Electrostatic Self-Assembly of Composite Nanofiber Yarn
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
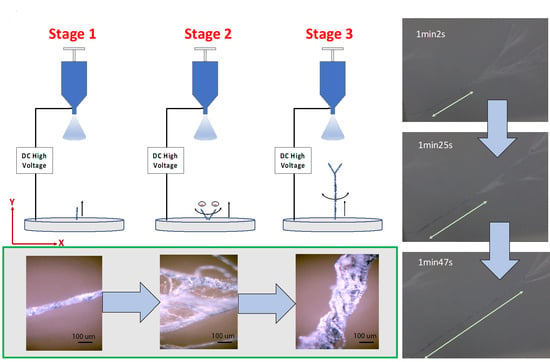
2.1. Yarn Formation
2.2. Experiment Setup
2.3. Finite Element Modelling of Yarn Formation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Field Considerations
3.3. Structural Densification-Electrospinning Time
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, S.L.P.; Stylios, G.K. An overview of smart technologies for clothing design and engineering. Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Technol. 2006, 18, 108–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.V.; Rahman, A.; Kumar, N.S.; Aditi, A.; Galluzzi, M.; Bovio, S.; Barozzi, S.; Montani, E.; Parazzoli, D. Bio-inspired approaches to design smart fabrics. Mater. Des. 2012, 36, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliuzza, A.; Drioli, E. A review on membrane engineering for innovation in wearable fabrics and protective textiles. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 350–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoppa, M.; Chiolerio, A. Wearable Electronics and Smart Textiles: A Critical Review. Sensors 2014, 14, 11957–11992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Honegger, E. Training for technical management in the textile industry at the swiss federal institute of technology. J. Text. Inst. Proc. 1938, 29, P298–P303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Gong, R.-H. Manufacturing technologies of polymeric nanofibres and nanofibre yarns. Polym. Int. 2008, 57, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, D.; Dijkstra, P.J.; Berg, J.W.A.; Feijen, J. Phase separation process in polymer solutions in relation to membrane for-mation, J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 117, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakarvarti, S.; Vetter, J. Template synthesis—A membrane based technology for generation of nano-/micro materials: A review. Radiat. Meas. 1998, 29, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Kotaki, M.; Inai, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Potential of Nanofiber Matrix as Tissue-Engineering Scaffolds. Tissue Eng. 2005, 11, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Brinker, C.J. Annual Review of Nano Research; Cao, G., Brinker, C.J., Eds.; World Scientific: Singapore, 2006; Volume 1, pp. 192–200. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, U.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Electrospinning of Continuous Nanofiber Bundles and Twisted Nanofiber Yarns; InTech: Kwun Tong, China, 2011; pp. 153–174. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning of Polymeric and Ceramic Nanofibers as Uniaxially Aligned Arrays. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazbouz, M.B.; Stylios, G.K. Alignment and optimization of nylon 6 nanofibers by electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 107, 3023–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, W.E.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on electrospinning design and nanofibre assemblies. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, R89–R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazbouz, M.B.; Stylios, G.K. Novel mechanism for spinning continuous twisted composite nanofiber yarns. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.A.; Wnek, G.E.; Simpson, D.G.; Bowlin, G.L. Electrospinning of Collagen Nanofibers. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.W.; Lee, K.H.; Khil, M.S.; Ho, Y.S.; Kim, H.Y. The effect of molecular weight and the linear velocity of drum surface on the properties of electrospun poly(ethylene terephthalate) nonwovens. Fibers Polym. 2004, 5, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning Nanofibers as Uniaxially Aligned Arrays and Layer-by-Layer Stacked Films. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, W.E.; Gopal, R.; Ramaseshan, R.; Fujihara, K.; Ramakrishna, S. A dynamic liquid support system for continuous elec-trospun yarn fabrication. Polymer 2007, 48, 3400–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, E.; Bűttner, U.; Sanderson, R.D. Continuous yarns from electrospun fibers. Polymer 2005, 46, 2419–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khil, M.S.; Bhattarai, S.R.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, S.Z.; Lee, K.H. Novel Fabricated Matrix Via Electrospinning for Tissue Engi-neering. J. Biomed. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2005, 72, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, S.Y.; Lee, J.R.; Kim, H.J.; Hong, Y.T.; Kim, S.; Park, S.J. Method of manufacturing a continuous filament by electrospinning. U.S. Patent 7799262, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Formhals, A. Artificial Thread and Method of Producing Same. U.S. Patent 2187306, 16 January 1940. [Google Scholar]
