Diffusion Mechanism of Aqueous Solutions and Swelling of Cellulosic Fibers in Silicone Non-Aqueous Dyeing System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Fluorescent Solution
2.3. Fiber Swelling Evaluation
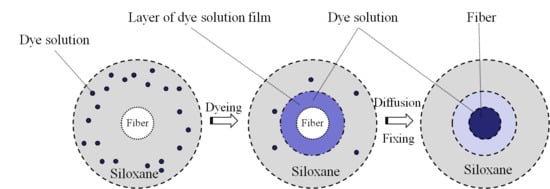
2.4. Disffusion of Reactive Dye Solution in the Siloxane Non-Aqueous Dyeing System
2.5. The Migration of Siloxane Media on Viscose
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fiber Swelling
3.2. The Wetting Time of Non-Aqueous Media and Aqueous Solution on Cellulosic Film
3.3. Influence of Non-Aqueous Media on the Adsorption of Aqueous Solution
3.4. Migration of Non-Aqueous Media Film
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sawada, K.; Takagi, T.; Jun, J.H.; Ueda, M.; Lewis, D.M. Dyeing natural fibers in supercritical carbon dioxide using a nonionic surfactant reverse micellar system. Color. Technol. 2010, 118, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cid, M.V.F.; Spronsen, J.V.; Kraan, M.V.D.; Veugelers, W.J.T.; Woerlee, G.F.; Witkamp, G.J. A significant approach to dye cotton in supercritical carbon dioxide with fluorotriazine reactive dyes. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2007, 40, 477–484. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Lee, C.H.; Tang, Y.L.; Kan, C.W. Dyeing cotton in alkane solvent using polyethylene glycol-based reverse micelle as reactive dye carrier. Cellulose 2016, 23, 965–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.; Ruan, X.; Yang, Y. Comprehensive Study on Cellulose Swelling for Completely Recyclable Nonaqueous Reactive Dyeing. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 2439–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banchero, M. Supercritical fluid dyeing of synthetic and natural textiles-a review. Color. Technol. 2013, 129, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, L.; Liu, J.; Cai, G.; Wang, J. Study of hydrolytic kinetics of vinyl sulfone reactive dye in siloxane reverse micro-emulsion. Text. Res. J. 2017, 87, 2368–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, L.; Wu, P.; Liu, J.; Wang, J. Effect of nonionic surfactant on the micro-emulsifying water in silicone media. J. Surf. Deterg. 2017, 20, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Miao, H.; Li, S. Non-aqueous dyeing of reactive dyes in D5. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 441, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Li, M. Study on the dyeing of PET fiber with disperse dyes in D5 media. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 331, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Fu, C.; Zhang, Y. Study on hydrolysis kinetics of reactive dyes in dye/D5 suspending system. J. Text. Res. 2013, 34, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, C.; Wang, J.; Shao, J.; Pu, D.; Chen, J.; Liu, J. A non-aqueous dyeing process of reactive dye on cotton. J. Text. Inst. 2015, 106, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns-Naas, L.A.; Mast, R.W.; Meeks, R.G.; Mann, P.C.; Thevenaz, P. Inhalation toxicology of decamethylcyclopentasiloxane (D5) following a 3-monthnose-only exposure in Fischer 344 rats. Toxicol. Sci. 1998, 43, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, M.B.; Looney, R.J.; Utell, M.J.; Plotzke, K.P.; Andersen, M.Z. Modeling of human dermalabsorption of octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane (D4) and decamethylcyclopentasiloxane (D5). Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 99, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovanovic, M.L.; McMahon, J.M.; McNett, D.A.; Tobin, J.M.; Plotzke, K.P. In vitro and in vivo percutaneousabsorption of 14C-octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane (14C-D4) and 14C-decamethylcyclopentasiloxane (14C-D5). Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 50, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Liu, J.; Li, Y. The impact of D5-washing on the fabric performance. J. Zhejiang Sci-Tech Univ. 2007, 24, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Fabià, S.; Norrman, J.; Sjöblom, J.; Paso, K. CO2 in lyotropic liquid crystals: Monoethanolamine-facilitated uptake and swelling. Polymers 2018, 10, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Pailthorpe, M.; David, S. A new method for improving the dye-ability of cotton with reactive dyes. Text. Res. J. 1999, 69, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybysz, K.; Czechowski, J. The effect of pulp fines on the drying process and paper strength properties. Cell. Chem. Technol. 1985, 19, 197–209. [Google Scholar]
