Polymer-Based Nanoparticle Strategies for Insulin Delivery
Abstract
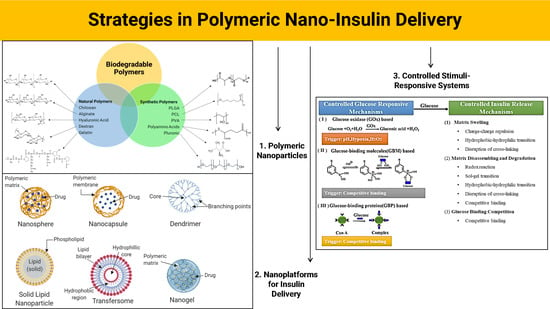
:1. Introduction
2. Polymeric Nanomaterials: Properties and Applications in Insulin Delivery
2.1. Natural Polymers
2.1.1. Chitosan (CS)
2.1.2. Alginate
2.1.3. Hyaluronic Acid (HA)
2.1.4. Dextran
2.1.5. Gelatin
2.2. Synthetic Polymers
2.2.1. PLGA (Poly-Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid)
2.2.2. PCL (Poly-ε-Caprolactone)
2.2.3. Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA)
2.2.4. Polyamino Acids
2.2.5. Pluronics
3. Nanoplatforms and Their Properties for Nano-Insulin Delivery
3.1. Nanoparticles (NPs)
3.2. Dendrimers
3.3. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs)
3.4. Transfersomes
3.5. Nanogels
4. Controlled Release and Stimuli-Responsive Systems for Nano-Insulin Delivery
4.1. Glucose Oxidase (GOx)
4.2. Phenylboronic Acid (PBA)
4.3. Concanavalin A (ConA)
5. Future Perspective for Insulin Nanotherapeutics
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cho, N.; Shaw, J.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; Fernandes, J.D.R.; Ohlrogge, A.; Malanda, B. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. 8 Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2018. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, S73–S85. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsarou, A.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S.; Rawshani, A.; Dabelea, D.; Bonifacio, E.; Anderson, B.J.; Jacobsen, L.M.; Schatz, D.A.; Lernmark, Å. Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taraghdari, Z.B.; Imani, R.; Mohabatpour, F. A Review on Bioengineering Approaches to Insulin Delivery: A Pharmaceutical and Engineering Perspective. Macromol. Biosci. 2019, 19, 1800458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondiah, P.P.D.; Choonara, Y.E.; Tomar, L.K.; Tyagi, C.; Kumar, P.; Du Toit, L.C.; Marimuthu, T.; Modi, G.; Pillay, V. Development of a Gastric Absorptive, Immediate Responsive, Oral Protein-Loaded Versatile Polymeric Delivery System. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 2479–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, P. Nanomedicine as a potential therapeutic agent in treatment of Diabetes. Life Sci. Edge 2018, 5, 14. [Google Scholar]
- NanoMedicine, E. Vision Paper and Basis for a Strategic Research Agenda for Nanomedicine; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Brannon-Peppas, L.; Blanchette, J.O. Nanoparticle and targeted systems for cancer therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.-S. Nanoparticles of biodegradable polymers for new-concept chemotherapy. Expert Rev. Med Devices 2004, 1, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigger, I.; Dubernet, C.; Couvreur, P.; Patrick, C. Nanoparticles in cancer therapy and diagnosis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhandayuthapani, B.; Yoshida, Y.; Maekawa, T.; Kumar, D.S. Polymeric Scaffolds in Tissue Engineering Application: A Review. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2011, 2011, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Tang, G.; Hua, D.; Xiong, R.; Han, J.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, C.; Han, J. Stimuli-responsive bio-based polymeric systems and their applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 709–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhumkar, D.R.; Joshi, H.M.; Sastry, M.; Pokharkar, V.B. Chitosan Reduced Gold Nanoparticles as Novel Carriers for Transmucosal Delivery of Insulin. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Kou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Dong, W.; Cheng, H.; Mao, S. Enhanced oral insulin delivery via surface hydrophilic modification of chitosan copolymer based self-assembly polyelectrolyte nanocomplex. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 554, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, A.; Al-Remawi, M.; Farouk, A.; Badwan, A. Insulin-chitosan polyelectrolyte _anocomplexes: Preparation, characterization and stabilization of insulin. Sudan J. Med Sci. 2010, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.S.; Sharma, A. Preparation and characterization of chitosan nanoparticles of insulin for nasal delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2018, 8, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansourpour, M.; Mahjub, R.; Amini, M.; Ostad, S.N.; Shamsa, E.S.; Tehrani, M.R.; Dorkoosh, F.A. Development of Acid-Resistant Alginate/Trimethyl Chitosan Nanoparticles Containing Cationic β-Cyclodextrin Polymers for Insulin Oral Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmento, B.; Martins, S.; Ribeiro, A.; Veiga, F.; Neufeld, R.; Ferreira, D. Development and Comparison of Different Nanoparticulate Polyelectrolyte Complexes as Insulin Carriers. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2006, 12, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Qi, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, S.; Xu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wu, W. Nanoemulsions coated with alginate/chitosan as oral insulin delivery systems: Preparation, characterization, and hypoglycemic effect in rats. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Sharma, S.; Gupta, P.K.; Singh, A.; Teja, B.V.; Dwivedi, P.; Gupta, G.K.; Trivedi, R.; Mishra, P.R. Vitamin B12 functionalized layer by layer calcium phosphate nanoparticles: A mucoadhesive and pH responsive carrier for improved oral delivery of insulin. Acta Biomater. 2016, 31, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Jiang, G.; Yu, W.; Li, L.; Tong, Z.; Kong, X.; Yao, J. Oral delivery of insulin using CaCO3 -based composite nanocarriers with hyaluronic acid coatings. Mater. Lett. 2017, 188, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yin, L.; Li, R.; Liang, Y.; Huang, H.; Pan, S.; Wu, C.; Feng, M. Insulin-Loaded pH-Sensitive Hyaluronic Acid Nanoparticles Enhance Transcellular Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2012, 13, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lopes, M.; Shrestha, N.; Correia, A.; Shahbazi, M.-A.; Sarmento, B.; Hirvonen, J.; Veiga, F.; Seiça, R.; Ribeiro, A.; Santos, H.A. Dual chitosan/albumin-coated alginate/dextran sulfate nanoparticles for enhanced oral delivery of insulin. J. Control. Release 2016, 232, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alibolandi, M.; Alabdollah, F.; Sadeghi, F.; Mohammadi, M.; Abnous, K.; Ramezani, M.; Hadizadeh, F. Dextran-b-poly(lactide-co-glycolide) polymersome for oral delivery of insulin: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Control. Release 2016, 227, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalasani, K.B.; Russell-Jones, G.J.; Jain, A.K.; Diwan, P.V.; Jain, S.K. Effective oral delivery of insulin in animal models using vitamin B12-coated dextran nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2007, 122, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, S.; Bajpai, J.; Bajpai, A.K. Designing Gelatin Nanocarriers as a Swellable System for Controlled Release of Insulin: An In-Vitro Kinetic Study. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2009, 47, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Z.; Li, X.; Lu, C.T.; Xu, Y.Y.; Lv, H.F.; Dai, D.D.; Zhang, L.; Sun, C.Z.; Yang, W.; Li, X.K.; et al. Experiment on the feasibility of using modified gelatin nanoparticles as insulin pulmonary administration system for diabetes therapy. Acta Diabetol. 2012, 49, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.S.; Ramakrishna, S.; Saini, T.R.; Diwan, P.V. Influence of microencapsulation method and peptide loading on formulation of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) insulin nanoparticles. Die Pharm. 2006, 61, 613–617. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Sun, H.; Song, C. Preparation, characterization and in vivo evaluation of pH-sensitive oral insulin-loaded poly(lactic-co-glycolicacid) nanoparticles. Diabetesobes. Metab. 2012, 14, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, Z.; Wen, X.; Xiaoyan, L.; Xiaowei, L.; Ning, Z.; Zhanzheng, Z.; Xuejun, W. Bioengineering Strategies for the Treatment of Type I Diabetes. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 581–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, S.M.; Chen, P.P.; Cheng, L.; Zhou, W.; Tang, W.X.; Chen, Z.W.; Ke, C.M. Controlled release of insulin from PLGA nanoparticles embedded within PVA hydrogels. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2007, 18, 2205–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araújo, T.M.; Teixeira, Z.; Barbosa-Sampaio, H.C.; Rezende, L.F.; Boschero, A.C.; Durán, N.; Höehr, N.F. Insulin-loaded poly(epsilon-caprolactone) nanoparticles: Efficient, sustained and safe insulin delivery system. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 1098–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damgé, C.; Maincent, P.; Ubrich, N. Oral delivery of insulin associated to polymeric nanoparticles in diabetic rats. J. Control. Release 2007, 117, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Zhu, W.-T.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Zeng, Q.-B. [Preparation of nanoparticles for sustained insulin release using poly (ethylene glycol) -poly (ε-caprolactone)-poly (N, N-diethylamino-2-ethylmethaerylate)]. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2017, 37, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shan, C.; Zu, S.; Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Ge, Y. Preparation and characterization of chitosan–polyvinyl alcohol blend hydrogels for the controlled release of nano-insulin. Int. J. Boil. Macromol. 2012, 50, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, P.; Suri, C.R.; Rawat, S.; Gupta, P.; Kumar, A.; Sahoo, D.K. Molecular Mechanism of Poly(vinyl alcohol) Mediated Prevention of Aggregation and Stabilization of Insulin in Nanoparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 1018–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Sonaje, K.; Lin, K.M.; Juang, J.