Microstructure Evolution of Immiscible PP-PVA Blends Tuned by Polymer Ratio and Silica Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Selective Phase Extraction Experiment
2.4. Microscopy Characterization and Image Analyses
2.5. Rheological Measurement
2.6. Surface Tension Measurement
3. Results and Discussions
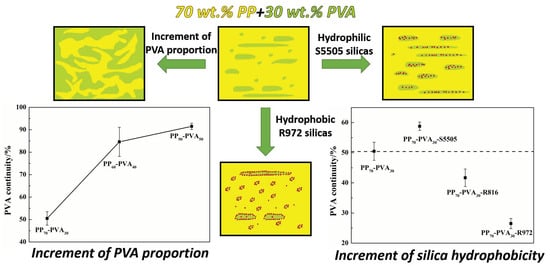
3.1. Influence of the Mass Ratio of PP-PVA Blends
3.1.1. Morphology of the Polymer Blends
3.1.2. Rheological Characterization
3.2. Tailoring the Microstructure via Introducing Silicas with Different Wettability
3.2.1. Prediction and Confirmation of Silica Localization
3.2.2. Morphology of the Polymer Blends
3.2.3. Rheological Analyses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fakirov, S.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Panamoottil, S.M. Converting of bulk polymers into nanosized materials with controlled nanomorphology. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2014, 63, 777–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.; Shah, D.; Giannelis, E.P. New advances in polymer/layered silicate nanocomposites. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2002, 6, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pötschke, P.; Paul, D.R. Formation of co-continuous structures in melt-mixed immiscible polymer blends. J. Macromol. Sci. Polym. Rev. 2003, 43, 87–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Mural, P.; Sharma, M.; Shukla, A.; Bhadra, S.; Padmanabhan, B.; Madras, G.; Bose, S. Porous membranes designed from bi-phasic polymeric blends containing silver decorated reduced graphene oxide synthesized via a facile one-pot approach. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 32441–32451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mural, P.K.S.; Banerjee, A.; Rana, M.S.; Shukla, A.; Padmanabhan, B.; Bhadra, S.; Madras, G.; Bose, S. Polyolefin based antibacterial membranes derived from PE/PEO blends compatibilized with amine terminated graphene oxide and maleated PE. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 17635–17648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baklavaridis, A.; Zuburtikudis, I.; Panayiotou, C. Porous composite structures derived from multiphase polymer blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2015, 55, 1856–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luna, M.S.; Galizia, M.; Wojnarowicz, J.; Rosa, R.; Lojkowski, W.; Leonelli, C.; Acierno, D.; Filippone, G. Dispersing hydrophilic nanoparticles in hydrophobic polymers: HDPE/ZnO nanocomposites by a novel template-based approach. Express Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.Q.; Bao, R.Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Yang, W.; Xie, B.H.; Yang, M.B. Effect of nano-silica on the phase inversion behavior of immiscible PA6/ABS blends. Polym. Test. 2013, 32, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Han, C.D. Evolution of a dispersed morphology from a co-continuous morphology in immiscible polymer blends. Polymer 1999, 40, 2521–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gegenhuber, T.; Krekhova, M.; Schöbel, J.; Gröschel, A.H.; Schmalz, H. “Patchy” Carbon Nanotubes as Efficient Compatibilizers for Polymer Blends. ACS Macro Lett. 2016, 5, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utracki, L.A. Compatibilization of polymer blends. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2002, 80, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguet, A.; Cassagnau, P.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.M. Structuration, selective dispersion and compatibilizing effect of (nano)fillers in polymer blends. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1526–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.W.; Hu, X.; Li, L.; Yue, C.Y.; Tam, K.C. Flow behaviour and microstructure evolution in novel SiO2/PP/LCP ternary composites: Effects of filler properties and mixing sequence. Polym. Int. 2003, 52, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kontopoulou, M. The structure and physical properties of polypropylene and thermoplastic olefin nanocomposites containing nanosilica. Polymer 2006, 47, 7731–7739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, M.; Wang, C.; Du, R.; Fu, Q. Study on the phase structures and toughening mechanism in PP/EPDM/SiO2 ternary composites. Polymer 2006, 47, 2106–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, X.; Qu, C.; Li, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. Largely improved toughness of PP/EPDM blends by adding nano-SiO2 particles. Polymer 2007, 48, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, L.; Fenouillot, F.; Majesté, J.C.; Cassagnau, P. Morphology and rheology of immiscible polymer blends filled with silica nanoparticles. Polymer 2007, 48, 6029–6040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, L.; Fenouillot, F.; Majesté, J.C.; Martin, G.; Cassagnau, P. Migration of nanosilica particles in polymer blends. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2008, 46, 1976–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, L.; Fenouillot, F.; Majesté, J.C.; Alcouffe, P.; Cassagnau, P. Immiscible polymer blends stabilized with nano-silica particles: Rheology and effective interfacial tension. Polymer 2008, 49, 4378–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Lee, D.K. Oxygen barrier properties of biaxially oriented polypropylene/polyvinyl alcohol blend films. Polymer 2004, 45, 1599–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, T.H.; Lin, C.A. Rheological properties of thermoplastic polyvinyl alcohol and polypropylene blend melts in capillary extrusions. J. Polym. Res. 2005, 12, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, T.H.; Lin, C.A. Elongational flow properties of thermoplastic polyvinyl alcohol/polypropylene from the melt spinning method. Text. Res. J. 2014, 84, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezanova, N.; Budash, Y.; Plavan, V.; Ishchenko, O.; Bulakh, V. Morphology and rheology of nanofilled PP/PVA blends. Mater. Plast. 2017, 54, 735–739. [Google Scholar]
- Steinmann, S.; Gronski, W.; Friedrich, C. Influence of selective filling on rheological properties and phase inversion of two-phase polymer blends. Polymer 2002, 43, 4467–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kontopoulou, M.; Park, C.B. Effect of nanosilica on the co-continuous morphology of polypropylene/polyolefin elastomer blends. Polymer 2010, 51, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmann, S.; Gronski, W.; Friedrich, C. Quantitative rheological evaluation of phase inversion in two-phase polymer blends with cocontinuous morphology. Rheol. Acta 2002, 41, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayla, A.; Campagne, C.; Rochery, M.; Devaux, E. Melt spun multifilament yarns of carbon nanotubes-based polymeric blends: Electrical, mechanical and thermal properties. Synth. Met. 2012, 162, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, D.K.; Wendt, R.C. Estimation of the surface free energy of polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1969, 13, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaün, F.; Bedek, G.; Devaux, E.; Dupont, D.; Deranton, D. Investigation of water absorption and diffusion in microparticles containing xylitol to provide a cooling effect by thermal analysis. Int. J. Thermophys. 2009, 30, 1242–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuai, C.Z.; Almdal, K.; Johannsen, I.; Lyngaae-Jørgensen, J. Morphology evolution of polycarbonate–polystyrene blends during compounding. Polymer 2001, 42, 8217–8223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, Y.; Kong, M.; Zhu, H.; Chen, G.; Yang, Q. Morphology and rheology of poly(l-lactide)/polystyrene blends filled with silica nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, A.S.; Parpaite, T.; Otazaghine, B.; Taguet, A.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.M. Viscoelastic properties of polystyrene/polyamide-6 blend compatibilized with silica/polystyrene Janus hybrid nanoparticles. J. Rheol. 2017, 61, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippone, G.; Romeo, G.; Acierno, D. Role of interface rheology in altering the onset of co-continuity in nanoparticle-filled polymer blends. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2011, 296, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Q.; Li, L. Morphology and properties of highly talc- and CaCO3-filled poly(vinyl alcohol) composites prepared by melt processing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 3050–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graebling, D.; Muller, R.; Palierne, J.F. Linear Viscoelastic Behavior of Some Incompatible Polymer Blends in the Melt. Interpretation of Data with a Model of Emulsion of Viscoelastic Liquids. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, H.H.; Chambon, F. Analysis of Linear Viscoelasticity of a Crosslinking Polymer at the Gel Point. J. Rheol. 1986, 30, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenouillot, F.; Cassagnau, P.; Majeste, J. Uneven distribution of nanoparticles in immiscible fluids: Morphology development in polymer blends. Polymer 2009, 50, 1333–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guggenheim, E.A. The principle of corresponding states. J. Chem. Phys. 1945, 13, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, M.; Mey-Marom, A.; Frank, R. Surface free energies of polymeric materials, additives and minerals. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2005, 16, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Maham, Y.; Masliyah, J.H.; Gray, M.R.; Mather, A.E. Measurement of contact angles for fumed silica nanospheres using enthalpy of immersion data. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 228, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, C.; García-Morales, M.; Gupta, J.; McNally, T. On the phase affinity of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in PMMA:LDPE immiscible polymer blends. Polymer 2017, 118, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plattier, J.; Benyahia, L.; Dorget, M.; Niepceron, F.; Tassin, J.F. Viscosity-induced filler localisation in immiscible polymer blends. Polymer 2015, 59, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Component | Surface Tension (mN/m) | γ0 | Tc (K) a | −dγ/dT (mN m−1 K−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 °C | 200 °C | ||||||||
| γ | γd | γp | γ | γd | γp | ||||
| PP | 24.7 | 24.5 | 0.2 | 16.4 | 16.3 | 0.1 | 40.0 | 914 | - |
| PVA | 60.2 | 32.6 | 27.6 | 41.0 | 22.2 | 18.8 | 95.5 | 948 | - |
| S5505 b | 91.1 | 0.7 | 90.4 | 73.6 | 0.6 | 73.0 | - | - | 0.1 |
| R816 b | 88.5 | 0.4 | 88.1 | 71.0 | 0.3 | 70.7 | - | - | 0.1 |
| R972 c | 32 | 30 | 2 | 14.5 | 13.6 | 0.9 | - | - | 0.1 |
| Component | Interfacial Energy with PP (mJ/m2) | Interfacial Energy with PVA (mJ/m2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geometric Mean | Harmonic Mean | Geometric Mean | Harmonic Mean | |
| S5505 | 78.3 | 87.3 | 33.2 | 52.5 |
| R816 | 77.7 | 85.8 | 33.9 | 51.4 |
| R972 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 12.5 | 18.3 |
| PP | - | - | 16.6 | 19.4 |
| Silica Nanoparticle | Wetting Parameter (Geometric Mean) | Wetting Parameter (Harmonic Mean) | Prediction |
|---|---|---|---|
| S5505 | −2.72 | −1.79 | PVA phase |
| R816 | −2.64 | −1.77 | PVA phase |
| R972 | 0.72 | 0.90 | interface |
| Silica Nanoparticle | Confirmation |
|---|---|
| S5505 | PVA phase |
| R816 | PVA phase, interface |
| R972 | PP phase, interface, PVA phase |
| Sample | Spherical PVA | Transitional PVA | Fibrous PVA | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dsv (μm) | Projection Fraction (%) | Dtn (μm) | Projection Fraction (%) | Dfn (μm) | Projection Fraction (%) | |
| PP70-PVA30 | 10.0 | 22.1 | 6.4 | 41.9 | 5.3 | 36.0 |
| PP70-PVA30-S5505 | 11.8 | 20.6 | 8.5 | 36.0 | 9.2 | 43.4 |
| PP70-PVA30-R816 | 11.4 | 29.3 | 7.1 | 33.0 | 8.1 | 37.7 |
| PP70-PVA30-R972 | 8.3 | 40.0 | 4.7 | 15.0 | 6.4 | 45.0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, X.; Cayla, A.; Devaux, E.; Salaün, F. Microstructure Evolution of Immiscible PP-PVA Blends Tuned by Polymer Ratio and Silica Nanoparticles. Polymers 2018, 10, 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10091031
Yan X, Cayla A, Devaux E, Salaün F. Microstructure Evolution of Immiscible PP-PVA Blends Tuned by Polymer Ratio and Silica Nanoparticles. Polymers. 2018; 10(9):1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10091031
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Xiang, Aurélie Cayla, Eric Devaux, and Fabien Salaün. 2018. "Microstructure Evolution of Immiscible PP-PVA Blends Tuned by Polymer Ratio and Silica Nanoparticles" Polymers 10, no. 9: 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10091031
APA StyleYan, X., Cayla, A., Devaux, E., & Salaün, F. (2018). Microstructure Evolution of Immiscible PP-PVA Blends Tuned by Polymer Ratio and Silica Nanoparticles. Polymers, 10(9), 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10091031