Drawbacks of Low Lattice Energy Ammonium Salts for Ion-Conducting Polymer Electrolyte Preparation: Structural, Morphological and Electrical Characteristics of CS:PEO:NH4BF4-Based Polymer Blend Electrolytes
Abstract
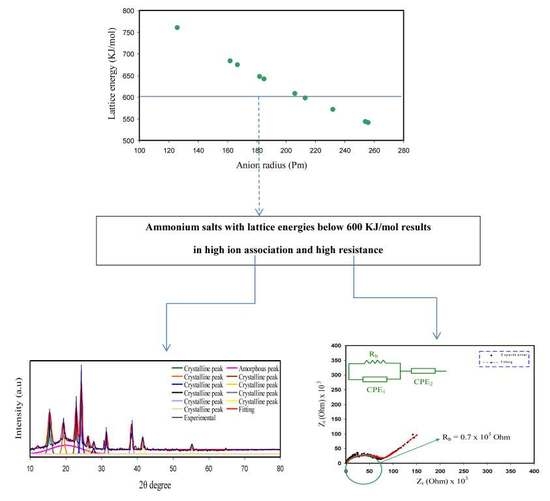
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Detail
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Structural, Morphological and Impedance Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Study
3.2. Morphological Study
3.3. Impedance Analysis
3.4. Dielectric Properties and Electric Modulus Analysis
3.5. Electric Modulus Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karan, N.; Pradhan, D.; Thomas, R.; Natesan, B.; Katiyar, R.S. Solid polymer electrolytes based on polyethylene oxide and lithium trifluoro-methane sulfonate (PEO–LiCF3SO3): Ionic conductivity and dielectric relaxation. Solid State Ion. 2008, 179, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, W.; Dürr, O.; Pendzig, P.; Bunde, A.; Nitzan, A. Percolation concepts in solid state ionics. Phys. A Stat. Theor. Phys. 1999, 266, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, M. Intercalation electrodes. In Materials for Advanced Batteries; Murphy, D.W., Broadhead, J., Steele, B.C.H., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980; p. 145. [Google Scholar]
- Mauger, A.; Julien, C.M.; Goodenough, J.B.; Zaghib, K. Tribute to Michel Armand: From Rocking Chair—Li-ion to Solid-State Lithium Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 070507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, P.V. Developments in Polymer Electrolytes for Lithium Batteries. MRS Bull. 2002, 27, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, F.M. Polymer Electrolytes (RSC Materials Monographs); Connor, J.A., Ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 1997; p. 175. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, S.B. Li+ ion conduction mechanism in poly (ε-caprolactone)-based polymer electrolyte. Iran. Polym. J. 2013, 22, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziz, S.B.; Abidin, Z.H.Z.; Arof, A. Influence of silver ion reduction on electrical modulus parameters of solid polymer electrolyte based on chitosan-silver triflate electrolyte membrane. Express Polym. Lett. 2010, 4, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, P.V. Electrical conductivity in ionic complexes of poly (ethylene oxide). Br. Polym. J. 1975, 7, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightfoot, P.; Mehta, M.A.; Bruce, P.G. Crystal Structure of the Polymer Electrolyte Poly (ethylene oxide) 3: LiCF3SO3. Science 1993, 262, 883–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, R.; Prabaharan, M.; Nair, S.; Tamura, H. Novel chitin and chitosan nanofibers in biomedical applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.; Cao, F.; Lan, X.; Zhao, F.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, C. Chitosan gel beads immobilized Cu (II) for selective adsorption of amino acids. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2008, 70, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Kong, L.; Sheng, B.; Wang, X.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, X.-F. Degradation of covalently cross-linked carboxymethyl chitosan and its potential application for peripheral nerve regeneration. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 3807–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Abidin, Z.H.Z. Electrical Conduction Mechanism in Solid Polymer Electrolytes: New Concepts to Arrhenius Equation. J. Soft Matter 2013, 2013, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noto, V.D.; Negro, E.; Lavina, S.; Dello, M.V. Polymer Electrolytes: Fundamentals and Applications, Hybrid Inorganic–Organic Polymer Electrolytes Wood Head Publishing Series in Electronic and Optical Materials; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 219–277. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, S.B.; Woo, T.J.; Kadir, M.F.; Ahmed, H.M.; Ahmed, H.M. A conceptual review on polymer electrolytes and ion transport models. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2018, 3, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.; Mohamad, A.A. Protonic battery based on a plasticized chitosan-NH4NO3 solid polymer electrolyte. J. Power Sources 2006, 163, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, Z.; Ibrahim, Z.; Arof, A. Conductivity enhancement due to ion dissociation in plasticized chitosan based polymer electrolytes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2001, 44, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Hamsan, M.; Brza, M.; Kadir, M.; Abdulwahid, R.T.; Ghareeb, H.O.; Woo, H. Fabrication of energy storage EDLC device based on CS:PEO polymer blend electrolytes with high Li+ ion transference number. Results Phys. 2019, 15, 102584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Hamsan, M.H.; Kadir, M.F.Z.; Karim, W.O.; Abdullah, R.M. Development of Polymer Blend Electrolyte Membranes Based on Chitosan: Dextran with High Ion Transport Properties for EDLC Application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziz, S.B.; Abidin, Z.; Arof, A. Effect of silver nanoparticles on the DC conductivity in chitosan—Silver triflate polymer electrolyte. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2010, 405, 4429–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patla, S.K.; Ray, R.; Asokan, K.; Karmakar, S. Investigation of ionic conduction in PEO–PVDF based blend polymer electrolytes. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 123, 125102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koduru, H.K.; Iliev, M.; Kondamareddy, K.K.; Karashanova, D.; Vlakhov, T.; Zhao, X.-Z.; Scaramuzza, N. Investigations on Poly (ethylene oxide) (PEO)—Blend based solid polymer electrolytes for sodium ion batteries. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 764, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Inoue, T.; Fujinami, T.; Mehta, M. Ionic conductivity and interfacial properties of polymer electrolytes based on PEO and boroxine ring polymer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 84, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-J.; Fan, C.-Y.; Zhang, J.-P.; Wu, X.-L. A promising PMHS/PEO blend polymer electrolyte for all-solid-state lithium ion batteries. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 14932–14937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarada, B.A.; Bhargav, P.B.; Sharma, A.K.; Rao, V.V.R.N. Studies on (PEO + PVA + KIO3) polymer blend electrolyte films for electrochemical cell applications. Mater. Res. Innov. 2011, 15, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, G.; Jeon, H.; Park, M.J. Synthesis of Polymer Electrolytes Based on Poly (ethylene oxide) and an Anion-Stabilizing Hard Polymer for Enhancing Conductivity and Cation Transport. ACS Macro Lett. 2015, 4, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Abdullah, R.M. Crystalline and amorphous phase identification from the tanδ relaxation peaks and impedance plots in polymer blend electrolytes based on [CS:AgNt]x:PEO(x–1) (10 ≤ x ≤ 50). Electrochim. Acta 2018, 285, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, C.P.; Rosa, D.D.S.; Gaboardi, F.; Neves, S. Development of a biodegradable polymer electrolyte for rechargeable batteries. J. Power Sources 2006, 155, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Hamsan, M.H.H.; Nofal, M.M.; San, S.; Abdulwahid, R.T.; Saeed, S.R.R.; Brza, M.A.; Kadir, M.; Mohammed, S.J.; Al-Zangana, S. From Cellulose, Shrimp and Crab Shells to Energy Storage EDLC Cells: The Study of Structural and Electrochemical Properties of Proton Conducting Chitosan-Based Biopolymer Blend Electrolytes. Polymers 2020, 12, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramya, C.S.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Hirankumar, G.; Savitha, T.; Angelo, P. Investigation on dielectric relaxations of PVP–NH4SCN polymer electrolyte. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2008, 354, 1494–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnawi, A.S.F.M.; Aziz, S.B.; Nofal, M.M.; Hamsan, M.H.; Brza, M.A.; Yusof, Y.M.; Abdulwahid, R.T.; Muzakir, S.K.; Kadir, M. Glycerolized Li+ Ion Conducting Chitosan-Based Polymer Electrolyte for Energy Storage EDLC Device Applications with Relatively High Energy Density. Polymers 2020, 12, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Abdullah, R.M.; Rasheed, M.A.; Ahmed, H.M. Role of Ion Dissociation on DC Conductivity and Silver Nanoparticle Formation in PVA: AgNt Based Polymer Electrolytes: Deep Insights to Ion Transport Mechanism. Polymers 2017, 9, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziz, S.B. Morphological and Optical Characteristics of Chitosan (1 − x):Cuox (4 ≤ x ≤ 12) Based Polymer Nano-Composites: Optical Dielectric Loss as an Alternative Method for Tauc’s Model. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aziz, S.B. The Mixed Contribution of Ionic and Electronic Carriers to Conductivity in Chitosan Based Solid Electrolytes Mediated by CuNt Salt. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2018, 28, 1942–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Abdullah, R.M.; Kadir, M.; Ahmed, H.M. Non suitability of silver ion conducting polymer electrolytes based on chitosan mediated by barium titanate (BaTiO3) for electrochemical device applications. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 296, 494–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Song, S.; Ma, Q.; Liu, R. High Performance Poly (vinyl alcohol)-Based Li-Ion Conducting Gel Polymer Electrolyte Films for Electric Double-Layer Capacitors. Polymers 2018, 10, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziz, S.B.; Hamsan, M.H.; Karim, W.O.; Marif, A.S.; Abdulwahid, R.T.; Kadir, M.F.Z.; Brza, M.A. Study of impedance and solid-state double-layer capacitor behavior of proton (H+)-conducting polymer blend electrolyte-based CS:PS polymers. Ionics 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Huang, H.; Fu, X.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Pan, L.; Xu, M. A flexible, high-voltage and safe zwitterionic natural polymer hydrogel electrolyte for high-energy-density zinc-ion hybrid supercapacitor. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 392, 123733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Brza, M.A.; Hamsan, H.M.; Kadir, M.F.Z.; Abdulwahid, R.T. Electrochemical characteristics of solid state double-layer capacitor constructed from proton conducting chitosan-based polymer blend electrolytes. Polym. Bull. 2020, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, S.A.; Latham, R.G.; Linford, R.G.; Schlindwein, W.S. Studies on all solid state electric double layer capacitors using proton and lithium ion conducting polymer electrolytes. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1997, 93, 4177–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Brza, M.; Mishra, K.; Hamsan, M.; Karim, W.O.; Abdullah, R.M.; Kadir, M.; Abdulwahid, R.T. Fabrication of high performance energy storage EDLC device from proton conducting methylcellulose: Dextran polymer blend electrolytes. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 1137–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.-S.; Teoh, K.; Liew, C.-W.; Ramesh, S. Capacitive behavior studies on electrical double layer capacitor using poly (vinyl alcohol)—Lithium perchlorate based polymer electrolyte incorporated with TiO2. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 143, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Brza, M.; Hamsan, M.; Kadir, M.; Muzakir, S.; Abdulwahid, R.T. Effect of ohmic-drop on electrochemical performance of EDLC fabricated from PVA:dextran:NH4I based polymer blend electrolytes. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 3734–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piana, G.; Bella, F.; Geobaldo, F.; Meligrana, G.; Gerbaldi, C. PEO/LAGP hybrid solid polymer electrolytes for ambient temperature lithium batteries by solvent-free, “one pot” preparation. J. Energy Storage 2019, 26, 100947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnawi, A.S.F.M.; Aziz, S.B.; Nofal, M.M.; Yusof, Y.M.; Brevik, I.; Hamsan, M.H.; Brza, M.A.; Abdulwahid, R.T.; Kadir, M. Metal Complex as a Novel Approach to Enhance the Amorphous Phase and Improve the EDLC Performance of Plasticized Proton Conducting Chitosan-Based Polymer Electrolyte. Membranes 2020, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassiouni, M.; Al-Shamy, F.; Madi, N.; Kassem, M. Temperature and electric field effects on the dielectric dispersion of modified polyvinyl chloride. Mater. Lett. 2003, 57, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Peng, Z.; Liu, J.