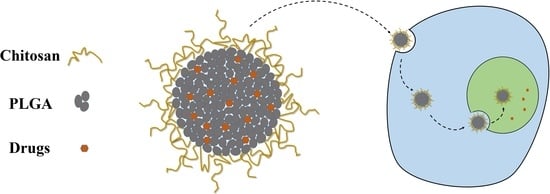
Chitosan-Modified PLGA Nanoparticles for Control-Released Drug Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PLGA NPs
2.3. Preparation of the CS-Modified PLGA NPs
2.4. Characterization of the NPs
2.4.1. Particle Size, Zeta Potential, and Surface Morphology of the NPs
2.4.2. TGA, FTIR, and XPS
2.4.3. Drug Loading and Encapsulation Efficiency
2.4.4. In Vitro Drug-Release Studies
2.4.5. MTT Assay
2.4.6. Cellular Uptake of the NPs
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Particle Size, Zeta Potential, and Surface Morphology of the NPs
3.2. TGA, FT-IR, and XPS
3.3. Drug Loading and Encapsulation Efficiency
3.4. In Vitro Drug-Release Behavior of NPs
3.5. MTT Assay
3.6. Cellular Uptake of the NPs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brigger, I.; Dubernet, C.; Couvreur, P. Nanoparticles in cancer therapy and diagnosis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danhier, F.; Ansorena, E.; Silva, J.M.; Coco, R.; Le Breton, A.; Preat, V. PLGA-based nanoparticles: An overview of biomedical applications. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varypataki, E.M.; Silva, A.L.; Barnier-Quer, C.; Collin, N.; Ossendorp, F.; Jiskoot, W. Synthetic long peptide-based vaccine formulations for induction of cell mediated immunity: A comparative study of cationic liposomes and PLGA nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2016, 226, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Deng, C.; Meng, F.; Zhang, J.; Sun, H.; Zhong, Z. Hyaluronic acid coated PLGA nanoparticulate docetaxel effectively targets and suppresses orthotopic human lung cancer. J. Control. Release 2017, 259, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Hammadi, M.M.; Delgado, A.V.; Melguizo, C.; Prados, J.C.; Arias, J.L. Folic acid-decorated and PEGylated PLGA nanoparticles for improving the antitumour activity of 5-fluorouracil. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 516, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Xie, L.Q.; Qin, J.; Jia, Y.; Cai, X.; Nan, W.; Yang, W.; Lv, F.; Zhang, Q.Q. Surface modification of PLGA nanoparticles with biotinylated chitosan for the sustained in vitro release and the enhanced cytotoxicity of epirubicin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 138, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, S.; Jiang, S.; Huang, C. PTX-loaded three-layer PLGA/CS/ALG nanoparticle based on layer-by-layer method for cancer therapy. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2018, 29, 1566–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Ahmed, S. A review on chitosan and its nanocomposites in drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ways, T.M.M.; Lau, W.M.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Chitosan and Its Derivatives for Application in Mucoadhesive Drug Delivery Systems. Polymers 2018, 10, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engin, K.; Leeper, D.B.; Cater, J.R.; Thistlethwaite, A.J.; Tupchong, L.; McFarlane, J.D. Extracellular pH distribution in human tumours. Int. J. Hyperthermia 1995, 11, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L. Chitosan and its derivatives as vehicles for drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abouelmagd, S.A.; Ku, Y.J.; Yeo, Y. Low molecular weight chitosan-coated polymeric nanoparticles for sustained and pH-sensitive delivery of paclitaxel. J. Drug Target. 2015, 23, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.L.; Wang, Y.X. Chitosan Surface-Modified PLGA Nanoparticles: Preparation, Characterization, and Evaluation of their In Vitro Drug-Release Behaviors and Cytotoxicities. Curr. Nanosci. 2014, 10, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavi, S.; Ramezani, M.; Alibolandi, M.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M. Chitosan-modified PLGA nanoparticles tagged with 5TR1 aptamer for in vivo tumor-targeted drug delivery. Cancer Lett. 2017, 400, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, M.E.; Szoka, F.C.; Frechet, J.M. Soluble polymer carriers for the treatment of cancer: the importance of molecular architecture. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, H.; Watanabe, R.; Choyke, P.L. Improving Conventional Enhanced Permeability and Retention (EPR) Effects; What Is the Appropriate Target? Theranostics 2014, 4, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Yang, W.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Gao, F.; Yang, X.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y. Surface modification of mitoxantrone-loaded PLGA nanospheres with chitosan. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 73, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariatinia, Z. Pharmaceutical applications of chitosan. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 263, 131–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu-Quang, H.; Vinding, M.S.; Xia, D.; Nielsen, T.; Ullisch, M.G.; Dong, M.; Nielsen, N.C.; Kjems, J. Chitosan-coated poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) perfluorooctyl bromide nanoparticles for cell labeling in (19) F magnetic resonance imaging. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrie, G.; Keen, I.; Drew, B.; Chandler-Temple, A.; Rintoul, L.; Fredericks, P.; Grondahl, L. Interactions between alginate and chitosan biopolymers characterized using FTIR and XPS. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2533–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessi, H.; Puisieux, F.; Devissaguet, J.P.; Ammoury, N.; Benita, S. Nanocapsule formation by interfacial polymer deposition following solvent displacement. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 55, R1–R4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez Rivas, C.J.; Tarhini, M.; Badri, W.; Miladi, K.; Greige-Gerges, H.; Nazari, Q.A.; Galindo Rodriguez, S.A.; Roman, R.A.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Nanoprecipitation process: From encapsulation to drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almoustafa, H.A.; Alshawsh, M.A.; Chik, Z. Technical aspects of preparing PEG-PLGA nanoparticles as carrier for chemotherapeutic agents by nanoprecipitation method. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 533, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues de Azevedo, C.; von Stosch, M.; Costa, M.S.; Ramos, A.M.; Cardoso, M.M.; Danhier, F.; Preat, V.; Oliveira, R. Modeling of the burst release from PLGA micro- and nanoparticles as function of physicochemical parameters and formulation characteristics. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Din, F.U.; Kim, D.W.; Choi, J.Y.; Thapa, R.K.; Mustapha, O.; Kim, D.S.; Oh, Y.K.; Ku, S.K.; Youn, Y.S.; Oh, K.T.; et al. Irinotecan-loaded double-reversible thermogel with improved antitumor efficacy without initial burst effect and toxicity for intramuscular administration. Acta Biomater. 2017, 54, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Yao, H.; Jiang, S.; YunzhuPu; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. To reduce premature drug release while ensuring burst intracellular drug release of solid lipid nanoparticle-based drug delivery system with clathrin modification. Nanomedicine 2019, 15, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.Y.; Hu, Z.H.; Jin, T. Sustained-release microspheres of amifostine for improved radio-protection, patient compliance, and reduced side effects. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 3704–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, G.; Tuncer, C.; Bütün, V. pH-Responsive polymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 144–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivek, R.; Nipun Babu, V.; Thangam, R.; Subramanian, K.S.; Kannan, S. pH-responsive drug delivery of chitosan nanoparticles as Tamoxifen carriers for effective anti-tumor activity in breast cancer cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 111, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E.; Yalinca, Z.; Yahya, K.; Sirotina, U. pH responsive graft copolymers of chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 90, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, S.; Adhikari, U.; Rijal, N.P.; Bhattarai, S.R.; Sankar, J.; Bhattarai, N. pH-Responsive PLGA Nanoparticle for Controlled Payload Delivery of Diclofenac Sodium. J. Funct. Biomater. 2016, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartiera, M.S.; Johnson, K.M.; Rajendran, V.; Caplan, M.J.; Saltzman, W.M. The uptake and intracellular fate of PLGA nanoparticles in epithelial cells. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2790–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Termsarasab, U.; Cho, H.J.; Kim, D.H.; Chong, S.; Chung, S.J.; Shim, C.K.; Moon, H.T.; Kim, D.D. Chitosan oligosaccharide-arachidic acid-based nanoparticles for anti-cancer drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chronopoulou, L.; Massimi, M.; Giardi, M.F.; Cametti, C.; Devirgiliis, L.C.; Dentini, M.; Palocci, C. Chitosan-coated PLGA nanoparticles: a sustained drug release strategy for cell cultures. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 103, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasturi, S.P.; Sachaphibulkij, K.; Roy, K. Covalent conjugation of polyethyleneimine on biodegradable microparticles for delivery of plasmid DNA vaccines. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6375–6385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Kong, Y.Y.; Sun, J.H.; Huo, S.J.; Zhou, M.; Gui, Y.L.; Mu, X.; Chen, H.; Yu, S.Q.; Xu, Q. Co-delivery nanoparticles with characteristics of intracellular precision release drugs for overcoming multidrug resistance. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 2081–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]









| NPs | Particle Size (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLGA | 132.8 ± 1.5 | 0.155 ± 0.03 | −20.8 ± 1.1 |
| CS/PLGA (w/w) = 0.2 | 140.5 ± 2.4 | 0.104 ± 0.02 | 10.1 ± 0.9 |
| CS/PLGA (w/w) = 0.4 | 154.2 ± 2.6 | 0.122 ± 0.04 | 21.5 ± 0.5 |
| CS/PLGA (w/w) = 0.8 | 172.7 ± 3.2 | 0.144 ± 0.06 | 25.6 ± 0.6 |
| NPs | C1s | O1s | N1s |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLGA | 64.98 | 35.02 | 0 |
| CS | 69.03 | 26.73 | 4.24 |
| CS/PLGA (w/w) = 0.2 | 65.02 | 32.2 | 2.78 |
| CS/PLGA (w/w) = 0.4 | 66.29 | 30.19 | 3.52 |
| CS/PLGA (w/w) = 0.8 | 68.21 | 27.73 | 4.06 |
| NPs | DL (%) | EE (%) |
|---|---|---|
| PLGA | 5.07 | 65.8 |
| CS/PLGA (w/w) = 0.2 | 6.42 | 80.5 |
| CS/PLGA (w/w) = 0.4 | 5.69 | 85.3 |
| CS/PLGA (w/w) = 0.8 | 4.59 | 87.1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, B.; Lv, X.; Le, Y. Chitosan-Modified PLGA Nanoparticles for Control-Released Drug Delivery. Polymers 2019, 11, 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020304
Lu B, Lv X, Le Y. Chitosan-Modified PLGA Nanoparticles for Control-Released Drug Delivery. Polymers. 2019; 11(2):304. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020304
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Boting, Xikun Lv, and Yuan Le. 2019. "Chitosan-Modified PLGA Nanoparticles for Control-Released Drug Delivery" Polymers 11, no. 2: 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020304
APA StyleLu, B., Lv, X., & Le, Y. (2019). Chitosan-Modified PLGA Nanoparticles for Control-Released Drug Delivery. Polymers, 11(2), 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020304