Boron Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Using a Novel Alginate-Based Sorbent: Comparison with Al2O3 Particles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Sorbents
2.3. Characterization of Sorbents
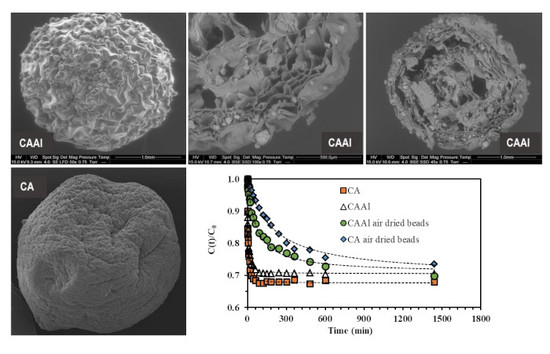
2.3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.3.2. Thermal-Gravimetric Analyses
2.4. Batch Sorption Experiments
- Hydrogel beads (Ø 2.3 mm)
- Air-dried beads (Ø 0.8 mm)
3. Fitting of Sorption Isotherms and Kinetics
3.1. Sorption Isotherms
3.2. Kinetic Studies
3.3. Effect of Temperature
3.4. Towards an Application with Ceramic Wastewater
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Characterization of the Materials
4.1.1. SEM–EDX Analyses
4.1.2. TGA
4.2. Effect of pH
4.3. Equilibrium Studies
- LF-200S: 63% G-blocks; 37% M-blocks
- LF-240D: 30% G-blocks; 70% M-blocks
4.4. Sorption Kinetics
4.5. Effect of Temperature
4.6. Sorbent Regeneration
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CA | calcium alginate beads |
| CAAl | composite alginate–alumina |
References
- Hilal, N.; Kim, G.J.; Somerfield, C. Boron removal from saline water: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2011, 273, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorchev, H.G.; Ozolins, G. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; Volume 1, p. 564. [Google Scholar]
- Morisada, S.; Rin, T.; Ogata, T.; Kim, Y.; Nakano, Y. Adsorption removal of boron in aqueous solutions by amine-modified tannin gel. Water Res. 1997, 45, 4028–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazicigil, Z.; Oztekin, Y. Boron removal by electrodialysis with anion-exchange membranes. Desalination 2006, 190, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itakura, T.; Sasai, R.; Itoh, H. Precipitation recovery of boron from wastewater by hydrothermal mineralization. Water Res. 2005, 39, 2543–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, A.E.; Boncukcuoğlu, R.; Kocakerim, M.M. A quantitative comparison between electrocoagulation and chemical coagulation for boron removal from boron-containing solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koparal, A.S. The removal of salinity from produced formation by conventional and electrochemical methods. Fresen. Environ. Bull. 2002, 12A, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar]
- Dosoretz, C.; Geffen, N.; Semiat, R.; Eisen, M.; Balazs, Y.; Katz, I. Boron removal from water by complexation to polyol compounds. J. Membr. Sci 2006, 286, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Del-Campo Marin, C.; Gideon, O. Boron removal by the duckweed Lemna gibba: A potential method for the remediation of boron-polluted waters. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4579–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonnot, M.; Castel, C.; Nicolai, M.; Rosin, C.; Sardin, M.; Jauffret, H. Boron removal from drinking water with a boron selective resin: Is the treatment really selective? Water Res. 2004, 34, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabay, N.; Sarp, S.; Yuksel, M.; Kitis, M.; Koseoglub, H.; Arar, Ö.; Bryjak, M.; Semiat, R. Removal of boron from SWRO permeates by boron selective ion exchange resins containing N-methylglucamine groups. Desalination 2008, 223, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prats, D.; Chillon-Arias, M.F.; Rodriguez-Pastor, M. Analysis of the influence of pH and pressure on the elimination of boron in reverse osmosis. Desalination 2000, 128, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Pastor, M.; Ferrándiz-Ruiz, A.; Chillon, M.F.; Prats-Rico, D. Influence of pH in the elimination of boron by means of reverse osmosis. Desalination 2001, 140, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengeloglu, Y.; Arslan, G.; Tor, A.; Kocak, I.; Dursun, N. Removal of boron from water by using reverse osmosis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 64, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, N.; Kavak, D. Boron removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption on waste sepiolite and activated waste sepiolite using full factorial design. Adsorption 2004, 10, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, Y.; Seyhan, S.; Yurdakoc, M. Removal of boron from aqueous solutions by adsorption on Al2O3 based materials using full factorial design. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 138, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karahan, S.; Yurdakoc, M.; Seki, Y.; Yurdakoc, K. Removal of boron from aqueous solution by clays and modified clays. J. Coll. Interf. Sci. 2006, 293, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cengeloglu, Y.; Tor, A.; Arslan, G.; Ersoz, M.; Gezgin, S. Removal of boron from aqueous solution by using neutralized red mud. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 142, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavak, D. Removal of boron from aqueous solutions by batch adsorption on calcined alunite using experimental design. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öztürk, N.; Kavak, D. Adsorption of boron from aqueous solutions using fly ash: Batch and column studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 127, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabarudin, A.; Oshita, K.; Oshima, M.; Motomizu, S. Synthesis of cross-linked chitosan possesing N-methyl-D-glucamine moiety (CCTS-NMDG) for adsortion/concentration of boron in water samples and its accurate measurement by ICP-MS and ICP-AES. Talanta 2005, 66, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Ma, W.; Jia, C.; Wang, L.; Li, H.Y. Effect of pH on biosorption of boron onto cotton cellulose. Desalination 2007, 207, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Matsui, T.; Kondo, K. Adsorption mechanism of boric acid on chitosan resin modified by saccharides. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 1999, 32, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.; Roset, L.; Demey, H.; Castro, S.; Sastre, A.M.; Pérez, J.J. Equilibrium and dynamic studies for adsorption of boron on calcium alginate gel beads using principal component analysis (PCA) and partial least squares (PLS). Materialwiss Werkst. 2013, 44, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.; Tobalina, C.; Demey-Cedeño, H.; Barron-Zambrano, J.; Sastre, A.M. Sorption of boron on calcium alginate gel beads. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demey, H.; Ruiz, M.; Barron-Zambrano, J.A.; Sastre, A.M. Boron removal from aqueous solutions using alginate gel beads in fixed bed systems. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 89, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiol, N.; Escudero, C.; Poch, J.; Villaescusa, I. Preliminary studies on Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solutions using grape stalk wastes encasulapted in calcium alginate beads in a packed bed up-flow column. React. Funct. Polym. 2006, 66, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, G.; Morris, E.; Rees, D.; Smith, P.; Thom, D. Biological interactions between polysaccharides and divalent cations: The egg-box model. FEBS Lett. 1973, 32, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouguerra, W.; Mnif, A.; Hamrouni, B.; Dhahbi, M. Boron removal by adsorption onto activated alumina and by reverse osmosis. Desalination 2008, 223, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.; Sastre, A.M.; Guibal, E. Palladium sorption on glutaraldehyde-crosslinked chitosan. React. Funct. Polym. 2005, 45, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption gelöster stoffe: Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.; McKay, G. Sorption of dye from aqueous solution by peat. Chem. Eng. J. 1998, 70, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, G.; Ho, Y. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, W.J.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. ASCE 1963, 89(2), 31–60. [Google Scholar]
- Tunali, A.; Ozel, E.; Turan, S. Production and characterization of granulated frit to achieve anorthite based glass-ceramic glaze. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 35, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, A.; Madamwar, D. Partial characterization of extracellular polysaccharides from cyanobacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1822–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasiruddin-Khan, M.; Sarwar, A. Determination of points of zero charge of natural and treated adsorbents. Surf. Rev. Lett. 2017, 14, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attar, K.; Bouazza, D.; Miloudi, H.; Tayeb, A.; Boos, A.; Sastre, A.M.; Demey, H. Cadmium removal by a low-cost magadiite-based material: Characterization and sorption applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5351–5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, A. Dissociation of alginic acid. Acta Chem. Scand. 