-H.; Mi, F.-L.; Yang, H.-W.; Sung, H.-W. Multi-ion-crosslinked nanoparticles with pH-responsive characteristics for oral delivery of protein drugs. J. Control. Release 2008, 132, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonaje, K.; Chen, Y.-J.; Chen, H.-L.; Wey, S.-P.; Juang, J.-H.; Nguyen, H.-N.; Hsu, C.-W.; Lin, K.-J.; Sung, H.-W. Enteric-coated capsules filled with freeze-dried chitosan/poly(γ-glutamic acid) nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3384–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Jiang, G.; Yu, W.; Liu, D.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Tong, Z.; Kong, X.; Yao, J. Preparation of chitosan-based multifunctional nanocarriers overcoming multiple barriers for oral delivery of insulin. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 70, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.C.; Huang, H.; Yao, L.; Sun, L.Z.; Xiong, X.Y.; Li, Y.P. Study on uptake of PLA-Pluronic P85-PLA nanoparticles with Caco-2 cells. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Advanced Engineering Materials and Technology, Guangzhou, China, 22–23 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, X.; Tam, K.; Gan, L.; Tam, M.K. Release kinetics of hydrophobic and hydrophilic model drugs from pluronic F127/poly(lactic acid) nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2005, 103, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.K.; Pal, D.K. Chitosan-based Interpenetrating Polymeric Network Systems for Sustained Drug Release. In Advanced Theranostic Materials; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 183–208. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, R.; Jiang, T.; Di, J.; Tai, W.; Gu, Z. Emerging micro- and nanotechnology based synthetic approaches for insulin delivery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Luo, Y. Recent advances of polysaccharide-based nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery. Int. J. Boil. Macromol. 2018, 120, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.Y.; Al-Salami, H.; Dass, C.R. Microparticles, microcapsules and microspheres: A review of recent developments and prospects for oral delivery of insulin. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 537, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Li, A.; Li, J. Advances in pH-Sensitive Polymers for Smart Insulin Delivery. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2017, 38, 1700413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, A.; Mukherjee, D.; Mishra, R.; Kundu, P. Preparation of polyurethane–alginate/chitosan core shell nanoparticles for the purpose of oral insulin delivery. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 92, 294–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.; Shah, P.A.; Shrivastav, P.S. Natural biodegradable polymers based nano-formulations for drug delivery: A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 561, 244–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; He, J.; Bai, M.; Huang, C.; Wang, K.; Zhang, H.; Yang, S.-M.; Zhang, W.; Yang, S.-M. Engineering synthetic artificial pancreas using chitosan hydrogels integrated with glucose-responsive microspheres for insulin delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 96, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Chen, Y.-S.; Rupenthal, I.D. Hyaluronic Acid Coated Albumin Nanoparticles for Targeted Peptide Delivery to the Retina. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalasani, K.B.; Russell-Jones, G.; Yandrapu, S.K.; Diwan, P.V.; Jain, S.K. A novel vitamin B12-nanosphere conjugate carrier system for peroral delivery of insulin. J. Control. Release 2007, 117, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Yadav, S.C. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles based drug delivery systems. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 75, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselmo, A.C.; Gokarn, Y.; Mitragotri, S. Non-invasive delivery strategies for biologics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 18, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.O.; Fathe, K.R.; Brunaugh, A.; Ferrati, S.; Li, S.; Montenegro-Nicolini, M.; Mousavikhamene, Z.; McConville, J.T.; Prausnitz, M.R.; Smyth, H.D.C. Challenges and Future Prospects for the Delivery of Biologics: Oral Mucosal, Pulmonary, and Transdermal Routes. AAPS J. 2017, 19, 652–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoellhammer, C.M.; Blankschtein, D.; Langer, R. Skin Permeabilization for Transdermal Drug Delivery: Recent Advances and Future Prospects. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmento, B.; Ribeiro, A.; Veiga, F.; Sampaio, P.; Neufeld, R.; Ferreira, D. Alginate/Chitosan Nanoparticles are Effective for Oral Insulin Delivery. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 2198–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bahman, F.; Greish, K.; Taurin, S. Nanotechnology in Insulin Delivery for Management of Diabetes. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2019, 7, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teodorescu, M.; Bercea, M.; Morariu, S. Biomaterials of Poly(vinyl alcohol) and Natural Polymers. Polym. Rev. 2018, 58, 247–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czuba, E.; Diop, M.; Mura, C.; Schaschkow, A.; Langlois, A.; Bietiger, W.; Neidl, R.; Virciglio, A.; Auberval, N.; Julien-David, D.; et al. Oral insulin delivery, the challenge to increase insulin bioavailability: Influence of surface charge in nanoparticle system. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 542, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladmiral, V.; Semsarilar, M.; Armes, S.P.; Charlot, A. Synthesis and characterization of poly(amino acid methacrylate)-stabilized diblock copolymer nano-objects. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 1805–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duro-Castano, A.; Talelli, M.; Rodríguez-Escalona, G.; Vicent, M. Smart Polymeric Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery. In Smart Polymers and their Applications, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 439–479. [Google Scholar]
- Kamboj, V.K.; Verma, P.K. Poloxamers based nanocarriers for drug delivery system. Der Pharm. Lett. 2015, 7, 264–269. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, W.; Xie, Q.; Wang, H.; Ma, Z.; Wu, B.; Zhang, X. Selenium nanoparticles as versatile carriers for oral delivery of insulin: Insight into the synergic antidiabetic effect and mechanism. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Boil. Med. 2017, 13, 1965–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thwala, L.N.; Préat, V.; Csaba, N.S. Emerging delivery platforms for mucosal administration of biopharmaceuticals: A critical update on nasal, pulmonary and oral routes. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Samaridou, E.; Jaumain, E.; Coëne, J.; Ullio, G.; Shrestha, N.; Garcia, J.; Durán-Lobato, M.; Tovar, S.; Santander-Ortega, M.J.; et al. PEG-PGA enveloped octaarginine-peptide nanocomplexes: An oral peptide delivery strategy. J. Control. Release 2018, 276, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Yang, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, L. A cell-penetrating peptide mediated chitosan nanocarriers for improving intestinal insulin delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbari, G.R.; Dorkoosh, F.; Amini, M.; Javan, N.B.; Sharifzadeh, M.; Atyabi, F.; Balalaie, S.; Tehrani, N.R.; Tehrani, M.R. Synthesis and characterization of a novel peptide-grafted Cs and evaluation of its nanoparticles for the oral delivery of insulin, in vitro, and in vivo study. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 5127–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, W.; Xie, C.; Wei, G.; Lu, W. Oligoarginine-modified biodegradable nanoparticles improve the intestinal absorption of insulin. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 448, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boushra, M.; Tous, S.; Fetih, G.; Xue, H.-Y.; Wong, H.-L. Development of bi-polymer lipid hybrid nanocarrier (BLN) to improve the entrapment and stability of insulin for efficient oral delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmento, B.; Martins, S.; Ferreira, D.; Souto, E.B. Oral insulin delivery by means of solid lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2007, 2, 743–749. [Google Scholar]
- Fonte, P.; Nogueira, T.; Gehm, C.; Ferreira, D.; Sarmento, B. Chitosan-coated solid lipid nanoparticles enhance the oral absorption of insulin. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2011, 1, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, D.; Liu, L.; Li, X. Development of poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate) nanogel for effective oral insulin delivery. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2018, 23, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.-Z.; Wang, X.-T.; Yan, X.-Y.; Zhang, Q. Phospholipid Deformable Vesicles for Buccal Delivery of Insulin. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 50, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.K.; Khar, R.K.; Ahmed, F.J.; Diwan, P.V. Effective insulin delivery using starch nanoparticles as a potential trans-nasal mucoadhesive carrier. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Katsumi, H.; Sakane, T.; Yamamoto, A. Effects of polyamidoamine (PAMAM) dendrimers on the nasal absorption of poorly absorbable drugs in rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 393, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Hamid, K.A.; Gao, Y.; Lin, Y.; Katsumi, H.; Sakane, T.; Yamamoto, A. Polyamidoamine Dendrimers Can Improve the Pulmonary Absorption of Insulin and Calcitonin in Rats. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 1866–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cevc, G. Transdermal Drug Delivery of Insulin with Ultradeformable Carriers. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2003, 42, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marwah, H.; Garg, T.; Rath, G.; Goyal, A.K. Development of transferosomal gel for trans-dermal delivery of insulin using iodine complex. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malakar, J.; Sen, S.O.; Nayak, A.K.; Sen, K.K. Formulation, optimization and evaluation of transferosomal gel for transdermal insulin delivery. Saudi Pharm. J. 2012, 20, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilczewska, A.Z.; Niemirowicz, K.; Markiewicz, K.H.; Car, H. Nanoparticles as drug delivery systems. Pharmacol. Rep. 2012, 64, 1020–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wang, L.; Yu, H.; Ur-Rahman, K. Advances in phenylboronic acid-based closed-loop smart drug delivery system for diabetic therapy. J. Control. Release 2019, 305, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, P.; Castro, P.M.; Madureira, A.R.; Sarmento, B.; Pintado, M. Recent insights in the use of nanocarriers for the oral delivery of bioactive proteins and peptides. Peptides 2018, 101, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanraj, V.; Chen, Y. Nanoparticles-a review. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2006, 5, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, M.; Nielsen, H.M. Cell-Penetrating Peptides as Carriers for Oral Delivery of Biopharmaceuticals. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 118, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, J.; Xu, D. Cell-penetrating peptides as noninvasive transmembrane vectors for the development of novel multifunctional drug-delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2016, 229, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in nanomedicine applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.-K.; Lin, S.-X.; Tsai, M.-J.; Leong, M.K.; Lin, S.-R.; Kankala, R.K.; Lee, C.-H.; Weng, C.-F. Encapsulation of 16-Hydroxycleroda-3,13-Dine-16,15-Olide in Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as a Natural Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Potentiated Hypoglycemia in Diabetic Mice. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.; Xia, D.; Zhu, Q.; Li, X.; He, S.; Zhu, C.; Guo, S.; Hovgaard, L.; Yang, M.; Gan, Y. Functional nanoparticles exploit the bile acid pathway to overcome multiple barriers of the intestinal epithelium for oral insulin delivery. Biomaterials 2018, 151, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Aramundiz, J.V.; Presas, E.; Dalmau-Mena, I.; Martínez-Pulgarín, S.; Alonso, C.; Escribano, J.M.; Alonso, M.J.; Csaba, N.S. Rational design of protamine nanocapsules as antigen delivery carriers. J. Control. Release 2017, 245, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesharwani, P.; Gorain, B.; Choudhury, H.; Pandey, M.; Low, S.Y.; Tan, S.A.; Ling, E.C.S.; Lim, Y.K.; Chin, C.M.; Lee, P.Y.; et al. Nanotechnology based approaches for anti-diabetic drugs delivery. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 136, 52–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, N. Biodegradable solid lipid nanoparticle flocculates for pulmonary delivery of insulin. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2012, 8, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, M.J.; Anwer, M.K.; Jamil, S.; Al-Shdefat, R.; Ali, B.E.; Ahmad, M.M.; Ansari, M.N. Enhanced oral bioavailability of insulin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: Pharmacokinetic bioavailability of insulin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles in diabetic rats. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 1972–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, R.; Jose, S.; Mukund, V.P.B.; Vasudevan, D.T. Transferosomes—A vesicular transdermal delivery system for enhanced drug permeation. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2011, 2, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Gupta, A.; Rath, G.; Goyal, A.; Mathur, R.B.; Dhakate, S.R. Electrospun composite nanofiber-based transmucosal patch for anti-diabetic drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 3410–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, K.S.; Desale, S.S.; Bronich, T.K. Nanogels: An overview of properties, biomedical applications and obstacles to clinical translation. J. Control. Release 2016, 240, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, M.C.; Cuggino, J.C. Stimulus-responsive nanogels for drug delivery. In Stimuli Responsive Polymeric Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery Applications; Elsevier: Cambridge, UK, 2018; Volume 1, pp. 321–341. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Van Nostrum, C.F.; Mastrobattista, E.; Vermonden, T.; Hennink, W.E. Nanogels for intracellular delivery of biotherapeutics. J. Control. Release 2017, 259, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Shi, X.; Liu, T.; Lu, X.; Qiu, G.; Shea, K.J. Synthesis of surfactant-free hydroxypropyl methylcellulose nanogels for controlled release of insulin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yang, L.; Fan, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, Z. Temperature and Glucose Dual-Responsive Carriers Bearing Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) and Phenylboronic Acid for Insulin Controlled Release: A Review. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2017, 66, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, W. Glucose and Temperature Dual Stimuli Responsiveness of Intelligent Hollow Nanogels. Chin. J. Mater. Res. 2012, 26, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Xiao, C.; Ding, J.; Zhuang, X.; Gai, G.; Wang, L.; Chen, X. Competitive binding-accelerated insulin release from a polypeptide nanogel for potential therapy of diabetes. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 3807–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cao, Z. Glucose-responsive insulin release: Analysis of mechanisms, formulations, and evaluation criteria. J. Control. Release 2017, 263, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreira, A.; Gonçalves, F.; Mendonça, P.; Gil, M.H.; Coelho, J. Temperature and pH responsive polymers based on chitosan: Applications and new graft copolymerization strategies based on living radical polymerization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 80, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Bi, F.; Zhao, J.; Gai, G.; Ding, J. Glucose Oxidase-Based Glucose-Sensitive Drug Delivery for Diabetes Treatment. Polymers 2017, 9, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Y.; DiSanto, R.; Sun, W.; Ranson, D.; Ligler, F.S.; Buse, J.B.; Gu, Z. Microneedle-array patches loaded with hypoxia-sensitive vesicles provide fast glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8260–8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakh, N.A.; Cortinas, A.B.; Weiss, M.A.; Langer, R.S.; Anderson, D.G.; Gu, Z.; Dutta, S.; Strano, M.S. Glucose-responsive insulin by molecular and physical design. Nat. Chem. 2017, 9, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Aimetti, A.A.; Wang, Q.; Dang, T.T.; Zhang, Y.; Veiseh, O.; Cheng, H.; Langer, R.S.; Anderson, D.G. Injectable Nano-Network for Glucose-Mediated Insulin Delivery. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 4194–4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oroval, M.; Díez, P.; Aznar, E.; Coll, C.; Marcos, M.D.; Sancenón, F.; Villalonga, R.; Martínez-Máñez, R. Self-Regulated Glucose-Sensitive Neoglycoenzyme-Capped Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Insulin Delivery. Chem. A Eur. J. 2017, 23, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, L.; Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z. Organization of Glucose-Responsive Systems and Their Properties. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 7855–7875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.X. Layer-by-layer multilayer films linked with reversible boronate ester bonds with glucose-sensitivity under physiological conditions. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, F.; Sun, Y.; Gao, M.; Chai, Z. Development of shell cross-linked nanoparticles based on boronic acid-related reactions for self-regulated insulin delivery. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2017, 28, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Ishii, T.; Nishida, J.; Matsumoto, H.; Kataoka, K.; Miyahara, Y. A synthetic approach toward a self-regulated insulin delivery system. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 2124–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhou, S. Responsive Materials for Self-R egulated Insulin Delivery. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 1464–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bomba, H.; Gu, Z. Stimuli-responsive delivery of therapeutics for diabetes treatment. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2016, 1, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Bai, M.; He, J.; Nie, J.; Zhang, W. Concanavalin A-sugar affinity based system: Binding interactions, principle of glucose-responsiveness, and modulated insulin release for diabetes care. Int. J. Boil. Macromol. 2019, 124, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Tong, Z.; Yang, D.; Nie, J. Glucose-responsive insulin delivery microhydrogels from methacrylated dextran/concanavalin A: Preparation and in vitro release study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.J.; Park, K. Glucose-Binding Property of Pegylated Concanavalin a. Pharm. Res. 2001, 18, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zion, T.C.; Tsang, H.H.; Ying, J.Y. Glucose-Sensitive Nanoparticles for Controlled Insulin Delivery. Available online: https://dspace.mit.edu/handle/1721.1/3783 (accessed on 15 August 2019).
