Enhanced Stability and Driving Performance of GO–Ag-NW-based Ionic Electroactive Polymer Actuators with Triton X-100-PEDOT:PSS Nanofibrils
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
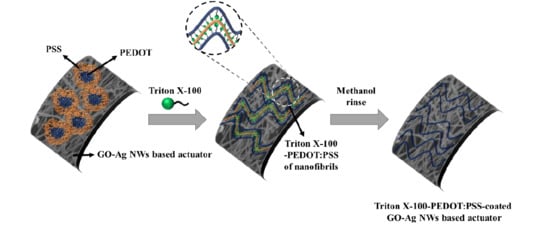
2.2. Fabrication of IEAP Actuators Based on TP/GO–Ag NW Electrode
2.3. Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of the TP/GO–Ag NW Electrode
3.2. Actuation Performance of IEAP Actuators Based on TP/GO–Ag NW Electrode
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, J.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lim, H.; Oh, I.K. Durable and water-floatable ionic polymer actuator with hydrophobic and asymmetrically laser-scribed reduced graphene oxide paper electrodes. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 2986–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Palmre, V.; Jeon, J.H.; Oh, I.K. IPMCs as EAPs: Materials. In Electromechanically Active Polymers: A Concise Reference; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 151–170. [Google Scholar]
- Shahinpoor, M.; Kim, K.J. Ionic polymer-metal composites: I. Fundamentals. Smart Mater. Struct. 2001, 10, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, N.; Asaka, K.; Nishimura, Y.; Oguro, K.; Torikai, E. Preparation of gold−solid polymer electrolyte composites as electric stimuli-responsive materials. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 1750–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmre, V.; Lust, E.; Jänes, A.; Koel, M.; Peikolainen, A.L.; Torop, J.; Johanson, U.; Aabloo, A. Electroactive polymer actuators with carbon aerogel electrodes. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 2577–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Park, I.S.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, K.J.; Heo, S. Ionic polymer–metal composite bending actuator loaded with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2007, 133, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akle, B.J.; Leo, D.J. Single-walled carbon nanotubes—Ionic polymer electroactive hybrid transducers. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2008, 19, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akle, B.; Nawshin, S.; Leo, D. Reliability of high strain ionomeric polymer transducers fabricated using the direct assembly process. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, S256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmre, V.; Brandell, D.; Mäeorg, U.; Torop, J.; Volobujeva, O.; Punning, A.; Johanson, U.; Kruusmaa, M.; Aabloo, A. Nanoporous carbon-based electrodes for high strain ionomeric bending actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2009, 18, 095028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, T.; Asaka, K.; Kosaka, A.; Aida, T. Fully plastic actuator through layer-by-layer casting with ionic-liquid-based bucky gel. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 2410–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akle, B.J.; Bennett, M.D.; Leo, D.J.; Wiles, K.B.; McGrath, J.E. Direct assembly process: A novel fabrication technique for large strain ionic polymer transducers. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 7031–7041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Park, M.; Kim, S.; Chung, P.S.; Jeon, M. Graphene Oxide-Silver Nanowires Paper Electrodes with Poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-Poly (styrenesulfonate) to Enhance the Driving Properties of Ionic Electroactive Polymer Actuators. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2018, 10, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, B.; Lim, S. PEDOT: PSS Overcoating Layer for Mechanically and Chemically Stable Ag Nanowire Flexible Transparent Electrode. J. Nanomater. 2017, 1489186. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, H.; Price, S.C.; Wiley, B.J.; You, W. Solution-processed flexible polymer solar cells with silver nanowire electrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 2011, 3, 4075–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayousse, C.; Celle, C.; Carella, A.; Simonato, J.P. Synthesis and purification of long copper nanowires. Application to high performance flexible transparent electrodes with and without PEDOT: PSS. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Kim, J.; Song, H.; Kim, S.; Jeon, M. Fast and Stable Ionic Electroactive Polymer Actuators with PEDOT: PSS/(Graphene–Ag-Nanowires) Nanocomposite Electrodes. Sensors 2018, 18, 3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koley, D.; Bard, A.J. Triton X-100 concentration effects on membrane permeability of a single HeLa cell by scanning electrochemical microscopy (SECM). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16783–16787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tevi, T.; Saint Birch, S.W.; Thomas, S.W.; Takshi, A. Effect of Triton X-100 on the double layer capacitance and conductivity of poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene): Poly (styrenesulfonate)(PEDOT: PSS) films. Synth. Met. 2014, 191, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JeongáLee, S. Improved stability of transparent PEDOT: PSS/Ag nanowire hybrid electrodes by using non-ionic surfactants. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 8292–8295. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, J.Y.; Shin, M.; Lee, J.B.; Ahn, J.H.; Baik, H.K.; Jeong, U. Effect of PEDOT nanofibril networks on the conductivity, flexibility, and coatability of PEDOT: PSS films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 2014, 6, 6954–6961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummers, W.S., Jr.; Offeman, R.E. Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Samples | Sheet Resistance (mΩ/sq.) | |
|---|---|---|
| Before Methanol Treatment | After Methanol Treatment | |
| GO–Ag NWs | 352.65 | 320.25 |
| 0.0 wt % (Pure PEDOT:PSS) | 319.36 | 284.16 |
| 1.0 wt % Triton X-100 | 255.52 | 214.73 |
| 2.5 wt % Triton X-100 | 232.15 | 195.57 |
| 5.0 wt % Triton X-100 | 213.80 | 183.57 |
| 7.5 wt % Triton X-100 | 200.08 | 161.00 |
| 10.0 wt % Triton X-100 | 201.00 | 174.00 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, M.; Yoo, S.; Bae, Y.; Kim, S.; Jeon, M. Enhanced Stability and Driving Performance of GO–Ag-NW-based Ionic Electroactive Polymer Actuators with Triton X-100-PEDOT:PSS Nanofibrils. Polymers 2019, 11, 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050906
Park M, Yoo S, Bae Y, Kim S, Jeon M. Enhanced Stability and Driving Performance of GO–Ag-NW-based Ionic Electroactive Polymer Actuators with Triton X-100-PEDOT:PSS Nanofibrils. Polymers. 2019; 11(5):906. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050906
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Minjeong, Seokju Yoo, Yunkyeong Bae, Seonpil Kim, and Minhyon Jeon. 2019. "Enhanced Stability and Driving Performance of GO–Ag-NW-based Ionic Electroactive Polymer Actuators with Triton X-100-PEDOT:PSS Nanofibrils" Polymers 11, no. 5: 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050906
APA StylePark, M., Yoo, S., Bae, Y., Kim, S., & Jeon, M. (2019). Enhanced Stability and Driving Performance of GO–Ag-NW-based Ionic Electroactive Polymer Actuators with Triton X-100-PEDOT:PSS Nanofibrils. Polymers, 11(5), 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11050906