1961, 15, 950–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demey, H.; Vincent, T.; Ruiz, M.; Nogueras, M.; Sastre, A.M.; Guibal, E. Boron recovery from seawater with a new low-cost adsorbent material. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demey, H.; Vincent, T.; Ruiz, M.; Sastre, A.M.; Guibal, E. Development of a new chitosan/Ni (OH)2-based sorbent for boron removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 244, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demey, H.; Melkior, T.; Chatroux, A.; Attar, K.; Thiery, S.; Miller, H.; Grateau, M.; Sastre, A.M.; Marchand, M. Evaluation of torrefied poplar-biomass as a low-cost sorbent for lead and terbium removal from aqueous solutions and energy co-generation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demey, H.; Vincent, T.; Guibal, E. A novel algal-based sorbent for heavy metal removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 332, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladipo, A.A.; Gazi, M. High boron removal by functionalized magnesium ferrite nanopowders. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2016, 14, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipçak, I.; Özdemir, M. Removal of boron from aqueous solution using calcined magnesite tailing. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 189–190, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelmanov, G.; Semiat, R. Boron removal from water and its recovery using iron (Fe+3) oxide/hydroxidebased nanoparticles (NanoFe) and NanoFe-impregnated granular activated carbon as adsorbent. Desalination 2014, 333, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarri, S.; Misaelides, P.; Zamboulis, D.; Warchol, J. Boron removal from aqueous solutions by a polyethylenimine-epichlorohydrin resin. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2018, 83, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Y.T.; Zheng, Y.M.; Chen, J.P. Design and fabrication of an innovative and environmental friendly adsorbent for boron removal. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2297–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkal, B.F.; Bicak, N. Polymer supported iminodipropylene glycol functions for removal of boron. React. Funct. Polym. 2003, 55, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluczka, J.; Gnus, M.; Kasek-Kesik, A.; Dudek, G. Zirconium-chitosan hydrogel beads for removal of boron from aqueous solutions. Polymer 2018, 150, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Yuan, J.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Q. Surface glycosylation of polysulfone membrane towards a novel complexing membrane for boron removal. J. Coll. Interf. Sci. 2012, 368, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Hu, H.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Q. Synthesis, characterization and application of a novel silica based adsorbent for boron removal. Desalination 2012, 294, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluczka, J.; Dudek, G.; Kasek-Kesik, A.; Gnus, M. Chitosan hydrogel beads supported with ceria for boron removal. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertagnolli, C.; Grishin, A.; Vincent, T.; Guibal, E. Boron removal by a composite sorbent: Polyethylenimine/tannic acid derivative immobilized in alginate hydrogel beads. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2016, 52, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polowczyk, I.; Ulatowska, J.; Kozlecki, T.; Bastrzyk, A.; Sawinsky, W. Studies on removal of boron from aqueous solution by flash ash agglomerates. Desalination 2013, 310, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurdakoç, M.; Seki, Y.; Karahan, S.; Yurdakoç, K. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of boron removal by Siral 5, Siral 40, and Siral 80. J. Coll. Interf. Sci. 2005, 286, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öztürk, N.; Ennil-Köse, T. Boron removal from aqueous solutions by ion-exchange resin: Batch studies. Desalination 2008, 227, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Experimental | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sorbent | qexp (mmol g−1) | qmax (mmol g−1) | kL (L mmol−1) | r2 | kF (mmol1-1/n g−1 L1/n) | nF | r2 |
