Active Edible Films Based on Arrowroot Starch with Microparticles of Blackberry Pulp Obtained by Freeze-Drying for Food Packaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
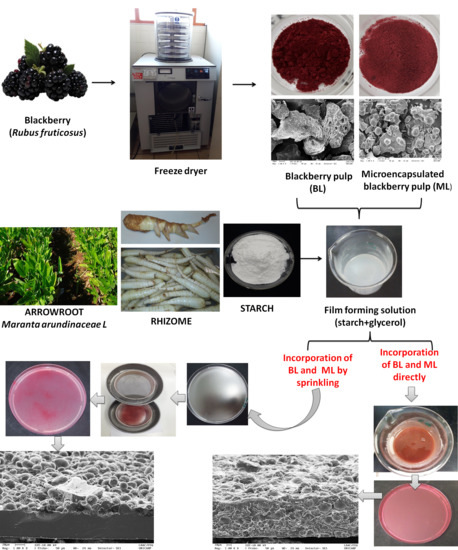
2.2. Production of Blackberry Pulp (BL) and Microencapsulated Blackberry Pulp (ML) Powders by Freeze-Drying
Characterization of Blackberry Powder
2.3. Incorporation of Blackberry Powders into Film-Forming Solution
2.3.1. Preparation of Film-Forming Solution
2.3.2. Direct Incorporation of Blackberry Powders (D) into Film-Forming Solution
2.3.3. Incorporation of Blackberry Powder by Sprinkling (S) into Film-Forming Suspension
2.4. Films Characterization
2.4.1. Visual Aspect
2.4.2. Microstructure
2.4.3. Colour Determination
2.4.4. Anthocyanins Content
2.4.5. Antioxidant Capacity
2.4.6. Film Thickness, Water Activity and Moisture Content
2.4.7. Solubility in Water
2.4.8. Water Vapor Permeability
2.4.9. Mechanical Properties
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Blackberry Powder
3.2. Films Characterization
3.2.1. Visual Aspect
3.2.2. Microstructure
3.2.3. Colour Determination
3.2.4. Anthocyanins Content and Antioxidant Capacity
3.2.5. Water Activity and Moisture Content
3.2.6. Film Thickness, Water Solubility, Water Vapor Permeability and Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dammak, I.; de Carvalho, R.A.; Trindade, C.S.F.; Lourenço, R.V.; Sobral, P.J.A. Properties of active gelatin films incorporated with rutin-loaded nanoemulsions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dammak, I.; Lourenço, R.V.; Sobral, P.J.A. Active gelatin films incorporated with Pickering emulsions encapsulating hesperidin: Preparation and physicochemical characterization. J. Food Eng. 2019, 240, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siripatrawan, U.; Noipha, S. Active film from chitosan incorporating green tea extract for shelf life extension of pork sausages. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 27, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Krochta, J.M. Physical properties of whey protein coating solutions and films containing antioxidants. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, E308–E314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez Estaca, J.; Giménez, B.; Gómez-Guillén, C.; Montero, P. Incorporation of antioxidant borage extract into edible films based on sole skin or a commercial fish skin gelatin. J. Food Eng. 2009, 92, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, P.R.; Ortiz, S.E.M.; Petruccelli, S.; Mauri, A.N. Biodegradable sunflower protein films naturally activated with antioxidant compounds. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siripatrawan, U.; Harte, B.R. Physical properties and antioxidant activity of an active film from chitosan incorporated with green tea extract. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 770–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Marcone, M.F.; Barbut, S.; Lim, L.T. The impact of anthocyanin-rich red raspberry extract (ARRE) on the properties of edible soy protein isolates (SPI) films. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, C497–C505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.J.; Jacquot, M.; Jasniewski, J.; Jacquot, C.; Imran, M.; Jamshidian, M.; Paris, C.; Desobry, S. Antioxidant capacity and light-aging study of HPMC films functionalized with natural plant extract. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, A.G.; Roura, S.I.; Vallea, C.E.D.; Moreira, M.R. Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of edible coatings enriched with natural plant extracts: In vitro and in vivo studies. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2008, 49, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, T.J. Surface and nutraceutical properties of edible films made from starchy sources with and without added blackberry pulp. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 165, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahedikia, N.; Garavand, F.; Tajeddin, B.; Cacciotti, I.; Jafari, S.M.; Omidi, T.; Zahedi, Z. Biodegradable zein film composites reinforced with chitosan nanoparticles and cinnamon essential oil: Physical, mechanical, structural and antimicrobial attributes. Colloid Surface B 2019, 177, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elisia, I.; Hu, C.; Popovich, D.G.; Kitts, D.D. Antioxidant assessment of an anthocyanin-enriched blackberry extract. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 1052–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, A.P.d.F.; Pasquel-Reátegui, J.L.; Barbero, G.F.; Martínez, J. Pressurized liquid extraction of bioactive compounds from blackberry (Rubus fruticosus L.) residues: A comparison with conventional methods. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Lin, H.S. Antioxidant activity in fruits and leaves of blackberry, raspberry, and strawberry varies with cultivar and developmental stage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyer, R.A.; Hummer, K.E.; Finn, C.E.; Frei, B.; Wrolstad, R.E. Anthocyanins, phenolics, and antioxidant capacity in diverse small fruits: Vaccinium, Rubus, and Ribes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.J.; Howard, L.R.; Prior, R.L.; Clark, J.R. Flavonoid glycosides and antioxidant capacity of various blackberry and red grape genotypes determined by high performance liquid chromatogrphy/mass spectrometry. J. Sci Food Agric. 2004, 84, 1771–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Han, X.Q. Encapsulation of food Ingredients. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1993, 33, 501–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouin, S. Microencapsulation: Industrial appraisal of existing technologies and trends. Trends Food Sci.Technol. 2004, 15, 330–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeredo, H.M.C. Nanocomposites for food packaging applications. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 1240–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamashita, C.; Chung, M.M.S.; dos Santos, C.; Mayer, C.R.M.; Moraes, I.C.F.; Branco, I.G. Microencapsulation of an anthocyanin-rich blackberry (spp.) by-product extract by freeze-drying. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 84, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avellone, G.; Salvo, A.; Costa, R.; Saija, E.; Bongiorno, D.; Stefano, V.D.; Calabrese, G.; Dugo, G. Investigation on the influence of spray-drying technology on the quality of Sicilian Nero d’Avola wines. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, G.F.; Fakhouri, F.M.; de Oliveira, R.A. Incorporation of spray dried and freeze dried blackberry particles in edible films: Morphology, stability to pH, sterilization and biodegradation. Food Packag. Shelf 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, G.F.; Fakhouri, F.M.; de Oliveira, R.A. Effect of incorporation of blackberry particles on the physicochemical properties of edible films of arrowroot starch. Dry. Technol. 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukurumbira, A.R.; Mellem, J.J.; Amonsou, E.O. Effects of amadumbe starch nanocrystals on the physicochemical properties of starch biocomposite films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 165, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez, R.; Barba, F.J.; Gómez, B.; Putnik, P.; Kovačević, D.B.; Pateiro, M.; Santos, E.M.; Lorenzo, J.M. Active packaging films with natural antioxidants to be used in meat industry: A review. Food Res. Int. 2018, 113, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talón, E.; Vargas, M.; Chiralt, A.; González-Martínez, C. Antioxidant starch-based films with encapsulated eugenol. Application to sunflower oil preservation. LWT 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-H.; Song, K.B. Characterization of Job’s tears (Coix lachryma-jobi L.) starch films incorporated with clove bud essential oil and their antioxidant effects on pork belly during storage. LWT 2019, 111, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, W.; Latimer, G.W. Official Methods of Analysis, 18th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zavareze, E.D.R.; El Halal, S.L.M.; Pereira, J.M.; Radünz, A.L.; Elias, M.C.; Dias, A.R.G. Chemical characterization and extraction yield of rice starch with different amylose contents. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2009, 2, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.Z.; Corke, H. Production and properties of spray-dried Amaranthus betacyanin pigments. J. Food Sci. 2000, 65, 1248–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Chauca, M.; Stringheta, P.C.; Ramos, A.M.; Cal-Vidal, J. Effect of the carriers on the microstructure of mango powder obtained by spray drying and its functional characterization. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2005, 5, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, G.F.; Fakhouri, F.M.; de Oliveira, R.A. Extraction and characterization of arrowroot (Maranta arundinaceae L.) starch and its application in edible films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 186, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sims, D.A.; Gamon, J.A. Relationships between leaf pigment content and spectral reflectance across a wide range of species, leaf structures and developmental stages. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontard, N.; Guilbert, S.; Cuq, J.L. Edible wheat gluten films: Influence of the main process variables on film properties using response surface methodology. J. Food Sci. 1992, 57, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E96 e 80. Annual Book of American Standard Testing Methods; ASTM: Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1989; Standard test methods for water vapor transmission of materials. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D 882-83. Annual Book of American Standard Testing Methods; ASTM: Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1980; Standard test methods for tensile properties of thin plastic sheeting. [Google Scholar]
- Tanada-Palmu, P.S.; Hélen, H.; Hyvonen, L. Preparation, properties and applications of wheat gluten edible biofilms. Agric. Food Sci. Finl. 2000, 9, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschinis, L.; Salvatori, D.M.; Sosa, N.; Schebor, C. Physical and functional properties of blackberry freeze-and spray-dried powders. Dry Technol. 2014, 32, 154–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, A.-M.; Wang, L.-J.; Li, D.; Adhikari, B. Characterization of starch films containing starch nanoparticles: Part 1: Physical and mechanical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 96, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodaran, S.; Parkin, K.L.; Fennema, O.R. Química de Alimentos de FENNEMA; Artmed: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2010; pp. 25–74. [Google Scholar]
- Daza, L.D.; Fujita, A.; Fávaro-Trindade, C.S.; Rodrigues-Ract, J.N.; Granato, D.; Genovese, M.I. Effect of spray drying conditions on the physical properties of Cagaita (Eugenia dysenterica DC.) fruit extracts. Food Bioprod. Process. 2016, 97, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, T.; Menegalli, F.C. Development and characterization of unripe banana starch films incorporated with solid lipid microparticles containing ascorbic acid. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 55, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, L.; López, O.; López, C.; Zaritzky, N.; García, M.A.; Barbosa, S.; Villar, M. Thermoplastic starch films reinforced with talc nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 95, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, F.; Giannuzzi, L.; Arce, V.B.; García, M.A. Active composite starch films containing green synthetized silver nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 70, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qiu, C.; Ji, N.; Sun, C.