Does Subunit Composition Influence the Intermolecular Crosslinking of Fish Collagen? A Study with Hake and Blue Shark Skin Collagens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Extraction of Acid Soluble Collagen
2.2. Characterization of ASC
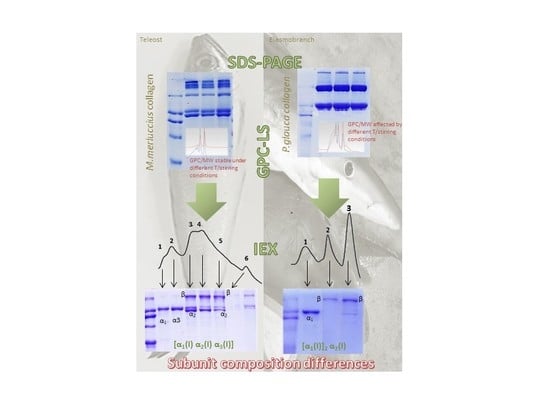
2.2.1. SDS-PAGE
2.2.2. Molecular Weight Determination of Collagen by GPC-LS
Temperature and Stirring Time Effect on Collagen GPC Mobile Phase Solubility
2.2.3. Cation-Exchange Chromatography (cIEX)
3. Results
3.1. SDS-PAGE
3.2. Molecular Weight Determination of Collagen by GPC-LS
3.3. Isolation of Collagen Components
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Addad, S.; Expósito, J.-Y.; Faye, C.; Ricard-Blum, S.; Lethias, C. Isolation, characterization and biological evaluation of jellyfish collagen for use in biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 967–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alves, A.L.; Marques, A.L.; Martins, E.; Silva, T.H.; Reis, R.L. Cosmetic potential of marine fish skin collagen. Cosmetics 2017, 4, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Z.; Yang, P.; Zhou, X.; Li, S.; Hong, P. Marine collagen peptides from the skin of nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus: Characterization and wound healing evalutation. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaidi, F.; Varatharajan, V.; Peng, H.; Senadheera, R. Utilization of marine by-products for the recovery of value-added products. J. Food Bioact. 2019, 6, 10–61. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco, M.; Sotelo, C.G.; Pérez-Martín, R.I. New strategy to cope with common fishery policy landing obligation: Collagen extraction from skins and bones of undersized hake. Polymers 2019, 11, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Chen, H.; Xie, Q.; Hong, B.; Chen, J.; Hua, F.; Bai, K.; He, J.; Yi, R.; Wu, H. Rapid isolation of high purity pepsin-soluble type I collagen from scales of red drum fish (Sciaenops ocellatus). Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotelo, C.; Blanco, M.; Ramos-Ariza, P.; Pérez-Martín, R.I. Characterization of collagen from different discarded fish species of the West Coast of the Iberian Peninsula. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2016, 25, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorushanova, A.; Delgado, M.L.; Wu, Z.; Shologu, N.; Kshirsagar, A.; Raghunath, R.; Mullen, A.M.; Bayon, Y.; Pandit, A.; Raghunath, M.; et al. The collagen suprafamily: From biosynthesis to advanced biomaterial development. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1801651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benjakul, S.; Nalinanon, S.; Shahidi, F. Fish collagen. In Food Biochemistry and Food Processing, 2nd ed.; Simpson, B.K., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2012; pp. 365–387. [Google Scholar]
- Miles, C.A.; Sims, T.J.; Camacho, N.P.; Bailey, A.J. The role of the α2 chain in the stabilization of the collagen type I heterotrimer: A study of the type I homotrimer in oim mouse tissues. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 321, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.J.; Chen, Y.; Jia, Y.L.; Liu, Y.Z.; Wang, W.H.; Zhang, G.R. Separation of β22 dimer from bovine collagen. Process Biochem. 2007, 42, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittiphattanabawon, P.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Shahidi, F. Isolation and properties of acid-and pepsin-soluble collagen from the skin of blacktip shark (Carcharhinus limbatus). Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2010, 230, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofman, K.A.; Hall, B.I. Ion Exchange HPLC of a Marine Collagen. J. Liq. Chrom. Rel. Technol. 2009, 32, 2512–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, T. Chemical nature of collagen in the dermis of the lamprey, Entosphenus japonicus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1993, 104, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittiphattanabawon, P.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Nagai, T.; Tanaka, M. Characterisation of acid-soluble collagen from skin and bone of bigeye snapper (Priacanthus tayenus). Food Chem. 2005, 89, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, T.; Araki, Y.; Suzuki, N. Collagen of the skin of ocellate puffer fish (Takifugu rubripes). Food Chem. 2002, 78, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Chang, S.F.C. Isolation and characterization of collagen extracted from channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) skin. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalinanon, S.; Benjakul, S.; Kishimura, H. Collagens from the skin of arabesque greenling (Pleurogrammus azonus) solubilized with the aid of acetic acid and pepsin from albacore tuna (Thunnys alalunga) stomach. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 1492–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folta-Stogniew, E.; Williams, K.R. Determination of molecular masses of proteins in solution: Implementation of an HPLC Size Exclusion Chromatography and laser light scattering service in a core laboratory. J. Biomol. Technol. 1999, 10, 51–63. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, M.; Morgenstern, B. Characterization of gelatin and acid soluble collagen by size exclusion chromatography coupled with multi angle light scattering. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 1727–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elango, J.; Lee, J.W.; Wang, S.; Henrotin, Y.; De Val, J.E.M.S.; Regenstein, J.M.; Lim, S.Y.; Bao, B.; Wu, W. Evaluation of Differentiated Bone Cells Proliferation by Blue Shark Skin Collagen via Biochemical for Bone Tissue Engineering. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montero, P.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Borderías, A.J. Functional Characterisation of Muscle and Skin Collagenous Material from Hake (Merluccius Merluccius L.). Food Chem. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, J.H.; Mizuta, S.; Yokoyama, Y.; Yoshinaka, R. Purification and characterization of molecular species of collagen in the skin of skate (Raja kenojei). Food Chem. 2007, 100, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theisen, A.; Johann, C.; Harding, S.E. Refractive Increment Data-Book for Polymer and Biomolecular Scientists; Nottingham University Press: Nottingham, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nomura, Y.; Yamano, M.; Hayakawa, C.; Ishii, Y.; Shirai, K. Structural property and in-vitro self assembly of shark type I collagen. Biosci. Biotech. Bioch. 1997, 61, 1919–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Takenouchi, Y.; Kunisaki, N.; Kimura, S. Complete primary structure of rainbow trout type I collagen consisting of α1(I), α2(I), α3 (I) heterotrimers. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 2817–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyre, D.R.; Weis, M.; Rai, J. Analysis of lysine aldehyde cross-linking in collagen reveal that the mature cross-link histidinohydrozylysinonerlucine is an artifact. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, S. Wide distribution of the skin type I collagen α3 chain in bony fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1992, 102, 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, S.; Ohno, Y.; Miyauchi, Y.; Uchida, N. Fish skin type I collagen: Wide distribution of an α3 subunit in teleosts. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1987, 88, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, M.; Vázquez, J.A.; Pérez-Martín, R.I.; Sotelo, C.G. Collagen Extraction Optimization from the skin of the small-spotted catshark (S. canicula) by Response Surface Methodology. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, A.H.; Gross, J. Relationship between the Intra and Intermolecular cross-links of collagen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1970, 67, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svensson, R.B.; Mulder, H.; Kovanen, V.; Magnusson, S.P. Fracture Mechanics of collagen fibrils. Influence of natural cross-links. Biophys. J. 2013, 104, 2476–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kittiphattanabawon, P.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Kishimura, H.; Shahidi, F. Isolation and Characterisation of collagen from the skin of brownbanded bamboo shark (Chiloscyllium punctatum). Food Chem. 2010, 119, 1519–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, S.; Ohno, Y. Fish type I collagen: Tissue-specific existence of two molecular forms, (α1)2α2 and α1α2α3, in Alaska Pollack. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1987, 88, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blanco, M.; Sanz, N.; Valcarcel, J.; Pérez-Martín, R.I.; Sotelo, C.G. Does Subunit Composition Influence the Intermolecular Crosslinking of Fish Collagen? A Study with Hake and Blue Shark Skin Collagens. Polymers 2020, 12, 1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081734
Blanco M, Sanz N, Valcarcel J, Pérez-Martín RI, Sotelo CG. Does Subunit Composition Influence the Intermolecular Crosslinking of Fish Collagen? A Study with Hake and Blue Shark Skin Collagens. Polymers. 2020; 12(8):1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081734
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlanco, María, Noelia Sanz, Jesús Valcarcel, Ricardo I. Pérez-Martín, and Carmen G. Sotelo. 2020. "Does Subunit Composition Influence the Intermolecular Crosslinking of Fish Collagen? A Study with Hake and Blue Shark Skin Collagens" Polymers 12, no. 8: 1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081734
APA StyleBlanco, M., Sanz, N., Valcarcel, J., Pérez-Martín, R. I., & Sotelo, C. G. (2020). Does Subunit Composition Influence the Intermolecular Crosslinking of Fish Collagen? A Study with Hake and Blue Shark Skin Collagens. Polymers, 12(8), 1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12081734