| CA | 1.88 | 4.56 | 1.36 × 10−2 | 0.989 | 2.83 | 2.16 × 10−2 | 0.988 |
| CA (Air-dried) | 1.29 | 1.99 | 2.72 × 10−2 | 0.950 | 1.41 | 3.41 × 10−2 | 0.941 |
| CAAl | 1.81 | 5.21 | 1.07 × 10−2 | 0.995 | 3.10 | 1.75 ×1 0−2 | 0.995 |
| CAAl (Air-dried) | 1.18 | 1.48 | 4.88 × 10−2 | 0.966 | 1.13 | 5.37 × 10−2 | 0.949 |
| Alumina | 0.41 | 0.59 | 4.64 × 10−2 | 0.994 | 5.02 × 10−2 | 1.82 | 0.974 |
| Experimental | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sorbent | qexp (mmol g−1) | qmax (mmol g−1) | kL (L mmol−1) | r2 | kF (mmol1-1/n g−1 L1/n) | nF | r2 |
| Alumina | 0.55 | 0.71 | 0.57 | 0.970 | 0.22 | 1.99 | 0.950 |
| CAAl | 1.15 | 1.33 | 1.06 | 0.975 | 0.58 | 2.33 | 0.991 |
| Sorbents | Temperature (K) | pH | qmax (mmol g−1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycidol-magnesium ferrite (GMF) | 298 | 7.0 | 6.4 | Oladipo and Gazi [44] |
| Calcined magnesite tailing | 318 | 6.0 | 6.1 | Kipçak and Özdemir [45] |
| NanoFe | 298 | 8.3 | 6.01 | Zelmanov and Semiat [46] |
| ChiNi(II) | 298 | 7.0 | 5.68 | Demey et al. [41] |
| CAAl | 298 | 9.5 | 5.21 | This work |
| Polyethylenimine-epichlorohydrin resin | 298 | 9.0 | 5.09 | Sarri et al. [47] |
| Fe-impregnated granular activated carbon (GAC) | 298 | 8.3 | 4.63 | Zelmanov and Semiat [46] |
| Chitosan/N-Methylglucamine | 298 | 7.0 | 3.25 | Wei et al. [48] |
| Polymer supported with iminodipropylene glycol functions | 298 | 6.0 | 3.0 | Senkal and Bicak [49] |
| Zirconium–Chitosan | 298 | 6.0 | 2.3 | Kluczca et al. [50] |
| Glycosylated polysulfone membrane (GlyPSF) | 303 | 7.0 | 2.09 | Meng et al. [51] |
| Silica-supported N-methyl-D-glucamine (Si-MG) | 298 | 7.0 | 1.54 | Xu et al. [52] |
| Ceria–Chitosan | 298 | 7.0 | 1.3 | Kluczca et al. [53] |
| Alginate/PEI/tannic acid material | 298 | 5.0 | 0.89 | Bertagnolli et al. [54] |
| Amberlite IRA-743 | 298 | 7.0 | 0.71 | Wei et al. [48] |
| Fly ash | 318 | 10.0 | 0.64 | Polowczyk et al. [55] |
| Calcined Alunite | 298 | 10.0 | 0.31 | Kavak [19] |
| Experimental | Pseudo-First Order Model (PFORE) | Pseudo-Second Order Model (PSORE) | Weber & Morris equation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sorbent | qexp (mmol g−1) | k1 (min−1) | q1 (mmol g−1) | r2 | k2 (g mmol−1 min−1) | q2 (mmol g−1) | r2 | Kp (mmol g−1 min−1/2) |
| CA | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.941 | 1.66 | 0.22 | 0.989 | 0.29 |
| CA (Air-dried) | 0.17 | 4.54 × 10−3 | 0.16 | 0.998 | 2.72 × 10−2 | 0.19 | 0.999 | 8.52 × 10−2 |
| CAAl | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.932 | 1.62 | 0.18 | 0.986 | 0.25 |
| CAAl (Air-dried) | 0.19 | 1.15 × 10−2 | 0.17 | 0.955 | 7.84 × 10−2 | 0.19 | 0.988 | 9.56 × 10−2 |
| Temperature (K) | Kc | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA | 293 | 6.80 × 10−2 | 6.54 | −95.82 | −0.34 |
| 308 | 1.01 × 10−2 | 11.78 | |||
| CAAl | 293 | 6.03 × 10−2 | 6.84 | −86.22 | −0.31 |
| 308 | 1.08 × 10−2 | 11.60 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Demey, H.; Barron-Zambrano, J.; Mhadhbi, T.; Miloudi, H.; Yang, Z.; Ruiz, M.; Sastre, A.M. Boron Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Using a Novel Alginate-Based Sorbent: Comparison with Al2O3 Particles. Polymers 2019, 11, 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091509
Demey H, Barron-Zambrano J, Mhadhbi T, Miloudi H, Yang Z, Ruiz M, Sastre AM. Boron Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Using a Novel Alginate-Based Sorbent: Comparison with Al2O3 Particles. Polymers. 2019; 11(9):1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091509
Chicago/Turabian StyleDemey, Hary, Jesus Barron-Zambrano, Takoua Mhadhbi, Hafida Miloudi, Zhen Yang, Montserrat Ruiz, and Ana Maria Sastre. 2019. "Boron Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Using a Novel Alginate-Based Sorbent: Comparison with Al2O3 Particles" Polymers 11, no. 9: 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091509
APA StyleDemey, H., Barron-Zambrano, J., Mhadhbi, T., Miloudi, H., Yang, Z., Ruiz, M., & Sastre, A. M. (2019). Boron Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Using a Novel Alginate-Based Sorbent: Comparison with Al2O3 Particles. Polymers, 11(9), 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091509