Electrochemical Polymerization of PEDOT–Graphene Oxide–Heparin Composite Coating for Anti-Fouling and Anti-Clotting of Cardiovascular Stents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
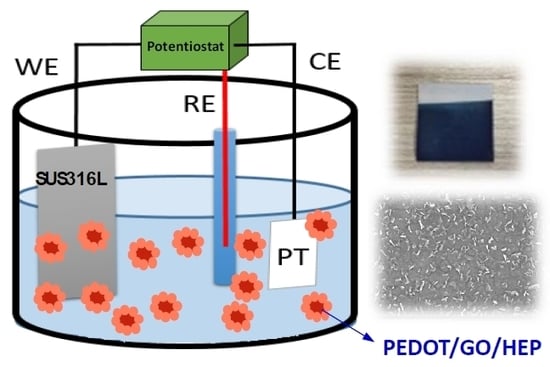
2.1. Preparation of Electrochemical Polymerization
2.2. Surface Characterization
2.3. Protein Adsorption
2.4. Blood Clotting Time (Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time, APTT)
2.5. Platelet Adhesion
2.6. Biocompatibility Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface Characterization
3.2. XPS Analysis
3.3. Water Contact Angle and Adhesion
3.4. Hemocompatibility
3.5. Cytotoxicity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Booth, F.; Roberts, C.K.; Laye, M. Lack of exercise is a major cause of chronic diseases. Compr. Physiol. 2012, 2, 1143–1211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Biglu, M.H.; Ghavami, M.; Biglu, S. Cardiovascular diseases in the mirror of science. J. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Res. 2016, 8, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gaziano, T.; Reddy, K.S.; Paccaud, F.; Horton, S.; Chaturvedi, V. Disease Control Priorities in Developing Countries, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cassar, A.; Holmes, D.R., Jr.; Rihal, C.S.; Gersh, B.J. Chronic coronary artery disease: Diagnosis and management. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2009, 84, 1130–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, R.; Qureshi, S.; Ghasemi, A.; Vincent, J.; Sievert, H.; Gruenstein, D.; Weber, H.; Alday, L.; Peirone, A.; Zellers, T.; et al. Stenting of aortic coarctation: Acute, intermediate, and long-term results of a prospective multi-institutional registry--Congenital Cardiovascular Interventional Study Consortium (CCISC). Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2010, 76, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butany, J.; Carmichael, K.; Leong, S.W.; Collins, M.J. Coronary artery stents: Identification and evaluation. J. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 58, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, G.; Feldman, M.D.; Patel, D.; Agrawal, C.M. Coronary stents: A materials perspective. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1689–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rack, H.J.; Qazi, J.I. Titanium alloys for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2006, 26, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liqing, H.; Guobiao, L.; Zidong, W.; Hong, Z.; Feng, L.; Long, Y. Study on Corrosion Resistance of 316L Stainless Steel Welded Joint. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2010, 39, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, A.C. Response of very small (2 mm) porcine coronary arteries to balloon angioplasty and stent implantation. Heart 2004, 90, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, P.K.; Shearier, E.R.; Zhao, S.; Guillory, R.J., 2nd; Zhao, F.; Goldman, J.; Drelich, J.W. Biodegradable Metals for Cardiovascular Stents: From Clinical Concerns to Recent Zn-Alloys. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 1121–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bünger, C.M.; Grabow, N.; Sternberg, K.; Goosmann, M.; Schmitz, K.P.; Kreutzer, H.J.; Ince, H.; Kische, S.; Nienaber, C.A.; Martin, D.P.; et al. A biodegradable stent based on poly(l-lactide) and poly(4-hydroxybutyrate) for peripheral vascular application: Preliminary experience in the pig. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2007, 14, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabow, N.; Bunger, C.M.; Schultze, C.; Schmohl, K.; Martin, D.P.; Williams, S.F.; Sternberg, K.; Schmitz, K.P. A biodegradable slotted tube stent based on poly(L-lactide) and poly(4-hydroxybutyrate) for rapid balloon-expansion. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 35, 2031–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Mario, C.; Griffiths, H.; Goktekin, O.; Peeters, N.; Verbist, J.; Bosiers, M.; Deloose, K.; Heublein, B.; Rohde, R.; Kasese, V.; et al. Drug-Eluting Bioabsorbable Magnesium Stent. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2004, 17, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, R.A.; Joner, M.; Kastrati, A. Stent thrombosis and restenosis: What have we learned and where are we going? The Andreas Gruntzig Lecture ESC 2014. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 3320–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byon, H.R.; Gallant, B.M.; Lee, S.W.; Shao-Horn, Y. Role of oxygen functional groups in carbon nanotube/graphene freestanding electrodes for high performance lithium batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hontoria-Lucas, C.; López-Peinado, A.J.; López-González, J.d.D.; Rojas-Cervantes, M.L.; Martín-Aranda, R.M. Study of oxygen-containing groups in a series of graphite oxides: Physical and chemical characterization. Carbon 1995, 33, 1585–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Ji, X.; Gomez-Mingot, M.; Lu, F.; Chen, Q.; Banks, C.E. Graphene electrochemical supercapacitors: The influence of oxygen functional groups. Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 2012, 48, 2770–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; An, J.; Jung, I.; Piner, R.D.; An, S.J.; Li, X.; Velamakanni, A.; Ruoff, R.S. Colloidal suspensions of highly reduced graphene oxide in a wide variety of organic solvents. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 1593–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Min, S.H.; Gu, M.; Jung, Y.K.; Lee, W.; Lee, J.U.; Seong, D.G.; Kim, B.S. Layer-by-layer assembly for graphene-based multilayer nanocomposites: Synthesis and applications. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 3785–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.B.; Wu, J.J.; Su, Y.; Zhou, J.; Gao, Y.; Yu, H.Y.; Gu, J.S. Layer-by-layer assembly of graphene oxide on polypropylene macroporous membranes via click chemistry to improve antibacterial and antifouling performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 332, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, L.; Zhu, W.; Xue, Y.; Liu, S. Construction of photoelectrochemical thrombin aptasensor via assembling multilayer of graphene-CdS nanocomposites. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lee, W.C.; Manga, K.K.; Ang, P.K.; Lu, J.; Liu, Y.P.; Lim, C.T.; Loh, K.P. Fluorinated graphene for promoting neuro-induction of stem cells. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 4285–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatavarty, R.; Ding, H.; Lu, G.; Taylor, R.J.; Bi, X. Synergistic acceleration in the osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells by graphene oxide-calcium phosphate nanocomposites. Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 2014, 50, 8484–8487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Weng, B.; Razal, J.M.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, C.; Hou, Y.; Seyedin, S.; Jalili, R.; Wallace, G.G.; Chen, J. High-performance flexible all-solid-state supercapacitor from large free-standing graphene-PEDOT/PSS films. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, W.; Lei, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, M.; Wang, F.; Hao, Q. Electrodeposition of graphene oxide doped poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) film and its electrochemical sensing of catechol and hydroquinone. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 85, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loriot, M.; Linossier, I.; Vallée-Réhel, K.; Faÿ, F. Influence of biodegradable polymer properties on antifouling paints activity. Polymers 2017, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilčíková, M.; Tkáč, J.; Kasák, P. Switchable materials containing polyzwitterion moieties. Polymers 2015, 7, 2344–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Liu, P.; Xia, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, R.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Q.; Xu, J.; Wang, F. Anti-Fouling and Anti-Bacterial Modification of Poly (vinylidene fluoride) Membrane by Blending with the Capsaicin-Based Copolymer. Polymers 2019, 11, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, B.; Bedwell, I.; Dimas, J.; Scardino, A.; Tang, Y.; Sammut, K. Effects of Various Antifouling Coatings and Fouling on Marine Sonar Performance. Polymers 2019, 11, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaux, L.; Lejars, M.; Margaillan, A.; Briand, J.F.; Bunet, R.; Bressy, C. Hydrolyzable Additive-Based Silicone Elastomers: A New Approach for Antifouling Coatings. Polymers 2019, 11, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, Y.; Ueda, K.; Yamagishi, S.I.; Sugiyama, M.; Yoshida, C.; Kurokawa, Y.; Nakamura, N.; Moriyama, T.; Kodama, G.; Minezaki, T.; et al. Compared effects of calcium and sodium polystyrene sulfonate on mineral and bone metabolism and volume overload in pre-dialysis patients with hyperkalemia. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2018, 22, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagkiozaki, V.; Karagiannidis, P.G.; Gioti, M.; Kavatzikidou, P.; Georgiou, D.; Georgaraki, E.; Logothetidis, S. Bioelectronics meets nanomedicine for cardiovascular implants: PEDOT-based nanocoatings for tissue regeneration. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 4294–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faham, S.; Hileman, R.E.; Fromm, J.R.; Linhardt, R.J.; Rees, D.C. Heparin structure and interactions with basic fibroblast growth factor. Science 1996, 271, 1116–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Periayah, M.H.; Halim, A.S.; Mat Saad, A.Z. Mechanism action of platelets and crucial blood coagulation pathways in hemostasis. Int. J. Hematol. Oncol. Stem Cell Res. 2017, 11, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Uchida, Y.; Uchida, Y.; Sakurai, T.; Kanai, M.; Shirai, S.; Morita, T. Characterization of coronary fibrin thrombus in patients with acute coronary syndrome using dye-staining angioscopy. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 1452–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsh, J.; Anand, S.S.; Halperin, J.L.; Fuster, V. Guide to anticoagulant therapy: Heparin. Circulation 2001, 103, 2994–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]














© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, M.-C.; Tsou, H.-M.; Hsiao, Y.-S.; Cheng, Y.-W.; Liu, C.-C.; Huang, L.-Y.; Peng, X.-Y.; Liu, T.-Y.; Yung, M.-C.; Hsu, C.-C. Electrochemical Polymerization of PEDOT–Graphene Oxide–Heparin Composite Coating for Anti-Fouling and Anti-Clotting of Cardiovascular Stents. Polymers 2019, 11, 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091520
Yang M-C, Tsou H-M, Hsiao Y-S, Cheng Y-W, Liu C-C, Huang L-Y, Peng X-Y, Liu T-Y, Yung M-C, Hsu C-C. Electrochemical Polymerization of PEDOT–Graphene Oxide–Heparin Composite Coating for Anti-Fouling and Anti-Clotting of Cardiovascular Stents. Polymers. 2019; 11(9):1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091520
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Ming-Chien, Hui-Ming Tsou, Yu-Sheng Hsiao, Yu-Wei Cheng, Che-Chun Liu, Li-Ying Huang, Xin-Yao Peng, Ting-Yu Liu, Ming-Chi Yung, and Chuan-Chih Hsu. 2019. "Electrochemical Polymerization of PEDOT–Graphene Oxide–Heparin Composite Coating for Anti-Fouling and Anti-Clotting of Cardiovascular Stents" Polymers 11, no. 9: 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091520
APA StyleYang, M.-C., Tsou, H.-M., Hsiao, Y.-S., Cheng, Y.-W., Liu, C.-C., Huang, L.-Y., Peng, X.-Y., Liu, T.-Y., Yung, M.-C., & Hsu, C.-C. (2019). Electrochemical Polymerization of PEDOT–Graphene Oxide–Heparin Composite Coating for Anti-Fouling and Anti-Clotting of Cardiovascular Stents. Polymers, 11(9), 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091520