-M. Dielectric behaviors of relaxor ferroelectric Pb (Mg1/2Nb1/2) O3–35% PbTiO3: Temperature and frequency dependences. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2005, 117, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Gupta, P. Study of dielectric relaxation in polymer electrolytes. Eur. Polym. J. 1998, 34, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B. Structural, Morphological and Electrochemical Impedance Study of CS:LiTf based Solid Polymer Electrolyte: Reformulated Arrhenius Equation for Ion Transport Study. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 11, 9228–9244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Marif, R.B.; Brza, M.; Hassan, A.N.; Ahmad, H.A.; Faidhalla, Y.A.; Kadir, M. Structural, thermal, morphological and optical properties of PEO filled with biosynthesized Ag nanoparticles: New insights to band gap study. Results Phys. 2019, 13, 102220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göktepe, F.; Çelik, S.Ü.; Bozkurt, A. Preparation and the proton conductivity of chitosan/poly (vinyl phosphonic acid) complex polymer electrolytes. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2008, 354, 3637–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Abidin, Z.H.Z.; Kadir, M. Innovative method to avoid the reduction of silver ions to silver nanoparticles (Ag+→Ag0) in silver ion conducting based polymer electrolytes. Phys. Scr. 2015, 90, 35808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Creber, K.A.; Peppley, B.; Bui, V.T. Chitosan-Based solid electrolyte composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 280, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B. Role of Dielectric Constant on Ion Transport: Reformulated Arrhenius Equation. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smitha, B.; Sridhar, S.; Khan, A.A. Chitosan—Sodium alginate polyion complexes as fuel cell membranes. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 1859–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, S.; Chandra, S. Experimental investigations on a sodium-ion-conducting polymer electrolyte based on poly (ethylene oxide) complexed with NaPF6. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 1995, 34, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, R.A.; Snow, A.G.; Frech, R.; Glatzhofer, D.T. A spectroscopic and conductivity comparison study of linear poly (N-methylethylenimine) with lithium triflate and sodium triflate. Electrochim. Acta 2003, 48, 2247–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, N.S.; Aziz, S.B.; Aspanut, Z.; Kadir, M. Electrical impedance and conduction mechanism analysis of biopolymer electrolytes based on methyl cellulose doped with ammonium iodide. Ionics 2016, 22, 2157–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamsan, M.H.; Shukur, M.F.; Kadir, M. NH4NO3 as charge carrier contributor in glycerolized potato starch-methyl cellulose blend-based polymer electrolyte and the application in electrochemical double-layer capacitor. Ionics 2017, 23, 3429–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Kadir, M.F.Z.; Hamsan, M.H.; Woo, H.J.; Brza, M.A. Development of Polymer Blends Based on PVA:POZ with Low Dielectric Constant for Microelectronic Applications. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kadir, M.; Majid, S.; Arof, A. Plasticized chitosan—PVA blend polymer electrolyte based proton battery. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukur, M.F.; Kadir, M. Hydrogen ion conducting starch-chitosan blend based electrolyte for application in electrochemical devices. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 158, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machappa, T.; Prasad, M.A. AC conductivity and dielectric behavior of polyaniline/sodium metavenadate (PANI/NaVO3) composites. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2009, 404, 4168–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsudin, A.S.; Isa, M.I.N. Characterization of carboxy methylcellulose doped with DTAB as new types of biopolymer electrolytes. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2012, 35, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzantowicz, M.; Dygas, J.; Krok, F. Impedance of interface between PEO:LiTFSI polymer electrolyte and blocking electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 7417–7425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B. Study of electrical percolation phenomenon from the dielectric and electric modulus analysis. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2015, 38, 1597–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B. Occurrence of electrical percolation threshold and observation of phase transition in chitosan (1 − x):AgI x (0.05 ≤ x ≤ 0.2)-based ion-conducting solid polymer composites. Appl. Phys. A 2016, 122, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariappan, C.; Govindaraj, G. AC conductivity, dielectric studies and conductivity scaling of NASICON materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2002, 94, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswarlu, M.; Satyanarayana, N. AC conductivity studies of silver based fast ion conducting glassy materials for solid state batteries. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 1998, 54, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, M.M.E.; Prabaharan, S.R.S.; Radhakrishna, S. Effect of PEO addition on the electrolytic and thermal properties of PVDF-LiClO4 polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 1997, 104, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, C.P.J.; Cavalcante, F.; Amaral, F.A.; Souza, C.A.Z.; Neves, S. Thermal and conduction properties of a PCL-biodegradable gel polymer electrolyte with LiClO4, LiF3CSO3, and LiBF4 salts. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2007, 2, 52–63. [Google Scholar]
- Pradhan, D.K.; Choudhary, P.; Samantaray, B.K.; Karan, N.K.; Katiyar, R.S. Effect of Plasticizer on Structural and Electrical Properties of Polymer Nanocompsoite Electrolytes. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2007, 2, 861–871. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, S.B.; Abidin, Z.H.Z. Ion-Transport study in nanocomposite solid polymer electrolytes based on chitosan: Electrical and dielectric analysis. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 132, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B. Advanced Polymeric Materials Research Lab, Department of Physics, College of Science, University of Sulaimani, Qlyasan Street, Sulaimani, Kurdistan Regional Government-Iraq Proton Ion Conducting Solid Polymer Electrolytes Based on Chitosan Incorporated with Various Amounts of Barium Titanate (BaTiO3). Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 6112–6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Chandra, S. Studies on a new proton conducting polymer system: Poly (ethylene succinate) + NH4ClO4. Eur. Polym. J. 2000, 36, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.A. Some Thermodynamic Aspects of inorganic Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1982; ISBN 0521242045. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, S.B.; Hamsan, M.H.; Abdullah, R.M.; Kadir, M.F.Z. A Promising Polymer Blend Electrolytes Based on Chitosan: Methyl Cellulose for EDLC Application with High Specific Capacitance and Energy Density. Molecules 2019, 24, 2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aziz, S.B.; Hamsan, M.H.; Abdullah, R.M.; Abdulwahid, R.T.; Brza, M.A.; Marif, A.S.; Kadir, M.F.Z. Protonic EDLC cell based on chitosan (CS): Methylcellulose (MC) solid polymer blend electrolytes. Ionics 2020, 26, 1829–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemalatha, R.; Alagar, M.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Sundaresan, B.; Moniha, V. Studies of proton conducting polymer electrolyte based on PVA, amino acid proline and NH4SCN. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2019, 4, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buraidah, M.; Arof, A. Characterization of chitosan/PVA blended electrolyte doped with NH4I. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2011, 357, 3261–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lide (National Institute of Standards and Technology). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 84th ed.; David, R., Ed.; CRC Press LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; ISBN 0-8493-0484-9. [Google Scholar]