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q. Mechanical: Barrier andmorphological properties of starch nanocrystals-reinforced pea starch films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 121, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Aguilar, D.M.; Ortega-Regules, A.E.; Lozada-Ramírez, J.D.; Pérez-Pérez, M.C.I.; Vernon-Carter, E.J.; Welti-Chanes, J. Color and chemical stability of spray-dried blueberry extract using mesquite gum as wall material. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2011, 24, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patras, A.; Brunton, N.P.; Donnell, C.O.; Tiwari, B.K. Effect of thermal processing on anthocyanin stability in foods; mechanisms and kinetics of degradation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniglia, B.C.; Tessaro, L.; Lucas, A.A.; Tapia-Blácido, D.R. Bioactive films based on babassu mesocarp flour and starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 70, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genskowsky, E.; Puente, L.A.; Pérez-Álvarez, J.A.; Fernandez-Lopez, J.; Muñoz, L.A.; Viuda-Martos, M. Assessment of antibacterial and antioxidant properties of chitosan edible films incorporated with maqui berry (Aristotelia chilensis). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turumtay, E.A.; Islamoglu, F.; Çavus, D.; Sahin, H.; Turumtay, H.; Vanholme, B. Correlation between phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity of Anzer tea (Thymus praecox Opiz subsp. caucasicus var. caucasicus). Ind Crop. Prod. 2014, 52, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, G.F.; Soares, C.T.; Cavasini, R.; Fakhouri, F.M.; Oliveira, R.A. Bioactive films of arrowroot starch and blackberry pulp: Physical, mechanical and barrier properties and stability to pH and sterilization. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang-Bravo, L.; López-Córdoba, A.; Martino, M. Biopolymeric matrices made of carrageenan and corn starch for the antioxidant extracts delivery of Cuban red propolis and yerba mate. React. Funct Polym. 2004, 85, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quek, S.Y.; Chok, N.K.; Swedlund, P. The physicochemical properties of spray-dried watermelon powders. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2007, 46, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavutsky, A.M.; Bertuzzi, M.A. Water barrier properties of starch films reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals obtained from sugarcane bagasse. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 110, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadegh-Hassani, F.; Mohammadi Nafchi, A. Preparation and characterization of bionanocomposite films based on potato starch/halloysitenanoclay. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 67, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garavand, F.; Rouhi, M.; Razavi, S.H.; Cacciotti, I.; Mohammadi, R. Improving the integrity of natural biopolymer films used in food packaging by crosslinking approach: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 687–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.W.; Ruiz-Garcia, L.; Qian, J.P.; Yang, X.T. Food packaging: A comprehensive review and future trends. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 860–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamróz, E.; Kulawik, P.; Kopel, P. The Effect of Nanofillers on the Functional Properties of Biopolymer-Based Films: A Review. Polymers 2019, 11, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, N.; Dutta, J. Development and in vitro characterization of chitosan/starch/halloysite nanotubes ternary nanocomposite films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 127, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivera, N.; Rouf, T.B.; Bonilla, J.C.; Carriazo, J.G.; Dianda, N.; Kokini, J.L. Effect of LAPONITE® addition on the mechanical, barrier and surface properties of novel biodegradable kafirin nanocomposite films. J. Food Eng. 2019, 245, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludueña, L.; Vázquez, A.; Alvarez, V. Effect of lignocellulosic filler type and content on the behavior of polycaprolactone based eco-composites for packaging applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Qiu, C.