- Luukko, K.; Maloney, C.T. Swelling of mechanical pulp fines. Cellulose 1999, 6, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joutsimo, O.; Asikainen, S. Effect of fiber wall pore structure on pulp sheet density of softwood kraft pulp fibers. BioResources 2013, 8, 2719–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantanis, G.I.; Young, R.A.; Rowell, R.M. Swelling of compressed cellulose fiber webs in organic liquids. Cellulose 1995, 2, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Wang, B.; Ruan, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y. Hydrolysis-free and fully recyclable reactive dyeing of cotton in green, non-nucleophilic solvents for a sustainable textile industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 107, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olejnik, K.; Skalski, B.; Stanislawska, A.; Wysocka-Robak, A. Swelling properties and generation of cellulose fines originating from bleached kraft pulp refined under different operating conditions. Cellulose 2017, 24, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remadevi, R.; Gordon, S.; Wang, X.; Rajkhowa, R. Investigation of the swelling of cotton fibers using aqueous glycine solutions. Text. Res. J. 2016, 87, 2204–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, V.K.; Thakur, M.K. Processing and characterization of natural cellulose fibers/thermoset polymer composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 109, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Peterrex, B.; Wang, X. The effect of pH on wool fiber diameter and fabric dimensions. Text. Res. J. 2009, 79, 953–957. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, H.; Kim, J.Y. Effects of washing parameters on dimensional stability of viscose rayon fabrics. Fiber Polym. 2016, 17, 1945–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padasala, S.; Kuperkar, K.; Bahadur, P. Solubilisation study of water-insoluble dye in cationic single/dimeric surfactant micelles: effect of headgroup, non-polar tail, and spacer chain in aqueous and salt solution. Color. Technol. 2016, 132, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhou, W.; Li, J.; Mi, Y.; Su, Z.; Ma, G. The construction of an aqueous two-phase system to solve weak-aggregation of gigaporous poly(styrene-divinyl benzene) microspheres. Polymers 2016, 8, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.Y.; Choi, H.M.; Oh, K.W. Rapid hydrophilic modification of poly(ethylene terephthalate) surface by using deep eutectic solvent and microwave irradiation. Text. Res. J. 2016, 86, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deen, G.R. Solution properties of water-soluble “smart” poly(n-acryloyl-n′-ethyl piperazine-co-methyl methacrylate). Polymers 2012, 4, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaizu, K.; Alexandridis, P. Effect of surfactant phase behavior on emulsification. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2016, 466, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, K.; Cheng, F.; Zhao, W.; Xu, L. Micelle dyeing with low liquor ratio for reactive dyes using dialkyl maleic acid ester surfactants. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.H.; Motomura, H.; Morita, Z. Diffusion/adsorption behaviour of reactive dyes in cellulose. Dyes Pigment. 1997, 34, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, H.; Yang, M.; Xu, D.; Chen, J.; Feng, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Y.; Kang, W. Stability mechanism of O/W Pickering emulsions stabilized with regenerated cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 181, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Medium | Surface Tension (dyn/cm) | Boiling Point (°C) | Viscosity (mm2/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Siloxane | 18 | 210 | 5 |
| Paraffin | 19 | 330 | 16 |
| C8H18 | 23 | 126 | 0.7 |
| C2H5OH | 22 | 78 | 1.1 |
| H2O | 72 | 100 | 1.0 |
| Medium | Siloxane | Paraffin | C8H18 | C2H5OH | H2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wetting time (s) | 0.11 | 1.28 | 0.99 | 2.34 | 3.01 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pei, L.; Luo, Y.; Gu, X.; Dou, H.; Wang, J. Diffusion Mechanism of Aqueous Solutions and Swelling of Cellulosic Fibers in Silicone Non-Aqueous Dyeing System. Polymers 2019, 11, 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030411
Pei L, Luo Y, Gu X, Dou H, Wang J. Diffusion Mechanism of Aqueous Solutions and Swelling of Cellulosic Fibers in Silicone Non-Aqueous Dyeing System. Polymers. 2019; 11(3):411. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030411
Chicago/Turabian StylePei, Liujun, Yuni Luo, Xiaomin Gu, Huashu Dou, and Jiping Wang. 2019. "Diffusion Mechanism of Aqueous Solutions and Swelling of Cellulosic Fibers in Silicone Non-Aqueous Dyeing System" Polymers 11, no. 3: 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030411
APA StylePei, L., Luo, Y., Gu, X., Dou, H., & Wang, J. (2019). Diffusion Mechanism of Aqueous Solutions and Swelling of Cellulosic Fibers in Silicone Non-Aqueous Dyeing System. Polymers, 11(3), 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11030411