- De Farias, R.F.; Kaya, S. Lattice Energies for Groups 1 and 2 Halides from Absolute Hardness. Cumhur. Sci. J. 2018, 39, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, H.D.B.; Thakur, K.P. Reappraisal of thermochemical radii for complex ions. J. Chem. Educ. 1979, 56, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Brza, M.; Mohamed, P.A.; Kadir, M.; Hamsan, M.; Abdulwahid, R.T.; Woo, H. Increase of metallic silver nanoparticles in Chitosan: AgNt based polymer electrolytes incorporated with alumina filler. Results Phys. 2019, 13, 102326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuyen, N.Q.; Zondaka, Z.; Harjo, M.; Torop, J.; Tamm, T.; Kiefer, R. Comparative Analysis of Fluorinated Anions for Polypyrrole Linear Actuator Electrolytes. Polymers 2019, 11, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kubota, S.; Ozaki, S.; Onishi, J.; Kano, K.; Shirai, O. Selectivity on Ion Transport across Bilayer Lipid Membranes in the Presence of Gramicidin A. Anal. Sci. 2009, 25, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vani, C.V.; Thanikaikarasan, S.; Mahalingam, T.; Sebastian, P.; Verea, L.E.; Shajan, X.S. Effect of X-ray Irradiation on Dielectric Properties of Polymer Electrolytes Complexed with LiCF3SO3. J. New Mater. Electrochem. Syst. 2014, 17, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziz, S.B.; Marif, R.B.; Brza, M.A.; Hamsan, M.H.; Kadir, M.F.Z. Brza Employing of Trukhan Model to Estimate Ion Transport Parameters in PVA Based Solid Polymer Electrolyte. Polymers 2019, 11, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pradhan, D.K.; Choudhary, R.N.P.; Samantaray, B.K. Studies of Dielectric Relaxation and AC Conductivity Behavior of Plasticized Polymer Nanocomposite Electrolytes. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2008, 3, 597–608. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, S.B.; Karim, W.O.; Brza, M.A.; Abdulwahid, R.T.; Saeed, S.R.; Al-Zangana, S.; Kadir, M.F.Z. Ion Transport Study in CS:POZ Based Polymer Membrane Electrolytes Using Trukhan Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamsan, M.H.; Shukur, M.F.; Aziz, S.B.; Kadir, M. Dextran from Leuconostoc mesenteroides-doped ammonium salt-based green polymer electrolyte. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2019, 42, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziz, S.B.; Abidin, Z.H.Z. Electrical and morphological analysis of chitosan: AgTf solid electrolyte. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 144, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B. Electrical and Dielectric Properties of Solid and Nanocomposite Polymer Electrolytes Based on Chitosan. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Natesan, B.; Karan, N.K.; Katiyar, R.S. Ion relaxation dynamics and nearly constant loss behavior in polymer electrolyte. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 74, 042801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natesan, B.; Karan, N.K.; Rivera, M.B.; Aliev, F.M.; Katiyar, R.S. Segmental relaxation and ion transport in polymer electrolyte films by dielectric spectroscopy. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2006, 352, 5205–5209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B. The Study of Dielectric Properties and Conductivity Relaxation of Ion Conducting Chitosan:NaTf Based Solid Electrolyte. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 10274–10288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.L.; Singh, M.; Tripathi, M.; Dwivedi, M.M.; Pandey, K. Dielectric relaxation studies on [PEO–SiO2]: NH4SCN nanocomposite polymer electrolyte films. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 6060–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, A.; Ghosh, A. Dielectric permittivity and electric modulus of polyethylene oxide (PEO)–LiClO4 composite electrolytes. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2012, 12, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, A.; Sadiq, M.; Sharma, A.L. Effect of variation of different nanofillers on structural, electrical, dielectric, and transport properties of blend polymer nanocomposites. Ionics 2017, 24, 2295–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziz, S.B. Study of Dielectric Properties and Ion Transport Parameters in Chitosan-Barium Nitrate Based Solid Polymer Electrolytes. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2019, 14, 11580–11595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marf, A.S.; Abdullah, R.M.; Aziz, S.B. Structural, Morphological, Electrical and Electrochemical Properties of PVA: CS-Based Proton-Conducting Polymer Blend Electrolytes. Membranes 2020, 10, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Electrolyte | Degree of Crystallinity (%) |
|---|---|
| CSPEH1 | 8.52 |
| CSPEH2 | 7.43 |
| CSPEH3 | 31.82 |
| CSPEH4 | 65.84 |
| Sample | P1 (rad) | P2 (rad) | K1 (F−1) | K2 (F−1) | C1 (F) | C2 (F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSPEH1 | 0.8784 | 0.3946 | 1.1 × 109 | 7.6 × 105 | 9.09 × 10−10 | 1.32 × 10−6 |
| CSPEH2 | 0.8847 | 0.6072 | 8.0 × 108 | 7.0 × 105 | 1.25 × 10−9 | 1.43 × 10−6 |
| CSPEH3 | 0.8338 | 0.5410 | 8.5 × 108 | 7.10 × 105 | 1.18 × 10−9 | 1.41 × 10−6 |
| CSPEH4 | 0.7765 | 0.5665 | 1.01 × 109 | 3.20 × 106 | 9.90 × 10−10 | 3.13 × 10−7 |
| Prepared Films | DC Conductivity (S cm−1) |
|---|---|
| CSPEH1 | 8.726 × 10−8 |
| CSPEH2 | 7.932 × 10−7 |
| CSPEH3 | 5.817 × 10−7 |
| CSPEH4 | 1.246 × 10−7 |
| Ammonium Salts | Lattice Energy (kJ/mol) | DC Conductivity (S cm−1) |
|---|---|---|
| NH4F | 759 | 2.96 × 10−3 [30] |
| NH4NO3 | 642 | 1.6 × 10−3 [62] |
| NH4I | 608.33 | 1.12 × 10−3 [42] |
| NH4SCN | 597.842 | 1.7 × 10−3 [31] |
| NH4BF4 | 571.141 | 1.246 × 10−7 [this work] |
| Ammonium Salts | Cation | Anion | Cation Radius (pm) [84] | Anion Radius (pm) [84] | Lattice Energy (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH4CF3SO3 | NH4+ | CF3SO3− | 151 | 256 [85] | 540.59 |
| NH4PF6 | NH4+ | PF6− | 151 | 254 [86] | 543.06 |
| NH4BF4 | NH4+ | BF4− | 151 | 232 | 571.141 |
| NH4SCN | NH4+ | SCN− | 151 | 213 [87] | 597.842 |
| NH4I | NH4+ | I− | 151 | 206 | 608.33 |
| NH4NO3 | NH4+ | NO3− | 151 | 185 | 642 |
| NH4Br | NH4+ | Br− | 151 | 182 | 647.13 |
| NH4Cl | NH4+ | Cl− | 151 | 167 | 674.02 |
| NH4CH3COO | NH4+ | CH3COO− | 151 | 162 | 683.41 |
| NH4F | NH4+ | F− | 151 | 126 | 759.82 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brza, M.A.; Aziz, S.B.; Nofal, M.M.; Saeed, S.R.; Al-Zangana, S.; Karim, W.O.; Hussen, S.A.; Abdulwahid, R.T.; Kadir, M.F.Z. Drawbacks of Low Lattice Energy Ammonium Salts for Ion-Conducting Polymer Electrolyte Preparation: Structural, Morphological and Electrical Characteristics of CS:PEO:NH4BF4-Based Polymer Blend Electrolytes. Polymers 2020, 12, 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091885
Brza MA, Aziz SB, Nofal MM, Saeed SR, Al-Zangana S, Karim WO, Hussen SA, Abdulwahid RT, Kadir MFZ. Drawbacks of Low Lattice Energy Ammonium Salts for Ion-Conducting Polymer Electrolyte Preparation: Structural, Morphological and Electrical Characteristics of CS:PEO:NH4BF4-Based Polymer Blend Electrolytes. Polymers. 2020; 12(9):1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091885
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrza, Mohamad A., Shujahadeen B. Aziz, Muaffaq M. Nofal, Salah R. Saeed, Shakhawan Al-Zangana, Wrya O. Karim, Sarkawt A. Hussen, Rebar T. Abdulwahid, and Mohd F. Z. Kadir. 2020. "Drawbacks of Low Lattice Energy Ammonium Salts for Ion-Conducting Polymer Electrolyte Preparation: Structural, Morphological and Electrical Characteristics of CS:PEO:NH4BF4-Based Polymer Blend Electrolytes" Polymers 12, no. 9: 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091885
APA StyleBrza, M. A., Aziz, S. B., Nofal, M. M., Saeed, S. R., Al-Zangana, S., Karim, W. O., Hussen, S. A., Abdulwahid, R. T., & Kadir, M. F. Z. (2020). Drawbacks of Low Lattice Energy Ammonium Salts for Ion-Conducting Polymer Electrolyte Preparation: Structural, Morphological and Electrical Characteristics of CS:PEO:NH4BF4-Based Polymer Blend Electrolytes. Polymers, 12(9), 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12091885