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q.J. Characterisation of corn starch-based films reinforced with taro starch nanoparticles. Food Chem. 2015, 174, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yu, J.; Yang, J.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q. Effects of chitin nano-whiskers on the antibacterial and physicochemical properties of maize starch films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, T.V. Applications of nanotechnology in food packaging and food safety: Barrier materials: Antimicrobials and sensors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 363, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, S.; Rhim, J.-W. Preparation and characterization of agar/lignin/silver nanoparticles composite films with ultraviolet light barrier and antibacterial properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 71, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, R.A.; Sapuan, S.M.; Ishak, M.R.; Zainudin, E.S. Development and characterization of sugar palm nanocrystalline cellulose reinforced sugar palm starch bionanocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 202, 186–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, S.; Kasapis, S.; Rhim, J.-W. Alginate-based nanocomposite films reinforced with halloysite nanotubes functionalized by alkali treatment and zinc oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacciotti, I.; Mor, S.; Cherubini, V.; Nanni, F. Eco-sustainable systems based on poly (lactic acid), diatomite and coffee grounds extract for food packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Analysis | Blackberry Pulp (BL) | Microencapsulated Blackberry Pulp (ML) |
|---|---|---|
| Process yield (%) | 89.24 ± 2.81 a | 95.86 ± 0.89 a |
| Moisture content (%) | 10.72 ± 2.81 a | 4.50 ± 0.31 a |
| Aw (decimal) | 0.13 ± 0.01 a | 0.11 ± 0.01 b |
| Hygroscopicity (g of adsorbed water/100 g solids) | 21.28 ± 0.45 a | 12.86 ± 0.1 b |
| Solubility in water (%) | 61.26 ± 0.49 a | 53.84 ± 0.76 b |
| Total Anthocyanins (mg/100 g of blackberry solids) | 125.27 ± 9.77 a | 125.99 ± 5.25 a |
| ABTS radical (µmol of Trolox/g of blackberry solids) | 288.43 ± 30.70 a | 309.18 ± 34.09 a |
| Color | ||
| L* | 47.29 ± 2.35 b | 57.23 ± 1.57 a |
| a* | 14.18 ± 2.97 a | 20.13 ± 1.17 a |
| b* | 4.95 ± 0.56 a | 3.59 ± 0.08 a |
| Films | L* | a* | b* | ΔE* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 91.54 ± 1.16 a | 1.96 ± 0.09 g | -8.64 ± 0.46 i | - |
| 20% BLD | 63.16 ± 0.40 b | 23.50 ± 0.18 e | 1.35 ± 0.09 hg | 37.00 ± 0.43 de |
| 30% BLD | 62.16 ± 0.48 b | 24.60 ± 0.30 dce | 1.69 ± 0.06 g | 38.50 ± 0.56 de |
| 40% BLD | 47.28 ± 0.66 edf | 35.05 ± 0.36 a | 4.30 ± 0.16 ba | 56.76 ± 0.76 a |
| 20% BLS | 57.89 ± 3.68 cb | 27.44 ± 2.88 c | 0.44 ± 0.29 h | 43.17 ± 4.62 dc |
| 30% BLS | 46.67 ± 1.51 edf | 34.31 ± 0.85 a | 1.86 ± 0.36 fg | 56.30 ± 1.75 ba |
| 40% BLS | 40.72 ± 3.87 gf | 35.92 ± 0.61 a | 3.52 ± 1.15 bdc | 62.33 ± 3.70 a |
| 20% MLD | 62.78 ± 1.54 b | 19.28 ± 0.68 f | 3.11 ± 0.31 dec | 35.57 ± 1.68 e |
| 30% MLD | 53.84 ± 0.37 cd | 24.27 ± 0.24 de | 4.09 ± 0.07 bac | 45.61 ± 0.43 c |
| 40% MLD | 42.70 ± 0.70 gf | 30.44 ± 0.11 b | 4.72 ± 0.08 a | 58.09 ± 0.66 a |
| 20% MLS | 49.89 ± 1.03 ed | 25.98 ± 0.34 dce | 2.21 ± 0.39 feg | 49.29 ± 0.95 bc |
| 30% MLS | 42.96 ± 2.19 egf | 30.62 ± 0.28 b | 2.90 ± 0.35 fde | 57.58 ± 1.93 a |
| 40% MLS | 36.27 ± 0.13 g | 26.82 ± 1.50 dc | 3.74 ± 0.29 bdac | 61.94 ± 4.85 a |
| Films | Total Anthocyanins (mg/100 g of Blackberry Solids) | ABTS (μmol of Trolox/g of Blackberry Solids) |
|---|---|---|
| 0% * | 0.32 ± 0.12 e | 9.15 ± 6.51 f |
