Role of PhaC Type I and Type II Enzymes during PHA Biosynthesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Class I and Class II PHA Synthases
1.2. Class III and Class IV PHA Synthases
1.3. Diversity and Spread of PhaC in Bacteria
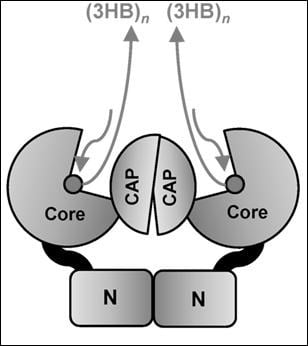
2. Crystal Structure
3. Catalytic Mechanism
4. Mutation and Amino Acid Substitution Studies
5. Production of PHA in Fermentors
6. Progress and Advancements in the PHA Field
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, P.; Jun, H.B.; Kim, B.S. Co-production of polyhydroxyalkanoates and carotenoids through bioconversion of glycerol by Paracoccus sp. strain LL1. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 2552–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.H.; Kim, B.S. Production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) by Ralstonia eutropha from soybean oil. New Biotechnol. 2011, 28, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Singh, M.; Mehariya, S.; Patel, S.K.; Lee, J.K.; Kalia, V.C. Ecobiotechnological approach for exploiting the abilities of Bacillus to produce co-polymer of Polyhydroxyalkanoate. Indian J. Microbiol. 2014, 54, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermann-Krauss, C.; Koller, M.; Muhr, A.; Fas, H.; Stelzer, F.; Braunegg, G. Archaeal production of polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) co- and terpolyesters from biodiesel industry-derived by-products. Archaea 2013, 2013, 129268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuge, T.; Hyakutake, M.; Mizuno, K. Class IV polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) synthases and PHA-producing Bacillus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 6231–6240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, S.; Fatma, T. Cyanobacterial polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB): Screening, optimization and characterization. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, G.-Y.A.; Chen, C.-L.; Li, L.; Ge, L.; Wang, L.; Ningtyas Razaad, I.M.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Mo, Y.; Wang, J.-Y. Start a research on biopolymer polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): A review. Polymers 2014, 6, 706–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poltronieri, P.; Mezzolla, V.; D’Urso, O.F. PHB production in biofermentors assisted through biosensor applications. Proceedings 2017, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-Q.; Hajnal, I.; Wu, H.; Lv, L.; Ye, J. Engineering biosynthesis mechanisms for diversifying Polyhydroxyalkanoates. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.-Q.; Hajnal, I. The ‘PHAome’. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Meur, S.; Zinn, M.; Egli, T.; Thöny-Meyer, L.; Ren, Q. Production of medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates by sequential feeding of xylose and octanoic acid in engineered Pseudomonas putida KT2440. BMC Biotechnol. 2012, 12, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, A.; Zuber, M.; Zia, K.M.; Noreen, A.; Anjum, M.N.; Tabasum, S. Microbial production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) and its copolymers: A review of recent advancements. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 89, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, D.C.; Shen, R.; Yao, H.; Chen, J.C.; Wu, Q.; Chen, G.Q. Engineering the diversity of polyesters. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 29, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezzolla, V.; D’Urso, O.F.; Poltronieri, P. Optimization of polyhydroxyalkanoate production by recombinant E. coli supplemented with different plant by-products. Biotechnol. Indian J. 2017, 13, 138. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, C.; Cao, R.; Maurmann, L.; Li, P. Inhibitors of polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) synthases: Synthesis, molecular docking, and implications. ChemBioChem 2015, 16, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhubalan, K.; Chuah, J.A.; Shozui, F.; Brigham, C.J.; Taguchi, S.; Sinskey, A.J.; Rha, C.; Sudesh, K. Characterization of the highly active polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase of Chromobacterium sp. strain USM2. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2926–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chek, M.F.; Kim, S.Y.; Mori, T.; Arsad, H.; Samian, M.R.; Sudesh, K.; Hakoshima, T. Structure of polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) synthase PhaC from Chromobacterium sp. USM2, producing biodegradable plastics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittenborn, E.C.; Jost, M.; Wei, Y.; Stubbe, J.; Drennan, C.L. Structure of the Catalytic Domain of the Class I Polyhydroxybutyrate Synthase from Cupriavidus necator. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 25264–25277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, K.-J. Crystal structure of Ralstonia eutropha polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase C-terminal domain and reaction mechanisms. Biotechnol. J. 2017, 12, 1600648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Ray, S.; Kalia, V.C. Production of co-polymers of polyhydroxyalkanoates by regulating the hydrolysis of biowastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mifune, J.; Nakamura, S.; Fukui, T. Targeted engineering of Cupriavidus necator chromosome for biosynthesis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) from vegetable oil. Can. J. Chem. 2008, 86, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, J.; Jin, K.