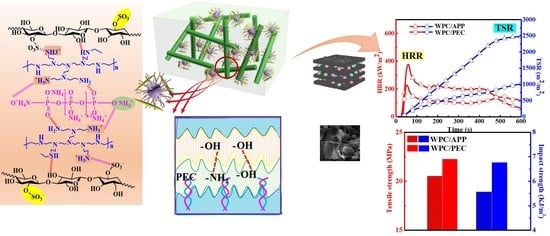
A Branched Polyelectrolyte Complex Enables Efficient Flame Retardant and Excellent Robustness for Wood/Polymer Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of PEC
2.3. Fabrication of WPCs
2.4. Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of PEC
3.2. Flame Retardancy of WPC/PEC Composites
3.3. Flame Retardancy Mechanism
3.4. Mechanical Properties of WPC/PEC Composites
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashori, A. Wood-plastic composites as promising green-composites for automotive industries! Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4661–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; He, J. Investigation of mechanical property, flame retardancy and thermal degradation of LLDPE-wood-fibre composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2004, 83, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, N.M.; White, R.H.; Mueller, S.A.; Osswald, T.A. Evaluation of various fire retardants for use in wood flour-polyethylene composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 1903–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Mei, C.; Du, J.; Li, G. Synergistic effect of nano silicon dioxide and ammonium polyphosphate on flame retardancy of wood fiber-polyethylene composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 66, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Peng, Y.; Chen, H.; Gao, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, W. Surface microencapsulated ammonium polyphosphate with beta-cyclodextrin and its application in wood-flour/polypropylene composites. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, 2312–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Deng, C.; Li, Y.; Lu, P.; Zhao, P.; Wang, Y. Novel amino glycerin decorated ammonium polyphosphate for the highly-efficient intumescent flame retardance of wood flour/polypropylene composite via simultaneous interfacial and bulk charring. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 172, 636–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priftis, D.; Laugel, N.; Tirrell, M. Thermodynamic characterization of polypeptide complex coacervation. Langmuir 2012, 28, 15947–15957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Mannen, S.; Morgan, A.B.; Chang, S.; Yang, Y.; Condon, B.; Grunlan, J.C. Intumescent all-polymer multilayer nanocoating capable of extinguishing flame on fabric. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3926–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Yan, H.; Shen, L.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B. Chitosan/phytic acid polyelectrolyte complex: A green and renewable intumescent flame retardant system for ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 19199–19207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Kandola, B.K.; Fang, Z. Layer by layer deposition of polyethylenimine and bio-based polyphosphate on ammonium polyphosphate: A novel hybrid for simultaneously improving the flame retardancy and toughness of polylactic acid. Polymer 2017, 108, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Pan, M.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S.; Mei, C. An anionic polyelectrolyte hybrid for wood-polyethylene composites with high strength and fire safety via self-assembly. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 248, 118661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trache, D.; Thakur, V.K.; Boukherroub, R. Cellulose nanocrystals/graphene hybrids-a promising new class of materials for advanced applications. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Deng, C.; Tan, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y. Ammonium polyphosphate chemically-modified with ethanolamine as an efficient intumescent flame retardant for polypropylene. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 13955–13965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bras, M.L.; Bourbigot, S. The Use of Intumescence. Fire Retardancy of Polymers, 2nd ed.; Bras, M.L., Camino, G., Bourbigot, S., Delobel, R., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Tyne and Wear, UK, 1998; pp. 64–75. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Zhou, C.; Wu, Y.; Liu, F.; Wu, Q. Self-assembling behavior of cellulose nanoparticles during freeze-drying: Effect of suspension concentration, particle size, crystal structure, and surface charge. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 1529–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, W.; Jin, L.; Zha, J.; Tao, T.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Z. Synthesis of amine-functionalized Fe3O4@C nanoparticles for lipase immobilization. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 18339–18444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Xu, Y.; Long, J.; Zhao, Q.; Ding, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y. Layer-by-layer assembled flame-retardant architecture toward high-performance carbon fiber composite. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 353, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xie, H.; Lin, J.; Xie, W.; Ma, X. Characterization and biodegradation of chitosan-alginate polyelectrolyte complexes. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2009, 94, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Chen, L.; Jian, R.; Kong, S.; Wang, Y. Intumescence: An effect way to flame retardance and smoke suppression for polystryene. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2012, 97, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Wu, Q.; Lei, Y.; Guo, W.; Xu, Y. Thermal decomposition kinetics of natural fibers: Activation energy with dynamic thermogravimetric analysis. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2008, 93, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Du, X.; Song, P.; Fang, Z. Green and scalable fabrication of core-shell biobased flame retardants for reducing flammability of polylactic acid. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 8954–8963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, W.; Lian, J.; Yuan, H. Influence of ammonium polyphosphate microencapsulation on flame retardancy, thermal degradation and crystal structure of polypropylene composite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 81, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Qian, M.; Song, P.; Huang, G.; Yu, Y.; Fu, S. Fabrication of green lignin-based flame retardants for enhancing the thermal and fire retardancy properties of polypropylene/wood composites. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2422–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalali, E.N.; Zhang, L.; Shabestari, M.E.; Jeremy, C.; Wang, D. Flame-retardant wood polymer composites (WPCs) as potential fire safe bio-based materials for building products: Preparation, flammability and mechanical properties. Fire Saf. J. 2019, 107, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Zhang, G.; Dong, S.; Zhang, Q.; Kong, J. Study on preparation and fire-retardant mechanism analysis of intumescent flame-retardant coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 7835–7841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Du, J.; Chen, W.; Pan, M.; Chen, D. Preparation and thermostability of cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibrils from two sources of biomass: Rice straw and poplar wood. Cellulose 2019, 26, 8625–8643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Bakar, M.B.; Ishak, Z.M.; Taib, R.M.; Rozman, H.D.; Jani, S.M. Flammability and mechanical properties of wood flour-filled polypropylene composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 2714–2722. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, G.; Guo, C.; Li, L. Synergistic effect of intumescent flame retardant and expandable graphite on mechanical and flame-retardant properties of wood flour-polypropylene composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 50, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Kuan, C.; Kuan, H.; Chen, C.; Liu, T.; Chiang, C. Preparation, characterization, and flame retardance of high-density polyethylene/sulfur-free expandable graphite composites. High. Perform. Polym. 2014, 26, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavdar, A.D.; Torun, S.B.; Ertas, M.; Mengeloglu, F. Ammonium zeolite and ammonium phosphate applied as fire retardants for microcrystalline cellulose filled thermoplastic composites. Fire Saf. J. 2019, 107, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Lai, J.; Lu, C.; Wu, X.; Cai, Y.; Gu, L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, G.; Shi, G. Soy protein and halloysite nanotubes-assisted preparation of environmentally friendly intumescent flame retardant for poly(butylene succinate). Polym. Test. 2020, 81, 106174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Yang, B.; Wang, D.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Miao, J.; Qian, J.; Xia, R.; Tu, Y.; et al. Investigation of the properties of polystyrene-based wood plastic composites: Effects of the flame retardant loading and magnetic fields. J. Polym. Eng. 2019, 39, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; He, H.; Yu, P.; Zhou, L.; Luo, Y.; Jia, D. Sustainable utilization of waste printed circuit boards powders in HDPE-wood composites: Synergistic effects of multicomponents on structure and properties. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; He, M.; Wang, H.; Ren, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y. PLLA/ABS blends compatibilized by reactive comb polymers: Double T-g depression and significantly improved toughness. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2542–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Samples | LOI (%) | UL-94 (3.2 mm) | Average HRR | Peak HRR | THR | TTI | SEA | TSR | MLR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rating | Dripping | (kW/m2) | (kW/m2) | (MJ/m2) | (s) | (m2/kg) | (m2/m2) | (mg/s) | ||
| WPC | 19.8 (0.15) | NR | No | 261.56 (15.5) | 621.58 (23.0) | 147.7 (5.0) | 20.5 (0.7) | 330.57 (89.1) | 1381.9 (308.3) | 63.6 (0.8) |
| WPC/APP 15% | 23.9 (0.37) | NR | No | 109.55 (0.6) | 373.92 (5.2) | 128.7 (0.7) | 22.5 (0.7) | 616.93 (159.2) | 2626.1 (469.0) | 32.3 (2.6) |
| WPC/PEC 15% | 24.4 (0.17) | NR | No | 102.11 (3.6) | 279.68 (11.9) | 119.9 (4.2) | 22.5 (0.7) | 470.20 (54.6) | 1897.8 (209.2) | 30.4 (0.005) |
| WPC/PEC 20% | 26.6 (0.15) | V-1 | No | 81.89 (8.6) | 283.90 (4.9) | 145.2 (15.5) | 27.0 (4.2) | 448.61 (0.8) | 2323.5 (289.8) | 25.75 (3.1) |
| WPC/PEC 25% | 28.7 (0.21) | V-0 | No | 84.11 (0.1) | 235.85 (9.8) | 148.9 (0.2) | 28.5 (0.7) | 256.85 (57.6) | 1313.78 (238.5) | 25.55 (1.1) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H.; Ding, C.; Xuan, Y.; Pan, M.; Mei, C. A Branched Polyelectrolyte Complex Enables Efficient Flame Retardant and Excellent Robustness for Wood/Polymer Composites. Polymers 2020, 12, 2438. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112438
Huang Y, Zhang S, Chen H, Ding C, Xuan Y, Pan M, Mei C. A Branched Polyelectrolyte Complex Enables Efficient Flame Retardant and Excellent Robustness for Wood/Polymer Composites. Polymers. 2020; 12(11):2438. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112438
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yanping, Shuai Zhang, He Chen, Chunxiang Ding, Yan Xuan, Mingzhu Pan, and Changtong Mei. 2020. "A Branched Polyelectrolyte Complex Enables Efficient Flame Retardant and Excellent Robustness for Wood/Polymer Composites" Polymers 12, no. 11: 2438. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112438
APA StyleHuang, Y., Zhang, S., Chen, H., Ding, C., Xuan, Y., Pan, M., & Mei, C. (2020). A Branched Polyelectrolyte Complex Enables Efficient Flame Retardant and Excellent Robustness for Wood/Polymer Composites. Polymers, 12(11), 2438. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112438