| 20% BLD | 47.53 ± 6.06 cd | 161.99 ± 10.54 e |
| 30% BLD | 40.23 ± 1.29 cd | 180.68 ± 22.48 ed |
| 40% BLD | 76.47 ± 0.98 a | 174.24 ± 51.73 ed |
| 20% BLS | 70.01 ± 9.65 ba | 253.57 ± 24.68 ed |
| 30% BLS | 71.63 ± 6.96 ba | 368.32 ± 37.02 bac |
| 40% BLS | 81.95 ± 12.83 a | 408.24 ± 32.04 a |
| 20% MLD | 38.13 ± 0.55 d | 272.64 ± 73.00 dc |
| 30% MLD | 41.79 ± 0.10 cd | 274.55 ± 46.66 dc |
| 40% MLD | 39.39 ± 9.41 cd | 278.93 ± 8.32 bdc |
| 20% MLS | 45.47 ± 2.13 cd | 385.62 ± 18.54 ba |
| 30% MLS | 56.09 ± 1.22 bc | 436.78 ± 24.48 a |
| 40% MLS | 55.68 ± 1.63 bcd | 446.82 ± 39.66 a |
| Films | Aw at 25 °C | Moisture Content (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0% | 0.43 ± 0.05 bc | 11.30 ± 0.10 bdc |
| 20% BLD | 0.37 ± 0.01 c | 9.94 ± 1.02 fedg |
| 30% BLD | 0.37 ± 0.01 c | 10.89 ± 0.62 bedc |
| 40% BLD | 0.40 ± 0.01 bc | 13.65 ± 1.00 a |
| 20% BLS | 0.55 ± 0.09 a | 8.72 ± 0.79 fhg |
| 30% BLS | 0.45 ± 0.03 bc | 8.50 ± 0.84 hg |
| 40% BLS | 0.41 ± 0.02 bc | 9.97 ± 1.17 fedg |
| 20% MLD | 0.40 ± 0.01 bc | 10.42 ± 0.13 fedc |
| 30% MLD | 0.38 ± 0.01 c | 12.14 ± 0.38 bac |
| 40% MLD | 0.39 ± 0.01 c | 12.30 ± 0.83 ba |
| 20% MLS | 0.42 ± 0.01 bc | 8.18 ± 0.28 hg |
| 30% MLS | 0.47 ± 0.03 ba | 7.88 ± 0.72 h |
| 40% MLS | 0.45 ± 0.02 bc | 9.22 ± 0.50 fehg |
| Films | Thickness (mm) | Solubility in Water (%) | Permeability to Water Vapor (gmm/m2daykPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 0.065 ± 0.005 d | 14.18 ± 0.26 g | 3.62 ± 0.27 hdfge | 22.71 ± 1.27 a | 3.18 ± 0.44 d |
| 20% BLD | 0.092 ± 0.005 dc | 21.64 ± 0.93 fe | 3.03 ± 0.10 hfge | 3.60 ± 0.33 ih | 23.53 ± 3.60 a |
| 30% BLD | 0.121 ± 0.014 bdaac | 22.76 ± 1.13 dfe | 6.63 ± 0.39 bc | 3.55 ± 0.12 ih | 23.33 ± 0.72 a |
| 40% BLD | 0.154 ± 0.054 bac | 26.14 ± 1.16 dce | 5.40 ± 0.47 dce | 2.73 ± 0.33 i | 26.42 ± 1.40 a |
| 20% BLS | 0.082 ± 0.006 d | 19.26 ± 1.68 fe | 1.67 ± 0.12 h | 10.84 ± 1.69 b | 7.46 ± 2.55 c |
| 30% BLS | 0.098 ± 0.013 bdc | 24.65 ± 1.95 dce | 2.38 ± 0.45 hg | 8.16 ± 0.64 dc | 5.26 ± 1.55 dc |
| 40% BLS | 0.113 ± 0.016 bdac | 27.98 ± 2.69 bc | 3.47 ± 0.14 hfge | 6.32 ± 0.85 fe | 18.32 ± 4.69 b |
| 20% MLD | 0.150 ± 0.024 bac | 21.74 ± 1.70 fe | 2.43 ± 0.36 hg | 7.02 ± 0.99 de | 3.99 ± 0.76 dc |
| 30% MLD | 0.146 ± 0.022 bac | 22.18 ± 0.36 dfe | 7.80 ± 0.07 ba | 5.62 ± 0.40 feg | 3.28 ± 0.42 d |
| 40% MLD | 0.154 ± 0.010 ba | 23.69 ± 0.77 dfce | 9.23 ± 0.47 a | 4.51 ± 0.29 hg | 7.72 ± 0.50 c |
| 20% MLS | 0.147 ± 0.017 bac | 27.14 ± 2.45 dc | 4.42 ± 0.17 dfge | 8.87 ± 0.86 c | 4.32 ± 0.40 dc |
| 30% MLS | 0.153 ± 0.005 bac | 33.89 ± 2.50 a | 5.08 ±1.87 dfce | 6.98 ± 0.60 de | 3.96 ± 0.71 dc |
| 40% MLS | 0.173 ± 0.011 a | 32.33 ± 1.39 ba | 5.57 ± 1.05 dc | 4.82 ± 0.67 fhg | 3.25 ± 0.96 d |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nogueira, G.F.; Fakhouri, F.M.; Velasco, J.I.; de Oliveira, R.A. Active Edible Films Based on Arrowroot Starch with Microparticles of Blackberry Pulp Obtained by Freeze-Drying for Food Packaging. Polymers 2019, 11, 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091382
Nogueira GF, Fakhouri FM, Velasco JI, de Oliveira RA. Active Edible Films Based on Arrowroot Starch with Microparticles of Blackberry Pulp Obtained by Freeze-Drying for Food Packaging. Polymers. 2019; 11(9):1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091382
Chicago/Turabian StyleNogueira, Gislaine Ferreira, Farayde Matta Fakhouri, José Ignacio Velasco, and Rafael Augustus de Oliveira. 2019. "Active Edible Films Based on Arrowroot Starch with Microparticles of Blackberry Pulp Obtained by Freeze-Drying for Food Packaging" Polymers 11, no. 9: 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091382
APA StyleNogueira, G. F., Fakhouri, F. M., Velasco, J. I., & de Oliveira, R. A. (2019). Active Edible Films Based on Arrowroot Starch with Microparticles of Blackberry Pulp Obtained by Freeze-Drying for Food Packaging. Polymers, 11(9), 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091382