Investigation of the Mechanical and Dynamic-Mechanical Properties of Electrospun Polyvinylpyrrolidone Membranes: A Design of Experiment Approach
Abstract
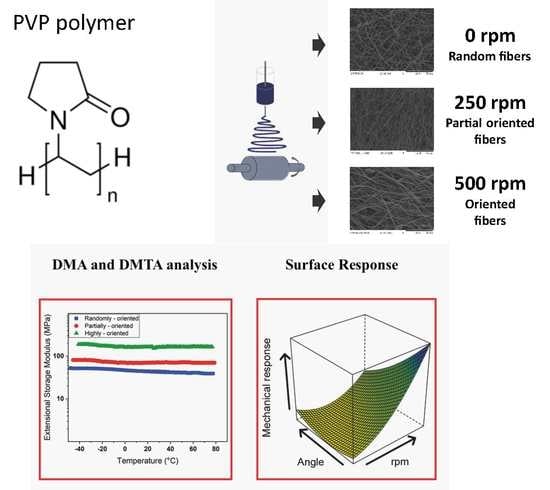
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Solution Preparation and Electrospinning
2.2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.2.3. Design of Experiments
2.2.4. Mechanical and Dynamic-Mechanical Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Morphology
3.2. Mechanical Properties
3.3. Dynamic-Mechanical Properties
3.4. Model Computation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, F.E.; Lalia, B.S.; Hashaikeh, R. A review on electrospinning for membrane fabrication: Challenges and applications. Desalination 2015, 356, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukáš, D.; Sarkar, A.; Martinová, L.; Vodsed’álková, K.; Lubasová, D.; Chaloupek, J.; Pokorný, P.; Mikeš, P.; Chvojka, J.; Komárek, M. Physical principles of electrospinning (Electrospinning as a nano-scale technology of the twenty-first century). Text. Prog. 2009, 41, 59–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bognitzki, M.; Czado, W.; Frese, T.; Schaper, A.; Hellwig, M.; Steinhart, M.; Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Nanostructured Fibers via Electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, S.; Fujihara, K.; Teo, W.E.; Yong, T.; Ma, Z.; Ramaseshan, R. Electrospun nanofibers: Solving global issues. Mater. Today 2006, 9, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persano, L.; Camposeo, A.; Tekmen, C.; Pisignano, D. Industrial Upscaling of Electrospinning and Applications of Polymer Nanofibers: A Review. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 504–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, M.; Zohoori, S. Review for application of electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers technology in textile industry. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2016, 6, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh Malik, D.; Mital, N.; Kaur, G. Topical drug delivery systems: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2016, 26, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodero, A.; Scarfi, S.; Pozzolini, M.; Vicini, S.; Alloisio, M.; Castellano, M.; Scarfì, S.; Pozzolini, M.; Vicini, S.; Alloisio, M.; et al. Alginate-Based Electrospun Membranes Containing ZnO Nanoparticles as Potential Wound Healing Patches: Biological, Mechanical, and Physicochemical Characterization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 3371–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodero, A.; Alloisio, M.; Vicini, S.; Castellano, M. Preparation of composite alginate-based electrospun membranes loaded with ZnO nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 227, 115371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, M.; Alloisio, M.; Darawish, R.; Dodero, A.; Vicini, S. Electrospun composite mats of alginate with embedded silver nanoparticles. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 137, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodero, A.; Brunengo, E.; Alloisio, M.; Sionkowska, A.; Vicini, S.; Castellano, M. Chitosan-based electrospun membranes: Effects of solution viscosity, coagulant and crosslinker. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 235, 115976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodero, A.; Vicini, S.; Alloisio, M.; Castellano, M. Sodium alginate solutions: Correlation between rheological properties and spinnability. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 8034–8046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sensini, A.; Gotti, C.; Belcari, J.; Zucchelli, A.; Focarete, M.L.; Gualandi, C.; Todaro, I.; Kao, A.P.; Tozzi, G.; Cristofolini, L. Morphologically bioinspired hierarchical nylon 6,6 electrospun assembly recreating the structure and performance of tendons and ligaments. Med. Eng. Phys. 2019, 71, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodero, A.; Alloisio, M.; Castellano, M.; Vicini, S. Multi-layer alginate-polycaprolactone electrospun membranes as skin wound patches with drug delivery abilities. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, S.S.; Chen, S.S.; Li, C.W.; Nguyen, N.C.; Nguyen, H.T. A comprehensive review: Electrospinning technique for fabrication and surface modification of membranes for water treatment application. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 85495–85514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbatly, R.; Krishnaiah, D.; Kamin, Z. A review of polymer nanofibres by electrospinning and their application in oil-water separation for cleaning up marine oil spills. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 106, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, S.; Ferretti, M.; Vicini, S.; Castellano, M.; Caratto, V. Porous polydimethylsiloxane membranes loaded with low-temperature crystallized TiO2 NPs for detachable antibacterial films. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 1665–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Zhu, M.