Dopamine Grafted Iron-Loaded Waste Silk for Fenton-Like Removal of Toxic Water Pollutants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
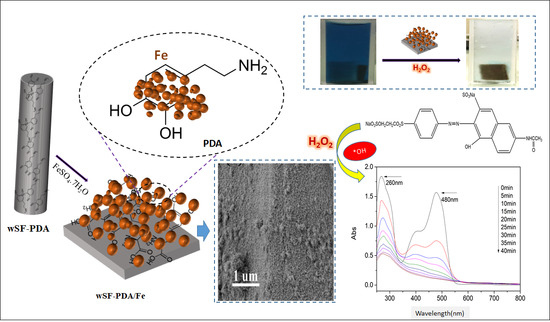
2.2.1. Preparation of Dopamine Grafted Waste Silk
2.2.2. Preparation of wSF-PDA/Fe
2.3. Material Characterizations
2.4. Catalytic Activity of wSF-DA/Fe
2.4.1. Effect of H2O2 Concentration on Removal Performance
2.4.2. Effect of Pollutant Concentration on Removal Performance
2.4.3. Effect of Reaction Temperature on Pollutant Removal Performance
2.4.4. Effect of Different Electrolytes (NaCl, Na2SO4) of Pollutant Removal Performance
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological Analysis
3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Analysis
3.3. Loading Analysis
3.4. Degradation of Dyes as a Function of Time
3.4.1. Kinetics of Dye Degradation
3.4.2. Postulated Mechanism of Dye Removal
- (i)
- The process of producing reactive speciesFe2+ + H2O2→Fe3+ + HO− + •OH
- (ii)
- The process of color removal of dyesDyes + •OH→Reaction intermediates
- (iii)
- The process of degradationReaction intermediates + •OH→CO2 + H2O
3.5. Factors Influencing the Removal of Dyes
3.5.1. Effect of Different Samples
3.5.2. Effect of H2O2 Concentration
3.5.3. Effect of Dye Concentration
3.5.4. Effect of Reaction Temperature
3.5.5. Effect of Different Electrolytes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, C.; Goyal, A.; Singhal, S. Nickel-doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: Efficient catalysts for the reduction of nitroaromatic compounds and photo-oxidative degradation of toxic dyes. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 7959–7970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernández, C.; Larrechi, M.S.; Callao, M.P. An analytical overview of processes for removing organic dyes from wastewater effluents. Trends Anal. Chem. 2010, 29, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacic, P.; Somanathan, R. Nitroaromatic compounds: Environmental toxicity, carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, therapy and mechanism. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2014, 34, 810–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, T.; McMullan, G.; Marchant, R.; Nigam, P. Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: A critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 77, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mo, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, C.; Han, L.; Guo, R.; Gou, H.; Wei, X.; Hu, R. Synthesis of flower-like TiO2 microsphere/graphene composite for removal of organic dye from water. Mater. Des. 2016, 99, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, A.; Abouseoud, M.; Amrane, A. Phenol Removal by a Sequential Combined Fenton-Enzymatic Process. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2017, 16, 321. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.X.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, W.C.; Wang, W.M.; Zhang, L.C. Rapid malachite green degradation using Fe73. 5Si13. 5B9Cu1Nb3 metallic glass for activation of persulfate under UV–Vis light. Mater. Des. 2017, 119, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, H.; Xiao, S.; Morshed, M.N.; Al Azad, S. Immobilization of Cationic Titanium Dioxide (TiO2+) on ElectrospunNanofibrous Mat: Synthesis, Characterization, and Potential Environmental Application. Fiber Polym. 2018, 19, 1715–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidheesh, P.V.; Gandhimathi, R.; Ramesh, S.T. Degradation of dyes from aqueous solution by Fenton processes: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 2099–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabil, B.; Morshed, M.N.; Nemeshwaree, B.; Christine, C.; Julien, V.; Olivier, T.; Abdelkrim, A. Development of new multifunctional filter based nonwovens for organics pollutants reduction and detoxification: High catalytic and antibacterial activities. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 356, 702–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieillard, J.; Bouazizi, N.; Mohammad, N.M.; Thomas, C.; Florie, D.; Radhouane, B.; Thébault, P.; Lesouhaitier, O.; Le Derf, F.; Azzouz, A. CuONanosheets Modified with Amine and Thiol Grafting for High Catalytic and Antibacterial Activities. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 10179–10189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augugliaro, V.; Palmisano, L.; Sclafani, A.; Minero, C.; Pelizzetti, E. Photocatalytic degradation of phenol in aqueous titanium dioxide dispersions. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 1988, 16, 89–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, F.; Calleja, G.; Melero, J.A.; Molina, R. Heterogeneous photo-Fenton degradation of phenolic aqueous solutions over iron-containing SBA-15 catalyst. Appl. Catal. B 2005, 60, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, B.H.; Lee, T.W. Degradation of malachite green in aqueous solution by Fenton process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babuponnusami, A.; Muthukumar, K. Degradation of phenol in aqueous solution by fenton, sono-fenton and sono-photo-fentonmethods. Clean Soil Air Water 2011, 39, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Chen, S.; Jiang, Y.; Xie, S.; Quan, H.; Hua, L.; Luo, X.; Guo, L. Heterogeneous Fenton-like catalysis of Fe-MOF derived magnetic carbon nanocomposites for degradation of 4-nitrophenol. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 49024–49030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.S.; Huang, S.T.; Lin, J.G. Degradation of 4-nitrophenol using the Fenton process. Water Sci. Technol. 2000, 42, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, A.; Aghbolaghy, M.; Khataee, A.; ShoaBargh, S. Use of enzymatic bio-Fenton as a new approach in decolorization of malachite green. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hermosilla, D.; Cortijo, M.; Huang, C.P. The role of iron on the degradation and mineralization of organic compounds using conventional Fenton and photo-Fenton processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 155, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morshed, M.N.; Shen, X.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Deb, H.; Azad, S.A. Effective Removal of Colorants from Aqueous Suspension through Cellulose Nano whisker Templated Titanium Dioxide/Cellulose Nanocomposite. In Proceedings of the 10th Textile Bioengineering and Informatics Symposium, Wuhan, China, 16–19 May 2017; pp. 1166–1173. [Google Scholar]
- Hermosilla, D.; Merayo, N.; Ordóñez, R.; Blanco, Á. Optimization of conventional Fenton and ultraviolet-assisted oxidation processes for the treatment of reverse osmosis retentate from a paper mill. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hermosilla, D.; Cortijo, M.; Huang, C.P. Optimizing the treatment of landfill leachate by conventional Fenton and photo-Fenton processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3473–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.C.; Tu, H.C.; Hung, C.H. Stability of nanoiron slurries and their transport in the subsurface environment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 58, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, H.; Morshed, M.N.; Xiao, S.; Al Azad, S.; Cai, Z.; Ahmed, A. Design and development of TiO2-Fe0 nanoparticle-immobilized nanofibrous mat for photocatalytic degradation of hazardous water pollutants. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 30, 4842–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Zhao, D. Preparation and characterization of a new class of starch-stabilized bimetallic nanoparticles for degradation of chlorinated hydrocarbons in water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 3314–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Jin, Z.H.; Li, T.L.; Zhang, H.; Gao, S. Preparation of spherical iron nanoclusters in ethanol—water solution for nitrate removal. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Hong, H.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Shin, H.J.; Yang, J.W. Degradation of trichloroethylene by zero-valent iron immobilized in cationic exchange membrane. Desalination 2008, 223, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Al-Abed, S.R.; Agarwal, S.; Dionysiou, D.D. Synthesis of reactive nano-Fe/Pd bimetallic system-impregnated activated carbon for the simultaneous adsorption and dechlorination of PCBs. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 3649–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, M.N.; Bouazizi, N.; Behary, N.; Guan, J.; Nierstrasz, V. Stabilization of zero valent iron (Fe0) on plasma/dendrimer functionalized polyester fabrics for Fenton-like removal of hazardous water pollutant. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 374, 658–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Zhou, Q.; Zhu, X.; Guo, J.; Mia, M.S.; Yan, X.; Chen, G.; Xing, T. A superhydrophobic bionic coating on silk fabric with flame retardancy and UV shielding ability. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 483, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouazizi, N.; Vieillard, J.; Bargougui, R.; Couvrat, N.; Thoumire, O.; Morin, S.; Ladam, G.; Mofaddel, N.; Brun, N.; Azzouz, A.; et al. Entrapment and stabilization of iron nanoparticles within APTES modified graphene oxide sheets for catalytic activity improvement. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 771, 1090–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Wu, W.; Zhou, S.; Xing, T.; Sun, G.; Chen, G. Polydopamine-induced growth of mineralized γ-FeOOH nanorods for construction of silk fabric with excellent superhydrophobicity, flame retardancy and UV resistance. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 122988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, A.R.; Kaplan, D.L. Biomedical applications of chemically-modified silk fibroin. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 6443–6450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, F.; Wei, Q.; Liu, Y.; Gao, W.; Huang, Y. Surface functionalization of silk fabric by PTFE sputter coating. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 8025–8028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, M.N.; Bouazizi, N.; Behary, N.; Vieillard, J.; Thoumire, O.; Nierstrasz, V.; Azzouz, A. Iron-loaded amine/thiol functionalized polyester fibers with high catalytic activities: A comparative study. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 8384–8399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.A.J.; Andrade, P.L.; Silva, M.P.C.; Valladares, L.D.L.S.; Aguiar, J.A. Synthesis and characterization of Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated with fucanpolysaccharides. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 343, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivanets, A.; Roshchina, M.; Srivastava, V.; Prozorovich, V.; Dontsova, T.; Nahirniak, S.; Pankov, V.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Tran, H.N.; Sillanpää, M. Effect of metal ions adsorption on the efficiency of Methylene Blue degradation onto MgFe2O4 as Fenton-like catalysts. Colloids Surf. A 2019, 571, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekbaş, M.; Yatmaz, H.C.; Bektaş, N. Heterogeneous photo-Fenton oxidation of reactive azo dye solutions using iron exchanged zeolite as a catalyst. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 115, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, T.L.P.; Mendonca, V.P.; Jose, H.J.; Rodrigues, A.E.; Moreira, R.F.P.M. Treatment of textile wastewater by heterogeneous Fenton process using a new composite Fe2O3/carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 118, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, S.; Ala’a, H.; Naushad, M.; Ghfar, A.A.; Ahamad, T.; Stadler, F.J. Fabrication and characterization of novel Fe0@ Guar gum-crosslinked-soya lecithin nanocomposite hydrogel for photocatalytic degradation of methyl violet dye. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 311, 895–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muruganandham, M.; Swaminathan, M. Decolourisation of Reactive Orange 4 by Fenton and photo-Fenton oxidation technology. Dyes Pigment. 2004, 63, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Pal, A.; Sahoo, C. Photocatalytic degradation of a mixture of Crystal Violet (Basic Violet 3) and Methyl Red dye in aqueous suspensions using Ag+ doped TiO2. Dyes Pigment. 2006, 69, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattri, S.D.; Singh, M.K. Removal of malachite green from dye wastewater using neem sawdust by adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadtochenko, V.; Kiwi, J. Photochemical reactions in the photo-Fenton system with ferric chloride. 2. Implications of the precursors formed in the dark. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 3282–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Samples | Atomic Percentage of Surface Elements | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C (%) | N (%) | O (%) | Fe (%) | |
| wSF | 71.07 | 10.99 | 17.94 | 0 |
| wSF-PDA | 76.14 | 5.56 | 17.13 | 1.17 |
| wSF-PDA/Fe | 74.47 | 0.12 | 21.18 | 4.23 |
| Samples | Methylene Blue | Cationic Violet X-5BLN | Reactive Orange GRN | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aTime (min) | bk (min−1) | cR2 | aTime (min) | bk (min−1) | cR2 | aTime (min) | bk (min−1) | cR2 | |
| wSF-PDA/Fe | 10 | 0.576 | 0.982 | 25 | 0.157 | 0.997 | 40 | 0.065 | 0.984 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mia, M.S.; Yan, B.; Zhu, X.; Xing, T.; Chen, G. Dopamine Grafted Iron-Loaded Waste Silk for Fenton-Like Removal of Toxic Water Pollutants. Polymers 2019, 11, 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11122037
Mia MS, Yan B, Zhu X, Xing T, Chen G. Dopamine Grafted Iron-Loaded Waste Silk for Fenton-Like Removal of Toxic Water Pollutants. Polymers. 2019; 11(12):2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11122037
Chicago/Turabian StyleMia, Md Shipan, Biaobiao Yan, Xiaowei Zhu, Tieling Xing, and Guoqiang Chen. 2019. "Dopamine Grafted Iron-Loaded Waste Silk for Fenton-Like Removal of Toxic Water Pollutants" Polymers 11, no. 12: 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11122037
APA StyleMia, M. S., Yan, B., Zhu, X., Xing, T., & Chen, G. (2019). Dopamine Grafted Iron-Loaded Waste Silk for Fenton-Like Removal of Toxic Water Pollutants. Polymers, 11(12), 2037. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11122037