DNA Compaction and Charge Neutralization Regulated by Divalent Ions in very Low pH Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Electrophoretic Mobility Measurement
2.2.2. AFM Imaging
2.2.3. Magnetic Tweezer Tethering
3. Results and Discussion
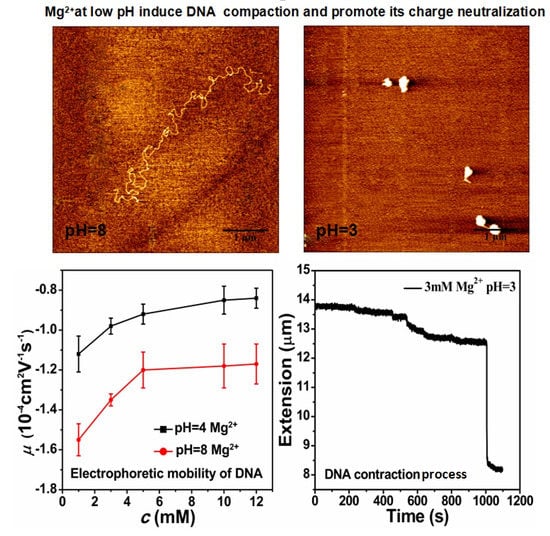
3.1. Electrophoretic Mobility of DNA Measurement
3.2. AFM Morphology of DNA
3.3. The Condensing Forces and the Unraveling Forces Measurement
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hong, F.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Yan, H. DNA Origami: Scaffolds for Creating Higher Order Structures. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 12584–12640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeman, S.C. DNA in a material world. Nature 2003, 421, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frutos, M.D.; Raspaud, E.; Leforestier, A.; Livolant, F. Aggregation of Nucleosomes by Divalent Cations. Biophys. J. 2001, 81, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Todd, B.A.; Rau, D.C. Interplay of ion binding and attraction in DNA condensed by multivalent cations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besteman, K.; Eijk, K.V.; Lemay, S.G. Charge inversion accompanies DNA condensation by multivalent ions. Nat. Phys. 2007, 3, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, M.; Yoshikawa, K.; Vasilevskaya, V.V.; Khokhlov, A.R. Discrete Coil−Globule Transition of Single Duplex DNAs Induced by Polyamines. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 9396–9401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, K.; Takahashi, M.; Vasilevskaya, V.V.; Khokhlov, A.R. Large discrete transition in a single DNA molecule appears continuous in the ensemble. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 76, 3029–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akitaya, T.; Seno, A.; Nakai, T.; Hazemoto, N.; Murata, S.; Yoshikawa, K. Weak interaction induces an ON/OFF switch, whereas strong interaction causes gradual change: Folding transition of a long duplex DNA chain by poly-L-lysine. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinchenko, A.A.; Yoshikawa, K.; Baigl, D. Compaction of single-chain DNA by histone-inspired nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 228101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinchenko, A.A.; Sakaue, T.; Araki, S.; Yoshikawa, K.; Baigl, D. Single-chain compaction of long duplex DNA by cationic nanoparticles: Modes of interaction and comparison with chromatin. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 3019–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Turro, N.J.; Tomalia, D.A. Using Ethidium Bromide To Probe the Interactions between DNA and Dendrimers. Langmuir 2000, 16, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongu, C.; Kenmotsu, T.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Zinchenko, A.; Chen, N.; Yoshikawa, K. Divalent cation shrinks DNA but inhibits its compaction with trivalent cation. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 144, 205101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mengarelli, V.; Auvray, L.; Pastré, D.; Zeghal, M. Charge inversion, condensation and decondensation of DNA and polystyrene sulfonate by polyethylenimine. Eur. Phys. J. E 2011, 34, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansma, H.G.; Golan, R.; Wan, H.; Lollo, C.P.; Mullenley, P.; Kwoh, D. DNA condensation for gene therapy as monitored by atomic force microscopy. Nucl. Acids Res. 1998, 26, 2481–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecconi, C.; Shank, E.; Dahlquis, F.W.; Marqusee, S.; Bustamante, C. Protein-DNA chimeras for single molecule mechanical folding studies with the optical tweezers. Eur. Biophy. J. 2008, 37, 729–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Skoko, D.; Marko, J.F. Near-field-magnetic-tweezer manipulation of single DNA molecules. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 70, 11905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, B.; Chen, K.L.; Zhou, R. Mechanism of Divalent-Ion-Induced Charge Inversion of Bacterial Membranes. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 2434–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, B.; Aksimentiev, A. Electric and Electrophoretic Inversion of the DNA Charge in Multivalent Electrolytes. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, Y.; Sakamaki, Y.; Sano, M. Elastic response of single DNA molecules exhibits a reentrant collapsing transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 18102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Cao, B.; Guo, Z.; Yang, G. Single Molecular Demonstration of Modulating Charge Inversion of DNA. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baigl, D.; Yoshikawa, K. Dielectric control of counterion-induced single-chain folding transition of DNA. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 3486–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohman, T.M.; Ferrari, M.E. Escherichia Coli Single-Stranded DNA-Binding Protein: Multiple DNA-Binding Modes and Cooperativities. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1994, 63, 527–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.; Nguyen, T.T.; Carloni, P. DNA like-charge attraction and overcharging by divalent counterions in the presence of divalent co-ions. J. Biol. Phys. 2017, 43, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koltover, I.; Wagner, K.; Safinya, C.R. DNA Condensation in Two Dimensions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 14046–14097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, T.; Li, S.; Xia, W.; Zhang, W.; Yang, G. Direct demonstration of DNA attraction mediated by divalent counterions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, M.J.; Bradbury, E.; Balhorn, R. AFM analysis of DNA-protamine complexes bound to mica. Nucl. Acids Res. 1997, 25, 2221–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ran, S.; Man, B.; Yang, G. Ethanol induces condensation of single DNA molecules. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 4425–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Gao, T.; Yang, G. The Mixing Counterion Effect on DNA Compaction and Charge Neutralization at Low Ionic Strength. Polymers 2018, 10, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Wang, Y.; Cao, B.; Guo, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, G. The suppression and promotion of DNA charge inversion by mixing counterions. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y. A dynamic light scattering study of counter-ions condensation on DNA. Acta Phys. Sin. 2013, 62, 118702. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, A.; Yang, G. The effect of pH on charge inversion and condensation of DNA. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 6669–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermann, P.; Fredericq, E. The role of the AT pairs in the acid denaturation of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977, 4, 2939–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeki, K.; Kunito, T. Adsorptions of DNA molecules by soils and variable-charged soil constituents. Curr Res. 2010, 1, 188–195. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, R.; Kondev, J.; Theriot, J. Physical Biology of the Cell; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 327–330. ISBN 978-0-8153-4163-5. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, B.; Aksimentiev, A. DNA Attraction in Monovalent and Divalent Electrolytes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 15754–15759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muntean, C.M.; Puppels, G.J. Raman microspectroscopic study on low-pH-induced DNA structural transitions in the presence of magnesium ions. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2002, 33, 784–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntean, C.M.; Segersnolten, G.M. Raman microspectroscopic study of effects of Na(I) and Mg(II) ions on low pH induced DNA structural changes. Biopolymers 2003, 72, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| pH Value | Fc (pN) | Fu (pN) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 mM | 10 mM | 100 mM | 3 mM | 10 mM | 100 mM | |
| 5.0 | 0.0±0.0 | 1.1±0.2 | 0.0±0.0 | 0.0±0.0 | 0.8±0.3 | 0.0±0.0 |
| 3.0 | 2.4±0.6 | 3.8±0.8 | 2.6±0.8 | 3.7±0.8 | 7.6±0.5 | 6.2±0.7 |
| 2.0 | 3.4±1.2 | 4.5±0.9 | 3.1±1.0 | 7.2±1.5 | 9.5±1.4 | 5.8±0.9 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, T.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, G. DNA Compaction and Charge Neutralization Regulated by Divalent Ions in very Low pH Solution. Polymers 2019, 11, 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020337
Gao T, Zhang W, Wang Y, Yang G. DNA Compaction and Charge Neutralization Regulated by Divalent Ions in very Low pH Solution. Polymers. 2019; 11(2):337. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020337
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Tianyong, Wei Zhang, Yanwei Wang, and Guangcan Yang. 2019. "DNA Compaction and Charge Neutralization Regulated by Divalent Ions in very Low pH Solution" Polymers 11, no. 2: 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020337
APA StyleGao, T., Zhang, W., Wang, Y., & Yang, G. (2019). DNA Compaction and Charge Neutralization Regulated by Divalent Ions in very Low pH Solution. Polymers, 11(2), 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11020337