Synthesis and Characterization of Stiff, Self-Crosslinked Thermoresponsive DMAA Hydrogels
Abstract
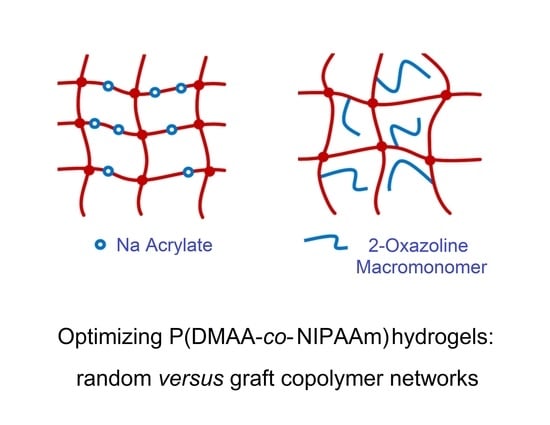
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.3. Procedures
2.3.1. Synthesis of 2-Oxazoline Macromonomer (MM)
2.3.2. Synthesis of Hydrogels (HG)
2.3.3. Hydrolysis of MM-Based Hydrogels
2.3.4. Water Absorption Degree (Q)
2.3.5. Sensitivity to Temperature
2.3.6. Water Absorption and Desorption Kinetics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Poly (2-Oxazoline) Macromonomer
3.2. Synthesis of Hydrogels (HG) and Hydrolysed Hydrogels (HG-H)
3.3. Characterization of Hydrogels
3.3.1. HR-MAS 1H NMR Spectroscopy
3.3.2. Water Absorption and Desorption
3.3.3. Temperature Sensitivity
3.3.4. Evaluation of the Mechanical Behavior and Thermal Stability of Hydrogels
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koeting, M.C.; Peters, J.T.; Steichen, S.D.; Peppas, N.A. Stimulus-responsive hydrogels: Theory, modern advances, and applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2015, 93, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döring, A.; Birnbaum, W.; Kuckling, D. Responsive hydrogels—Structurally and dimensionally optimized smart frameworks for applications in catalysis, micro-system technology and material science. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7391–7420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, A.S. Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Mooney, D.J. Designing hydrogels for controlled drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanaswamy, R.; Torchilin, V.P. Hydrogels and their application in targeted drug delivery. Molecules 2019, 24, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pertici, V.; Pin-Barre, C.; Rivera, C.; Pellegrino, C.; Laurin, J.; Gigmes, D.; Trimaille, T. Degradable and injectable hydrogel for drug delivery in soft tissues. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.; Syu, S.; Chang, J.; Aimar, P.; Chang, Y. Bioinspired pseudozwitterionic hydrogels with bioactive enzyme immobilization via pH-responsive regulation. Langmuir 2019, 35, 1909–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cole, M.A.; Voelcker, N.H.; Thissen, H.; Griesser, H.J. Stimuli-responsive interfaces and systems for the control of protein-surface and cell-surface interactions. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 1827–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlach, G.; Arndt, K.-F. Hydrogels Sensors and Actuators: Engineering and Technology, 6th ed.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Schild, H.G. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide): Experiment, theory and application. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1992, 17, 163–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, Y.M.; Premkumar, T.; Joseph, D.K.; Geckeler, K.E. Stimuli-responsive poly (N-isopropylacrylamide-co-sodium acrylate) hydrogels: A swelling study in surfactant and polymer solutions. React. Funct. Polym. 2007, 67, 844–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needles, H.L.; Whitfield, R.E. Crosslinking of copolymers containing N, N-dimethylacrylamide. J. Polym. Sci. Part A 1965, 3, 3543–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriano, B.H.; Banik, S.J.; Sharma, R.; Rumore, D.; Hwang, W.; Briber, R.M.; Raghavan, S.R. Superabsorbent hydrogels that are robust and highly stretchable. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 4445–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Huang, Y.; Li, D.; Chen, E.; Zhong, Y.; Fan, Q. Blue light initiated photopolymerization: Kinetics and synthesis of superabsorbent and robust poly(N, N-dimethylacrylamide/sodium acrylate) hydrogels. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 9266–9275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, A.T.; Zschoche, S.; Rohn, M.; Hempel, C.; Richter, A.; Appelhans, D.; Voit, B. Swelling behavior of bisensitive IPNs for microfluidic applications. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 5529–5536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimitrov, I.; Trzebicka, B.; Müller, A.H.E.; Dworak, A.; Tsvetanov, C. Thermosensitive water-soluble copolymers with doubly responsive reversibly interacting entities. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 1275–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda, J.; Zschoche, S.; Komber, H.; Schmaljohann, D.; Voit, B. Synthesis and characterization of thermoresponsive graft copolymers of NIPAAm and 2-alkyl-2-oxazolines by the “grafting from” method. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 7330–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräfe, D.; Frank, P.; Erdmann, T.; Richter, A.; Appelhans, D.; Voit, B. Tetra-sensitive graft copolymer gels as active material of chemomechanical valves. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 7565–7576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbraeken, B.; Monnery, B.; Lava, K.; Hoogenboom, R. The chemistry of poly(2-oxazoline)s. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 88, 451–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda, J.C.; Suárez, C.; Komber, H.; Zschoche, S.; Voit, B. Synthesis and characterization of pH- and thermo-responsive hydrogels based on poly(2-cyclopropyl-2-oxazoline) macromonomer, sodium acrylate, and acrylamide. Polym. Bull. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda, J.C.; Campos, E.; Komber, H.; Zschoche, S.; Häussler, L.; Voit, B. Synthesis and characterization of new pH- and thermoresponsive hydrogels based on N-isopropylacrylamide and 2-oxazolines. Des. Monomers Polym. 2014, 17, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Witte, H.; Seeliger, W. Cyclische Imidsäureester aus Nitrilen und Aminoalkoholen. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 1974, 1974, 996–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, A.; Litt, M. Polymerization of cyclic iminoethers. V. 1, 3-oxazolines with hydroxyl-, acetoxy-, and carboxymethyl- alkyl groups in the 2 position and their polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part Apolym. Chem. 1968, 5, 1883–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouten, P.J.M.; Hersten, D.; Vergaelen, M.; Monnery, B.D.; Boerman, M.A.; Gossens, H.; Catak, S.; van Hest, J.C.M.; Van Speybroeck, V.; Hoogenboom, R. Accelerated living cationic ring-opening polymerization of a methyl ester functionalized 2-oxazoline monomer. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zschoche, S.; Rueda, J.C.; Binner, M.; Komber, H.; Janke, A.; Arndt, K.-F.; Lehmann, S.; Voit, B. Reversibly switchable pH- and thermoresponsive core-shell nanogels based on poly(NiPAAm)-graft-poly(2-carboxyethyl-2-oxazoline)s. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2012, 213, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappoport, Z. CRC Handbook of Tables for Organic Compound Identification, 3rd ed.; CRC Press/Taylor and Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Spěváček, J. NMR investigations of phase transition in aqueous polymer solutions and gels. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 14, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Hydrogel | DMAA a(mol%) | NIPAAm a(mol%) | NaAc a(mol%) | Yield (%) | Q b | DMAANMR c (mol%) | NIPAAmNMR c (mol%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HG-1 | 82.0 | 16.3 | 1.66 | 82 | 48 (31) | 84 | 16 |
| HG-2 | 59.9 | 38.9 | 1.1 | 81 | 44 (47) | 62 | 38 |
| HG-3 | 39.3 | 59.5 | 1.2 | 94 | 87 (83) | 42 | 58 |
| HG-4 | 19.1 | 79.9 | 1.0 | 91 | - d | 24 | 76 |
| HG-5 | 39.1 | 60.9 | 0 | 81 | 24 (28) | 41 | 59 |
| Hydro-Gel | DMAA (mol%) | MM (mol%) | NIPAAm (mol%) | COOH b (mol%) | Yield (%) | Q cHG HG-H | DMAANMR d (mol%) | NIPAAmNMR d (mol%) | MMNMR d,e(mol%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HG-6 | 39.54 | 0.09 | 60.38 | 0.45 | 71.1 | 25 | 33 (48) | 38 | 62 | 0.08 |
| HG-7 | 39.5 | 0.18 | 60.32 | 0.90 | 87.9 | 24 | 34 (50) | 39 | 61 | 0.14 |
| HG-8 | 38.57 | 0.35 | 61.05 | 1.75 | 85.0 | 21 | 34 (71) | 38 | 62 | 0.25 |
| HG-9 | 37.9 | 0.52 | 61.54 | 2.60 | 81.2 | 20 | 48 (93) | 37 | 63 | 0.33 |
| Hydrogel | Q a | G’ (Pa) | G’’ (Pa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HG-1 | 48 | 3590 | 3045 |
| HG-2 | 44 | 3880 | 2790 |
| HG-3 | 87 | 1170 | 700 |
| HG-4 | - | 1010 | 125 |
| HG-5 | 24 | 5770 | 1465 |
| Hydrogel | Q a | G’ (Pa) | G’’ (Pa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HG-6 | 25 | 4220 | 1780 |
| HG-7 | 24 | 2750 | 2010 |
| HG-8 | 21 | 2880 | 3180 |
| HG-9 | 20 | 9240 | 4710 |
| HG-6H | 33 | 4270 | 770 |
| HG-7H | 34 | 6300 | 1130 |
| HG-8H | 34 | 5810 | 2680 |
| HG-9H | 48 | 1740 | 2380 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rueda, J.C.; Santillán, F.; Komber, H.; Voit, B. Synthesis and Characterization of Stiff, Self-Crosslinked Thermoresponsive DMAA Hydrogels. Polymers 2020, 12, 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12061401
Rueda JC, Santillán F, Komber H, Voit B. Synthesis and Characterization of Stiff, Self-Crosslinked Thermoresponsive DMAA Hydrogels. Polymers. 2020; 12(6):1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12061401
Chicago/Turabian StyleRueda, Juan Carlos, Fátima Santillán, Hartmut Komber, and Brigitte Voit. 2020. "Synthesis and Characterization of Stiff, Self-Crosslinked Thermoresponsive DMAA Hydrogels" Polymers 12, no. 6: 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12061401
APA StyleRueda, J. C., Santillán, F., Komber, H., & Voit, B. (2020). Synthesis and Characterization of Stiff, Self-Crosslinked Thermoresponsive DMAA Hydrogels. Polymers, 12(6), 1401. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12061401