- Chang, R.; Li, M.; Ge, S.; Yang, J.; Sun, Q.; Xiong, L. Glucose-responsive biopolymer nanoparticles prepared by co-assembly of concanavalin A and amylopectin for insulin delivery. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 112, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurkat, P.; Jain, A.; Jain, A.; Shilpi, S.; Gulbake, A.; Jain, S.K. Concanavalin A conjugated biodegradable nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Yan, S.; Hu, Y.; Ding, L.; Wu, W. Synthesis and volume phase transition of concanavalin A-based glucose-responsive nanogels. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phase 2a Trial for Oral Insulin Film | Aquestive. Available online: https://aquestive.com/monosol-rx-announces-initiation-of-phase-2a-trial-for-oral-insulin-film/ (accessed on 1 August 2019).
- Patel, B.; Gupta, V.; Ahsan, F. PEG–PLGA based large porous particles for pulmonary delivery of a highly soluble drug, low molecular weight heparin. J. Control. Release 2012, 162, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kankala, R.K.; Lin, X.-F.; Song, H.-F.; Wang, S.-B.; Yang, D.-Y.; Zhang, Y.S.; Chen, A.-Z. Supercritical Fluid-Assisted Decoration of Nanoparticles on Porous Microcontainers for Codelivery of Therapeutics and Inhalation Therapy of Diabetes. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 4225–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Polymer | Advantages | Polymeric Complex and Delivery System | Route of Administration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural | |||
| CS |
|
| |
| Alginate |
|
| |
| HA |
|
| |
| Dextran |
|
| |
| Gelatin |
| ||
| Synthetic | |||
| PLGA |
|
| |
| PCL |
|
| |
| PVA |
| ||
| Polyamino Acids |
|
| |
| Pluronic |
|
|
| Delivery Approach | Advantages | Challenges | Polymeric Systems | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oral |
|
| Nanoparticles (NPs) Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs) Cell Penetrating Peptides (CPP) Nanogel | [6,44,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72] |
| Buccal |
|
| Transfersomes | [53,73] |
| Nasal |
|
| NPs Dendrimers | [53,64,74,75] |
| Pulmonary |
|
| Dendrimers | [53,54,76] |
| Transdermal |
|
| NPs Transfersomes | [53,55,77,78,79] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mansoor, S.; Kondiah, P.P.D.; Choonara, Y.E.; Pillay, V. Polymer-Based Nanoparticle Strategies for Insulin Delivery. Polymers 2019, 11, 1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091380
Mansoor S, Kondiah PPD, Choonara YE, Pillay V. Polymer-Based Nanoparticle Strategies for Insulin Delivery. Polymers. 2019; 11(9):1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091380
Chicago/Turabian StyleMansoor, Shazia, Pierre P. D. Kondiah, Yahya E. Choonara, and Viness Pillay. 2019. "Polymer-Based Nanoparticle Strategies for Insulin Delivery" Polymers 11, no. 9: 1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091380
APA StyleMansoor, S., Kondiah, P. P. D., Choonara, Y. E., & Pillay, V. (2019). Polymer-Based Nanoparticle Strategies for Insulin Delivery. Polymers, 11(9), 1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091380