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, K.-J. Structure and function of the N-terminal domain of Ralstonia eutropha polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase, and the proposed structure and mechanisms of the whole enzyme. Biotechnol. J. 2017, 12, 1600649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuge, T.; Imazu, S.; Takase, K.; Taguchi, S.; Doi, Y. An extra large insertion in the polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase from Delftia acidovorans DS-17: Its deletion effects and relation to cellular proteolysis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 231, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Oh, D.H.; Ahn, W.S.; Lee, Y.; Choi, J.; Lee, S.Y. Production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) by high-cell-density cultivation of Aeromonas hydrophila. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2000, 67, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Rehm, B.H. Polyhydroxybutyrate biosynthesis in Caulobacter crescentus: Molecular characterization of the polyhydroxybutyrate synthase. Microbiology 2001, 147, 3353–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilham, M.; Nakanomori, S.; Kihara, T.; Hokamura, A.; Matsusaki, H.; Tsuge, T.; Mizuno, K. Characterization of polyhydroxyalkanoate synthases from Halomonas sp. O-1 and Halomonas elongata DSM2581: Site-directed mutagenesis and recombinant expression. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 109, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-Y.; Song, G.; Chen, G.-Q. A lower specificity PhaC2 synthase from Pseudomonas stutzeri catalyses the production of copolyesters consisting of short-chain-length and medium-chain-length 3-hydroxyalkanoates. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2006, 89, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebergesell, M.; Rahalkar, S.; Steinbüchel, A. Analysis of the Thiocapsa pfennigii polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase: Subcloning, molecular characterization and generation of hybrid synthases with the corresponding Chromatium vinosum enzyme. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 54, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Hou, J.; Liu, H.; Cai, S.; Feng, B.; Zhou, J.; Xiang, H. Wide distribution among Halophilic Archaea of a novel Polyhydroxyalkanoate Synthase subtype with homology to bacterial type III Synthases. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7811–7819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kihara, T.; Hiroe, A.; Ishii-Hyakutake, M.; Mizuno, K.; Tsuge, T. Bacillus cereus-type polyhydroxyalkanoate biosynthetic gene cluster contains R-specific enoyl-CoA hydratase gene. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2017, 81, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyakutake, M.; Tomizawa, S.; Mizuno, K.; Abe, H.; Tsuge, T. Alcoholytic cleavage of polyhydroxyalkanoate chains by class IV synthases induced by endogenous and exogenous ethanol. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montenegro, E.M.D.S.; Delabary, G.S.; Silva, M.A.C.D.; Andreote, F.D.; Lima, A.O.S. Molecular diagnostic for prospecting polyhydroxyalkanoate-producing bacteria. Bioengineering 2017, 4, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quelas, J.I.; Mongiardini, E.J.; Pérez-Giménez, J.; Parisi, G.; Lodeiro, A.R. Analysis of two polyhydroxyalkanoate synthases in Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA 110. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 3145–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheu, D.S.; Chen, W.M.; Lai, Y.W.; Chang, R.C. Mutations derived from the thermophilic polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase PhaC enhance the thermostability and activity of PhaC from Cupriavidus necator H16. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 2620–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takase, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Taguchi, S.; Doi, Y. Alteration of substrate chain-length specificity of type II synthase for polyhydroxyalkanoate biosynthesis by in vitro evolution: In vivo and in vitro enzyme assays. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Cao, R.; Shrestha, R.; Ward, C.; Katz, B.B.; Fischer, C.J.; Tomich, J.M.; Li, P. Trapping of intermediates with substrate analog HBOCoA in the polymerizations catalyzed by class III polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) synthase from Allochromatium vinosum. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, C.T.; Taguchi, S. PHA synthase engineering toward superbiocatalysts for custom-made biopolymers. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 73, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, K.; Takase, K.; Aoki, E.; Doi, Y.; Taguchi, S. Synergistic effects of Glu130Asp substitution in the type II polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) synthase: Enhancement of PHA production and alteration of polymer molecular weight. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, K.; Aoki, E.; Takase, K.; Doi, Y.; Taguchi, S. In vivo and in vitro characterization of Ser477X mutations in polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) synthase 1 from Pseudomonas sp. 61–3: Effects of beneficial mutations on enzymatic activity, substrate specificity, and molecular weight of PHA. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 2436–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amara, A.A.; Rehm, B.H. Replacement of the catalytic nucleophile cysteine-296 by serine in class II polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa-mediated synthesis of a new polyester: Identification of catalytic residues. Biochem. J. 2003, 374, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Shi, M.; Zhang, T.; Li, L.; Li, L.; Xian, M. Natural and engineered polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) synthase: Key enzyme in biopolyester production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 7417–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.Y.; Liu, T.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, J.C.; Chen, G.-Q. Polyhydroxyalkanoate synthases PhaC1 and PhaC2 from Pseudomonas stutzeri 1317 had different substrate specificities. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 234, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuah, J.A.; Tomizawa, S.; Yamada, M.; Tsuge, T.; Doi, Y.; Sudesh, K.; Numata, K. Characterization of site-specific mutations in a short-chain-length/medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase: In vivo and in vitro studies of enzymatic activity and substrate specificity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 3813–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Normi, Y.M.; Hiraishi, T.; Taguchi, S.; Sudesh, K.; Najimudin, N.; Doi, Y. Site-directed saturation mutagenesis at residue F420 and recombination with another beneficial mutation of Ralstonia eutropha polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase. Biotechnol. Lett. 2005, 27, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuge, T.; Saito, Y.; Kikkawa, Y.; Hiraishi, T.; Doi, Y. Biosynthesis and compositional regulation of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)-co-(3-hydroxyhexanoate) in recombinant Ralstonia eutropha expressing mutated polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase genes. Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shozui, F.; Matsumoto, K.; Sasaki, T.; Taguchi, S. Engineering of polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase by Ser477X/Gln481X saturation mutagenesis for efficient production of 3-hydroxybutyrate-based copolyesters. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsuge, T.; Watanabe, S.; Shimada, D.; Abe, H.; Doi, Y.; Taguchi, S. Combination of N149S and D171G mutations in Aeromonas caviae polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase and impacton polyhydroxyalkanoate biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 277, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Yuan, X.X.; Shi, Z.Y.; Guo, Y.Y.; Shen, X.W.; Chen, J.C.; Wu, Q.; Chen, G.-Q. Production of copolyesters of 3-hydroxybutyrate and medium-chain-length 3-hydroxyalkanoates by E. coli containing an optimized PHA synthase gene. Microb. Cell Fact. 2012, 11, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.W.; Shi, Z.Y.; Song, G.; Li, Z.J.; Chen, G.-Q. Engineering of polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) synthase PhaC2Ps of Pseudomonas stutzeri via site-specific mutation for efficient production of PHA copolymers. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 91, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koller, M. A review on established and emerging fermentation schemes for microbial production of Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) biopolyesters. Fermentation 2018, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.E.; Na, H.Y.; Yang, T.H.; Rhee, S.K.; Song, J.K. A lipophilic fluorescent LipidGreen1-based quantification method for high-throughput screening analysis of intracellular poly-3-hydroxybutyrate. AMB Express 2015, 5, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madkour, M.H.; Heinrich, D.; Alghamdi, M.A.; Shabbaj, I.I.; Steinbüchel, A. PHA recovery from biomass. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 2963–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koller, M.; Niebelschütz, H.; Braunegg, G. Strategies for recovery and purification of poly [(R)-3-hydroxyalkanoates](PHA) biopolyesters from surrounding biomass. Eng. Life Sci. 2013, 13, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jendrossek, D.; Pfeiffer, D. New insights in the formation of polyhydroxyalkanoate granules (carbonosomes) and novel functions of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate). Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2357–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mezzolla, V.; D’Urso, O.F.; Poltronieri, P. Role of PhaC Type I and Type II Enzymes during PHA Biosynthesis. Polymers 2018, 10, 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10080910
Mezzolla V, D’Urso OF, Poltronieri P. Role of PhaC Type I and Type II Enzymes during PHA Biosynthesis. Polymers. 2018; 10(8):910. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10080910
Chicago/Turabian StyleMezzolla, Valeria, Oscar Fernando D’Urso, and Palmiro Poltronieri. 2018. "Role of PhaC Type I and Type II Enzymes during PHA Biosynthesis" Polymers 10, no. 8: 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10080910
APA StyleMezzolla, V., D’Urso, O. F., & Poltronieri, P. (2018). Role of PhaC Type I and Type II Enzymes during PHA Biosynthesis. Polymers, 10(8), 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10080910