- Formhals, A. Production of artificial fibers from fiber forming liquids. U.S. Patent 2323025, 29 June 1943. [Google Scholar]
- Dalton, P.D.; Klee, D.; Möller, M. Electrospinning with dual collection rings. Polymer 2005, 46, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.-Q.; Eder, M.; Burgert, I.; Tasis, D.; Prato, M.; Wagner, H.D. One-step electrospun nanofiber-based composite ropes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 83108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effect of incorporation of ethylene glycol into PEDOT:PSS on electron phonon coupling and conductivity. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 215501. [CrossRef]
- Yarin, A.L.; Koombhongse, S.; Reneker, D.H. Bending instability in electrospinning of nanofibers. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 3018–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chou, T.; Chen, S.; Chiang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Chao, C. Highly conductive PEDOT:PSS films by post-treatment with dimethyl sulfoxide for ITO-free liquid crystal display. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 3760–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriev, O.; Grinko, D.; Noskov, Y.; Ogurtsov, N.; Pud, A. PEDOT:PSS films—Effect of organic solvent additives and annealing on the film conductivity. Synth. Met. 2009, 159, 2237–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Johansson, M.; Andersson, M.; Hummelen, J.; Inganäs, O. Polymer Photovoltaic Cells with Conducting Poly-mer Anodes. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Chu, C.; Chen, F.; Xu, Q.; Yang, Y. High-Conductivity Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene): Poly(styrene sul-fonate) Film and Its Application in Polymer Optoelectronic Devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-C.; Chiang, Y.-H.; Wu, C.-W.; Estroff, B. Inkjet-printed multi-parameter measuring sensor. Nanosens. Biosens. Info-Tech Sens. 3D Syst. 2017, 10167, 1016713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seekaew, Y.; Lokavee, S.; Phokharatkul, D.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Kerdcharoen, T.; Wongchoosuk, C. Low-cost and flexible printed graphene–PEDOT:PSS gas sensor for ammonia detection. Org. Electron. 2014, 15, 2971–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample # | Material A (6% PVA Dissolved in PEDOT:PSS) | DMSO | Ethylene Glycol (EG) | CNC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 93.7% | 6.3% | ||
| 2 | 95% | 5% | ||
| 3 | 100% | |||
| Material B (7% PVA dissolved in PEDOT:PSS) | ||||
| 4 | 93.1% | 4.9% | 2% | |
| 5 | 93.1% | 4.9% | 2% |
| Test # | Voltage (kV) | Distance (cm) | Sample # | E field (kV cm−1) | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 15 | 8.0 | 1 | 1.875 | Yarn |
| B | 15 | 8.0 | 2 | 1.875 | Yarn |
| C | 17 | 7.0 | 3 | 2.43 | No yarn |
| D | 17 | 8.0 | 4 | 2.13 | No yarn |
| E | 17 | 7.0 | 4 | 2.42 | Yarn |
| F | 19 | 8.5 | 4 | 2.24 | No yarn |
| G | 19 | 7.5 | 4 | 2.53 | Yarn |
| H | 17 | 8.0 | 5 | 2.13 | Yarn |
| I | 15 | 8.0 | 5 | 1.87 | Yarn |
| J | 15 | 8.5 | 5 | 1.76 | Yarn generated after 3 min |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.-C.; Cheng, Y.-T.; Estroff, B. Electrostatic Self-Assembly of Composite Nanofiber Yarn. Polymers 2021, 13, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010012
Wang W-C, Cheng Y-T, Estroff B. Electrostatic Self-Assembly of Composite Nanofiber Yarn. Polymers. 2021; 13(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wei-Chih, Yen-Tse Cheng, and Benjamin Estroff. 2021. "Electrostatic Self-Assembly of Composite Nanofiber Yarn" Polymers 13, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010012
APA StyleWang, W. -C., Cheng, Y. -T., & Estroff, B. (2021). Electrostatic Self-Assembly of Composite Nanofiber Yarn. Polymers, 13(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010012