.3 | 6.72 ± 0.3 | 7.07 ± 0.4 | 7.17 ± 0.3 |
| Storage modulus (MPa, 20 °C) | 12.29 ± 0.03 | 13.28 ± 0.02 | 13.35 ± 0.02 | 13.51 ± 0.02 |
| Shore hardness (A) | 44 ± 0.8 | 47 ± 1 | 49 ± 0.8 | 53 ± 1 |
| Fracture energy (×10−3, J/mm2) | 41.7 ± 1.1 | 43.8 ± 1 | 44.7 ± 1.2 | 46.6 ± 1.3 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Tan, H.; Cao, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, S. Mechanical and Unlubricated Sliding Wear Properties of Nitrile Rubber Reinforced with Micro Glass Flake. Polymers 2018, 10, 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070705
Guo Y, Tan H, Cao Z, Wang D, Zhang S. Mechanical and Unlubricated Sliding Wear Properties of Nitrile Rubber Reinforced with Micro Glass Flake. Polymers. 2018; 10(7):705. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070705
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yanbao, Hai Tan, Zhiqiang Cao, Deguo Wang, and Siwei Zhang. 2018. "Mechanical and Unlubricated Sliding Wear Properties of Nitrile Rubber Reinforced with Micro Glass Flake" Polymers 10, no. 7: 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070705
APA StyleGuo, Y., Tan, H., Cao, Z., Wang, D., & Zhang, S. (2018). Mechanical and Unlubricated Sliding Wear Properties of Nitrile Rubber Reinforced with Micro Glass Flake. Polymers, 10(7), 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10070705