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Green Electrospun Nanofibers and Their Application in Air Filtration. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303, 1800336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Han, J.; Wang, F.; Shao, W.; Xiong, R.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, H.; Yang, Y.; Samal, S.K.; Zhang, F.; et al. Electrospun Nanofibers Membranes for Effective Air Filtration. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1600353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Wang, R.; Tang, G.; Mou, Z.; Lei, J.; Han, J.; De Smedt, S.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Ecofriendly Electrospun Membranes Loaded with Visible-Light-Responding Nanoparticles for Multifunctional Usages: Highly Efficient Air Filtration, Dye Scavenging, and Bactericidal Activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 12880–12889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haider, A.; Haider, S.; Kang, I.K. A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Huang, H.; Mai, Y.W.; Zhou, L. Electrospun carbon-based nanostructured electrodes for advanced energy storage—A review. Energy Storage Mater. 2016, 5, 58–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercante, L.A.; Scagion, V.P.; Migliorini, F.L.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Correa, D.S. Electrospinning-based (bio)sensors for food and agricultural applications: A review. Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 91, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafat, M.M.; Dinan, B.; Akbar, S.A.; Haseeb, A.S.M.A. Gas Sensors Based on One Dimensional Nanostructured Metal-Oxides: A Review. Sensors 2012, 12, 7207–7258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Nair, S.V.; Menon, D. Integrating Substrateless Electrospinning with Textile Technology for Creating Biodegradable Three-Dimensional Structures. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 5420–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Garcia, W.; Jayathilaka, W.A.D.M.; Chinnappan, A.; Tran, T.Q.; Baskar, C.; Thomas, S.W.; Ramakrishna, S. Nanocomposites for electronic applications that can be embedded for textiles and wearables. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2019, 62, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, C.; Xue, J.; Ke, Q.; Xia, Y. Enhancing the Mechanical Properties of Electrospun Nanofiber Mats through Controllable Welding at the Cross Points. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2017, 38, 1600723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flores-Hernandez, D.R.; Cardenas-Benitez, B.; Martinez-Chapa, S.O.; Bonilla-Rios, J. Tailoring the Diameters of Electro-Mechanically Spun Fibers by Controlling Their Deborah Numbers. Polymers 2020, 12, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anindyajati, A.; Boughton, P.; Ruys, A. The Effect of Rotating Collector Design on Tensile Properties and Morphology of Electrospun Polycaprolactone Fibres. MATEC Web Conf. 2015, 27, 02002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, I.; Han, H.-S.; Edwards, J.; Jeon, H. Electrospun Fibrous Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering: Viewpoints on Architecture and Fabrication. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahirwal, D.; Hébraud, A.; Kádár, R.; Wilhelm, M.; Schlatter, G. From self-assembly of electrospun nanofibers to 3D cm thick hierarchical foams. Soft Matter. 2013, 9, 3164–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavielle, N.; Hébraud, A.; Schlatter, G.; Thöny-Meyer, L.; Rossi, R.M.; Popa, A.M. Simultaneous electrospinning and electrospraying: A straightforward approach for fabricating hierarchically structured composite membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 10090–10097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baji, A.; Mai, Y.W.; Wong, S.C.; Abtahi, M.; Chen, P. Electrospinning of polymer nanofibers: Effects on oriented morphology, structures and tensile properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.D.; Mitchell, G.R.; Mohan, S.D.; Olley, R.H. Development of orientation during electrospinning of fibres of poly(e-caprolactone). Eur. Polym. J. 2010, 46, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stepanyan, R.; Subbotin, A.V.; Cuperus, L.; Boonen, P.; Dorschu, M.; Oosterlinck, F.; Bulters, M.J.H. Nanofiber diameter in electrospinning of polymer solutions: Model and experiment. Polymer 2016, 97, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.; Maksoud, F.J.; Ghaddar, N.; Ghali, K.; Tehrani-Bagha, A. A mathematical model to predict the effect of electrospinning processing parameters on the morphological characteristic of nano-fibrous web and associated filtration efficiency. J. Aerosol. Sci. 2017, 113, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodero, A.; Pianella, L.; Vicini, S.; Alloisio, M.; Ottonelli, M.; Castellano, M. Alginate-based hydrogels prepared via ionic gelation: An experimental design approach to predict the crosslinking degree. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 118, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad Khanlou, H.; Chin Ang, B.; Talebian, S.; Muhammad Afifi, A.; Andriyana, A. Electrospinning of polymethyl methacrylate nanofibers: Optimization of processing parameters using the Taguchi design of experiments. Text. Res. J. 2015, 85, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasprilla-Botero, J.; Álvarez-Láinez, M.; Lagaron, J.M. The influence of electrospinning parameters and solvent selection on the morphology and diameter of polyimide nanofibers. Mater. Today Commun. 2018, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, S.F.; Golbabaei, F.; Maddah, B.; Latifi, M.; Pezeshk, H.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Akbar-Khanzadeh, F. Optimization of electrospinning parameters for polyacrylonitrile-MgO nanofibers applied in air filtration. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2016, 66, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khanlou, H.M.; Ang, B.C.; Talebian, S.; Barzani, M.M.; Silakhori, M.; Fauzi, H. Multi-response analysis in the processing of poly (methyl methacrylate) nano-fibres membrane by electrospinning based on response surface methodology: Fibre diameter and bead formation. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2015, 65, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vita, S.; Ricotti, R.; Malegori, C.; Oliveri, P.; Castellano, M.; Vicini, S. Univariate and multivariate strategies for the rheological tests evaluation: Influence of additives in composite materials. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 49019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Nishino, M.; Sohn, D.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, I.S. Control of the morphology of cellulose acetate nanofibers via electrospinning. Cellulose 2018, 25, 2829–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenmozhi, S.; Dharmaraj, N.; Kadirvelu, K.; Kim, H.Y. Electrospun nanofibers: New generation materials for advanced applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2017, 217, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar-Mohammadi, M.; Kargozar, S.; Bahrami, S.H.; Joghataei, M. Fabrication of curcumin-loaded gum tragacanth/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers with optimized electrospinning parameters. J. Ind. Text. 2017, 46, 1170–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasouri, K.; Shoushtari, A.M.; Mojtahedi, M.R.M. Evaluation of effective electrospinning parameters controlling polyvinylpyrrolidone nanofibers surface morphology via response surface methodology. Fibers Polym. 2015, 16, 1941–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Kim, J.; Shim, H. Fiber formation model for PVP (polyvinyl pyrrolidone) electrospinning. I. Critical voltage. Fibers Polym. 2017, 18, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chang, M.W.; Ahmad, Z.; Zheng, H.; Li, J.S. Mass and controlled fabrication of aligned PVP fibers for matrix type antibiotic drug delivery systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Hu, S.C.-S.; Huang, P.-H.; Lin, T.-C.; Yen, F.-L. Electrospun Resveratrol-Loaded Polyvinylpyrrolidone/Cyclodextrin Nanofibers and Their Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungst, T.; Muerza-Cascante, M.L.; Brown, T.D.; Standfest, M.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Groll, J.; Dalton, P.D. Melt electrospinning onto cylinders: Effects of rotational velocity and collector diameter on morphology of tubular structures. Polym. Int. 2015, 64, 1086–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doergens, A.; Roether, J.A.; Dippold, D.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Schubert, D.W. Identifying key processing parameters for the electrospinning of aligned polymer nanofibers. Mater. Lett. 2015, 140, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ner, Y.; Asemota, C.; Olson, J.R.; Sotzing, G.A. Nanofiber alignment on a flexible substrate: Hierarchical order from macro to nano. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 2093–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Clark, R.L. Electrohydrodynamic atomization: A versatile process for preparing materials for biomedical applications. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2008, 19, 573–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, D.; Higaki, Y.; Ma, W.; Wu, H.; Shinohara, T.; Yano, T.; Takahara, A. Chain orientation in poly(glycolic acid)/halloysite nanotube hybrid electrospun fibers. Polymer 2015, 60, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Li, J.; Li, Q.; Ni, T.; Wei, G. Chain conformation, crystallization behavior, electrical and mechanical properties of electrospun polymer-carbon nanotube hybrid nanofibers with different orientations. Carbon N. Y. 2012, 50, 5605–5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, N.; Kim, H.-K.; Kim, B.-S.; Lee, K.-H.; Kim, I.-S. Molecular Orientation and Crystalline Structure of Aligned Electrospun Nylon-6 Nanofibers: Effect of Gap Size. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2010, 295, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsano, E.; Bianchi, E.; Vicini, S.; Compagnino, L.; Sionkowska, A.; Skopińska, J.; Wiśniewski, M. Stimuli responsive gels based on interpenetrating network of chitosan and poly(vinylpyrrolidone). Polymer 2005, 46, 1595–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccalero, G.; Jean-Mistral, C.; Castellano, M.; Boragno, C. Soft, hyper-elastic and highly-stable silicone-organo-clay dielectric elastomer for energy harvesting and actuation applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 146, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertasa, M.; Dodero, A.; Alloisio, M.; Vicini, S.; Riedo, C.; Sansonetti, A.; Scalarone, D.; Castellano, M. Agar gel strength: A correlation study between chemical composition and rheological properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 123, 109442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vita, S.; Ricotti, R.; Dodero, A.; Vicini, S.; Borchardt, P.; Pinori, E.; Castellano, M. Rheological, Mechanical and Morphological Characterization of Fillers in the Nautical Field: The Role of Dispersing Agents on Composite Materials. Polymers (Basel) 2020, 12, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodero, A.; Williams, R.; Gagliardi, S.; Vicini, S.; Alloisio, M.; Castellano, M. A micro-rheological and rheological study of biopolymers solutions: Hyaluronic acid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 203, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oulevey, F.; Burnham, N.A.; Gremaud, G.; Kulik, A.J.; Pollock, H.M.; Hammiche, A.; Reading, M.; Song, M.; Hourston, D.J. Dynamic mechanical analysis at the submicron scale. Polymer 2000, 41, 3087–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bier, J.M.; Verbeek, C.J.R.; Lay, M.C. Identifying transition temperatures in bloodmeal-based thermoplastics using material pocket DMTA. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 112, 1303–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.S.; Tian, Y.; Abu-Diak, O.; Andrews, G.P. Pharmaceutical applications of dynamic mechanical thermal analysis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gearing, J.; Malik, K.P.; Matejtschuk, P. Use of dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) to determine critical transition temperatures in frozen biomaterials intended for lyophilization. Cryobiology 2010, 61, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunengo, E.; Luciano, G.; Canu, G.; Canetti, M.; Conzatti, L.; Castellano, M.; Stagnaro, P. Double-step moulding: An effective method to induce the formation of β-phase in PVDF. Polymer 2020, 193, 122345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunengo, E.; Castellano, M.; Conzatti, L.; Canu, G.; Buscaglia, V.; Stagnaro, P. PVDF-based composites containing PZT particles: How processing affects the final properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Factor | Variable | Unit | Low Level | High Level | Central Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x1 | Rotating speed | rpm | 0 | 500 | 250 |
| x2 | Angle of investigation | degree (°) | 0 | 90 | 45 |
| Rotating Speed (rpm) | Angle (°) | Y (MPa) | σr (MPa) | εr (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 45 90 | 44 ± 1 45 ± 2 45 ± 2 | 1.2 ± 0.2 1.1 ± 0.2 1.2 ± 0.1 | 22 ± 5 17 ± 5 19 ± 4 |
| 250 | 0 45 90 | 71 ± 2 50 ± 1 46 ± 3 | 1.4 ± 0.1 0.8 ± 0.2 0.4 ± 0.1 | 16 ± 4 16 ± 5 22 ± 1 |
| 500 | 0 45 90 | 165 ± 6 93 ± 3 71 ± 3 | 4.0 ± 0.2 1.3 ± 0.1 0.8 ± 0.2 | 8 ± 1 14 ± 2 30 ± 2 |
| Rotating Speed (rpm) | Angle (°) | E′ at T = −40 °C (MPa) | E′ at T = 20 °C (MPa) | E′ at T = 80 °C (MPa) | Tφ (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 90 | 48.3 ± 1.2 48.7 ± 0.9 | 42.4 ± 0.8 41.9 ± 0.2 | 39.5 ± 0.6 40.1 ± 0.4 | 45 ± 2 44 ± 3 |
| 250 | 0 90 | 79.5 ± 1.1 49.1 ± 1.4 | 69.6 ± 1.2 42.6 ± 1.5 | 62.7 ± 1.2 40.2 ± 3.0 | 24 ± 1 0 ± 3 |
| 500 | 0 90 | 186.1 ± 4.3 84.4 ± 3.6 | 160.4 ± 6.8 70.1 ± 4.3 | 142.4 ± 1.2 66.3 ± 1.1 | 5 ± 1 −10 ± 3 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dodero, A.; Brunengo, E.; Castellano, M.; Vicini, S. Investigation of the Mechanical and Dynamic-Mechanical Properties of Electrospun Polyvinylpyrrolidone Membranes: A Design of Experiment Approach. Polymers 2020, 12, 1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071524
Dodero A, Brunengo E, Castellano M, Vicini S. Investigation of the Mechanical and Dynamic-Mechanical Properties of Electrospun Polyvinylpyrrolidone Membranes: A Design of Experiment Approach. Polymers. 2020; 12(7):1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071524
Chicago/Turabian StyleDodero, Andrea, Elisabetta Brunengo, Maila Castellano, and Silvia Vicini. 2020. "Investigation of the Mechanical and Dynamic-Mechanical Properties of Electrospun Polyvinylpyrrolidone Membranes: A Design of Experiment Approach" Polymers 12, no. 7: 1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071524
APA StyleDodero, A., Brunengo, E., Castellano, M., & Vicini, S. (2020). Investigation of the Mechanical and Dynamic-Mechanical Properties of Electrospun Polyvinylpyrrolidone Membranes: A Design of Experiment Approach. Polymers, 12(7), 1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071524