Reactive Comb Polymer Compatibilized Immiscible PVDF/PLLA Blends: Effects of the Main Chain Structure of Compatibilizer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.3.3. Mechanical Properties
2.3.4. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA)
3. Results
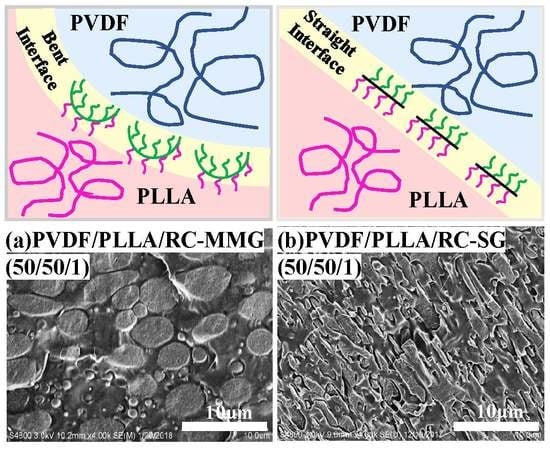
3.1. Morphologies
3.2. Mechanical Properties
3.3. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, D.; Wen, T.J.; Han, G.; Deng, Y.Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. Synthesis of Janus POSS star polymer and exploring its compatibilization behavior for PLLA/PCL polymer blends. Polymer 2018, 136, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, L.; Greenfeld, H.; Blumer-Ganon, B. In-situ compatibilization of an immiscible liquid hydroxyl-terminated polymer pair by rate controlled reactions with a diisocyanate. Polymer 2018, 138, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tsou, A.H.; Passino, H.L.; Favis, B.D. PPE-g-HDPE in high-performance Poly(p-Phenylene ether)/polyethylene blends: Synthesis and compatibilization effects. Polymer 2018, 138, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.H.; Xue, Y.; Wang, L.K.; Zhou, Y.C.; Yin, Y.F.; Chuang, Y.; Chang, C.; Yin, R.; Rafailovich, M.; Guo, Y.C. Engineering styrenic blends with poly(lactic acid). Macromolecules 2019, 52, 7547–7556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, B.; Culp, T.; Gomez, E.; Ilavsky, J.; Krishnamoorti, R.; Robertson, M. Nanostructured thermoset/thermoset blends compatibilized with an amphiphilic block copolymer. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 3104–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, N.; Shan, P.; Song, P.; Liu, X.; Chen, J. Toward fully bio-based and supertough PLA blends via in situ formation of cross-linked biopolyamide continuity network. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 8415–8429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, M.; Song, H.; Hyun, K. Characterization of the effect of clay on morphological evaluations of PLA/biodegradable polymer blends by FT-Rheology. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 7904–7919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Bai, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. Toward supertough and heat-resistant stereocomplex-type polylactide/elastomer blends with impressive melt stability via in situ formation of graft copolymer during one-pot reactive melt blending. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 1718–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, A.D.; McEneany, R.J.; Topolkaraev, V.A.; Macosko, C.W.; Hillmyer, M.A. Reactive compatibilization of poly(ethylene terephthalate) and high-density polyethylene using amino-telechelic polyethylene. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 8988–8994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifkovic, M.; Hedegaard, A.T.; Sheikhzadeh, M.; Huang, S.; Macosko, C.W. Stabilization of PE/PEO cocontinuous blends by interfacial nanoclays. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 4631–4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.B.; Lodge, T.P.; Macosko, C.W. Interfacial morphology development during PS/PMMA reactive coupling. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 6586–6591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.R.; Chang, K.; López-Barrón, C.R.; Macosko, C.W.; Morse, D.C. Annealing of cocontinuous polymer blends: Effect of block copolymer molecular weight and architecture. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 5024–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebovitz, A.H.; Khait, K.; Torkelson, J.M. In situ block copolymer formation during solid-state shear pulverization: An explanation for blend compatibilization via interpolymer radical reactions. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 9716–9722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Gray, M.K.; Zhou, H.Y.; Nguyen, S.T.; Torkelson, J.M. Polymer blend compatibilization by gradient copolymer addition during melt processing: Stabilization of dispersed phase to static coarsening. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 1037–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.J.; Yuan, G.C.; Han, C.C. Influences of hyperbranched polyethylenimine on the reactive compatibilization of polycarbonate/polyamide blends. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 33, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.X.; Yu, C.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhou, H.P.; Zhao, L.F. Fully biodegradable poly(lactic acid)/poly(propylene carbonate) shape memory materials with low recovery temperature based on in situ compatibilization by dicumyl peroxide. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 36, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worasak, P.; Varaporn, T.; Neeranuch, P. Synergistic effect of nucleation and compatibilization on the polylactide and poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blend films. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 34, 1129–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Phetwarotai, W.; Phusunti, N.; Aht-Ong, D. Preparation and characteristics of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/polylactide blend films via synergistic efficiency of plasticization and compatibilization. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2019, 37, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, H.; Sreenath, P.R.; Bhowmick, A.K.; Kumar, K.D. Unique compatibilized thermoplastic elastomer from polypropylene and epichlorohydrin rubber. Polymer 2019, 183, 121866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.W.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.J.; You, J.C. Graft Ratio: Quantitative measurement and direct evidence for its blending sequence dependence during reactive compatibilization in PVDF/PLLA. Polymer 2019, 185, 121970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gere, D.; Czigany, T. Future trends of plastic bottle recycling: Compatibilization of PET and PLA. Polymer 2019, 81, 106160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubinville, D.; Chang, B.P.; Pin, J.M.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Synergistic thermo-oxidative maleation of PA11 as compatibilization strategy for PA6 and PBT blend. Polymer 2019, 179, 121594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, H.T.; Chen, J.L.; Fu, Z.A.; Zhao, X.W.; Li, Y.J. Copolymers containing two types of reactive groups: New compatibilizer for immiscible PLLA/PA11 polymer blends. Polymer 2019, 177, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Lin, Q.Q.; Zheng, X.; Gu, X.Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, J.C.; Li, Y.J. Reactive splicing compatibilization of immiscible polymer blends: Compatibilizer synthesis in the melt state and compatibilizer architecture effects. Polymer 2019, 185, 121952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.P.; Wang, H.T.; Li, Y.J. Reactive compatibilization: Formation of double-grafted copolymers by in situ binary grafting and their compatibilization effect. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 33091–33099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.T.; Fu, Z.A.; Zhao, X.W.; Li, Y.J.; Li, J.Y. Reactive nanoparticles compatibilized immiscible polymer blends: Synthesis of reactive SiO2 with long poly(methyl methacrylate) chains and the in situ formation of Janus SiO2 nanoparticles anchored exclusively at the interface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 14358–14370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.W.; Wang, H.T.; Fu, Z.A.; Li, Y.J. Enhanced interfacial adhesion by reactive carbon nanotubes: New route to high-performance immiscible polymer blend nanocomposites with simultaneously enhanced toughness, tensile strength, and electrical conductivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 8411–8416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.A.; Wang, H.T.; Zhao, X.W.; Horiuchi, S.; Li, Y.J. Immiscible polymer blends compatibilized with reactive hybrid nanoparticles: Morphologies and properties. Polymer 2017, 132, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.Y.; Wang, H.T.; Ren, F.L.; Zhang, J.Q.; He, M.F.; Wu, T.; Li, Y.J. Dramatic improvement in toughness of PLLA/PVDF Blends: The effect of compatibilizer architectures. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4480–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.Y.; Wang, H.T.; He, M.F.; Ren, F.L.; Wu, T.; Zheng, Q.R.; Li, Y.J. Synthesis of reactive comb polymers and their applications as a highly efficient compatibilizer in immiscible polymer blends. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 2081–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhao, X.W.; Wang, H.T.; Chen, Q.; Wang, S.H.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhou, X.Y.; Fan, W.C.; Li, Y.J.; You, J.C. Sub-100 nm cocontinuous structures fabricated in immiscible commodity polymer blend with extremely low volume/viscosity ratio. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.T.; Dong, W.Y.; Li, Y.J. Compatibilization of immiscible polymer blends using in situ formed Janus nanomicelles by reactive blending. ACS Macro Lett. 2015, 4, 1398–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.T.; Fu, Z.A.; Dong, W.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Li, J.Y. Formation of interfacial Janus nanomicelles by reactive blending and their compatibilization effects on immiscible polymer blends. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 9240–9252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundararaj, U.; Macosko, C.W.; Shih, C.K. Evidence for inversion of phase continuity during morphology development in polymer blending. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1996, 36, 1769–1781. [Google Scholar]
- López-Barrón, C.R.; Macosko, C.W. A new model for the coarsening of cocontinuous morphologies. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 2637–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, W.; Yu, W. Control of the dispersed-to-continuous transition in polymer blends by viscoelastic asymmetry. Polymer 2018, 134, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifkovic, M.; Hedegaard, A.; Huston, K.; Sheikhzadeh, M.; Macosko, C.W. Porous films via PE/PEO cocontinuous blends. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 6036–6044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.H.; Favis, B.D. Coarsening of immiscible co-continuous blends during quiescent annealing. AIChE J. 2005, 51, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.A.; Jeon, H.K.; Bell, J.R.; Macosko, C.W. Block copolymer compatibilization of cocontinuous polymer blends. Polymer 2005, 46, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarazin, P.; Favis, B.D. Morphology control in co-continuous poly(l-lactide)/polystyrene blends: A route towards highly structured and interconnected porosity in poly(l-lactide) materials. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 1669–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Yang, Z.X.; Deng, B.W.; Yin, B.; Yang, M.B. Tuning PVDF/PS/HDPE polymer blends to tri-continuous morphology by grafted copolymers as the compatibilizers. Polymer 2018, 140, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Huang, H.X.; Wu, M. Promoting compatibilization effect of graphene oxide on immiscible PS/PVDF blend via water-assisted mixing extrusion. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 149, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Sample | Experimental Formula (Weight Ratio) | Mna/×104 (g/mol) | PDI a |
|---|---|---|---|
| RC–SG | [St]:[GMA]:[MMA macromer] 7:2:1 | 1.35 | 2.05 |
| RC–MMG | [MMA]:[GMA]:[MMA macromer] 7:2:1 | 1.28 | 2.03 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Song, J.; Wang, H.; Lin, Q.; Jin, X.; Yang, X.; Li, Y. Reactive Comb Polymer Compatibilized Immiscible PVDF/PLLA Blends: Effects of the Main Chain Structure of Compatibilizer. Polymers 2020, 12, 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030526
Yang X, Song J, Wang H, Lin Q, Jin X, Yang X, Li Y. Reactive Comb Polymer Compatibilized Immiscible PVDF/PLLA Blends: Effects of the Main Chain Structure of Compatibilizer. Polymers. 2020; 12(3):526. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030526
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xin, Jinxing Song, Hengti Wang, Qingqing Lin, Xianhua Jin, Xin Yang, and Yongjin Li. 2020. "Reactive Comb Polymer Compatibilized Immiscible PVDF/PLLA Blends: Effects of the Main Chain Structure of Compatibilizer" Polymers 12, no. 3: 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030526
APA StyleYang, X., Song, J., Wang, H., Lin, Q., Jin, X., Yang, X., & Li, Y. (2020). Reactive Comb Polymer Compatibilized Immiscible PVDF/PLLA Blends: Effects of the Main Chain Structure of Compatibilizer. Polymers, 12(3), 526. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030526