Formulation and Characterization of Alginate-Based Membranes for the Potential Transdermal Delivery of Methotrexate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
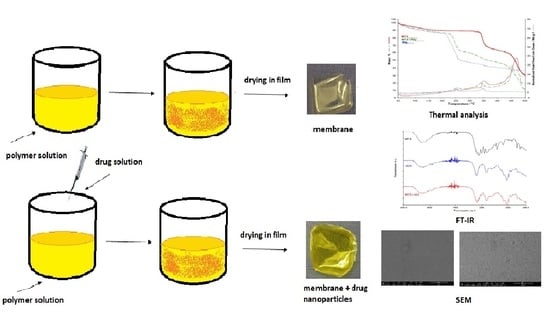
2.2. Synthesis of Membranes
2.3. Thermogravimetrical Analysis
2.4. FT-IR Spectroscopy
2.5. UV-Vis Spectrophotometry
2.6. SEM Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Obtaining the Membranes
3.2. Thermal Analysis
3.2.1. MTX in Solution
3.2.2. The Study of Binary Mixtures
3.2.3. Thermal Analysis of Membranes
3.3. FTIR Study
3.3.1. FTIR Study for Binary Mixtures
3.3.2. FTIR Study of Membranes
3.4. SEM Analysis
3.5. UV/Vis Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chandak, A.R.; Verma, P.R. Transdermal Delivery of Methotrexate Using Mixed Grades of Eudragit: Physico-Chemical, In-Vitro, and In-Vivo Evaluations. Clin. Res. Regul. Aff. 2008, 25, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunduru, K.R.; Basu, A.; Domb, A.J. Biodegradable Polymers: Medical Applications. In Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Technology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Rehm, B.H.; Moradali, M.F. Alginates and Their Biomedical Applications; Springer Series in Biomaterials Science and Engineering 11; Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Puscaselu, R.G.; Lobiuc, A.; Dimian, M.; Covasa, M. Alginate: From Food Industry to Biomedical Applications and Management of Metabolic Disorders. Polymers 2020, 12, 2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.A.; Saag, K.G.; Bridges, S.L., Jr.; Akl, E.A.; Bannuru, R.R.; Sullivan, M.C.; Vaysbrot, E.; McNaughton, C.; Osani, M.; Shmerling, R.H.; et al. 2015 American College of Rheumatology guideline for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewé, R.; Bijlsma, J.; Burmester, G.; Chatzidionysiou, K.; Dougados, M.; Nam, J.; Ramiro, S.; Voshaar, M.; Van Vollenhoven, R.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 960–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.K.; Hernán, M.A.; Seeger, J.D.; Robins, J.M.; Wolfe, F. Methotrexate and mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A prospective study. Lancet 2002, 359, 1173–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Methotrexate, CID = 126941. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/126941 (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- Wasko, M.C.; Dasgupta, A.; Hubert, H.; Fries, J.F.; Ward, M.M. Propensity-adjusted association of methotrexate with overall survival in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, A.; Arora, S. Formulation and in vitro evaluation of ufasomes for dermal administration of methotrexate. ISRN Pharm. 2012, 2012, 873653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wohlrab, J.; Neubert, R.H.; Michael, J.; Naumann, S. Methotrexate for topical application in an extemporaneous preparation. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2015, 13, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuliaş, A.; Popoiu, C.; Vlase, G.; Vlase, T.; Oneţiu, D.; Sǎvoiu, G.; Simu, G.; Pǎtruţescu, C.; Ilia, G.; Ledeţi, I. Thermoanalytical and spectroscopic study on methotrexate—Active substance and tablet. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2014, 9, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Qadariyah, L.; Sumarno, M.; Machmudah, S.; Sasaki, M.; Goto, M. Degradation of glycerol using hydrothermal process. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 9267–9271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blajovan, R.; Ledeţi, I.; Vlase, G.; Ledeţi, A.; Vlase, T. Study of thermal induced excipient–excipient interactions: Polyvinyl alcohol and polyvinylpyrrolidone with other pharmaceutical excipients. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 126, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlase, G.; Blajovan, R.; Albu, P.; Vlase, T. Study of thermally induced interaction between hydroxyethylcellulose and carboxymethylcellulose with different excipients. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 130, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, N.; Akhavan, A.; Kassaee, M.Z. Synthesis of antibacterial silver nanoparticles by γ-irradiation. Phys. E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2009, 42, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Park, H.G.; Choi, S.-H. γ-Irradiation-induced preparation of Ag and Au nanoparticles and their characterizations. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2007, 105, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravuri, S.K.; Pappenberger, K.A.; Dauphin, I.B.; Ross, A.; Buergi, B.; Staempfli, A.; Mahler, H.-C. Degradation of Polysorbates 20 and 80: Studies on Thermal Autoxidation and Hydrolysis. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 721–731. [Google Scholar]
- Santacesaria, E.; Gelosa, D.; Diserio, M.; Tesser, R. Thermal stability of nonionic polyoxyalkylene surfactants. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1991, 42, 2053–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Tafoya, M.C.; Tecante, A. Physicochemical characterization of sodium stearoyl lactylate (SSL), polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurate (Tween 20) and κ-carrageenan. Data Brief 2018, 19, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budiul, M.; Albu, P.; Vlase, G.; Turcuş, V.; Vlase, T. Thermogravimetric and calorimetric studies performed on memantine hydrochloride to determine its thermal behaviour and possible drug–excipient interactions. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 127, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albu, P.; Budiul, M.; Mateescu, M.; Chiriac, V.; Vlase, G.; Vlase, T. Studies regarding the induced thermal degradation, kinetic analysis and possible interactions with various excipients of an osseointegration agent: Zoledronic acid. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 130, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donbrow, M. Stability of polyoxyethylene chain in non-ionic surfactants. In Nonionic Surfactants: Physical Chemistry; Schick, M.J., Ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Soo, J.; Choi, G.; Eun, C.; Jae-Min, O.; Yeon-Ji, O.; Myung-Chul, P.; Jin-Ho, C. Anticancer drug encapsulated in inorganic lattice can overcome drug resistance. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 9463–9469. [Google Scholar]
- Daemi, H.; Barikani, M. Synthesis and characterization of calcium alginate nanoparticles, sodium homopolymannuronate salt and its calcium nanoparticles. Sci. Iran. F 2012, 19, 2023–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ledeti, I.; Vlase, G.; Vlase, T.; Suta, L.M.; Todea, A.; Fulias, A. Selection of solid-state excipients for simvastatin dosage forms through thermal and nonthermal techniques. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 121, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlase, G.; Budiul, M.; Pătruţescu, C.; Albu, P.; Vlase, T. An extensive compatibility study of mycophenolate mofetil with different excipients by spectroscopic and thermoanalytical investigation techniques. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 131, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayarza, J.; Coello, Y.; Nakamatsu, J. SEM–EDS study of ionically cross-linked alginate and alginic acid bead formation. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2017, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martău, G.A.; Mihai, M.; Vodnar, D.C. The Use of Chitosan, Alginate, and Pectin in the Biomedical and Food Sector—Biocompatibility, Bioadhesiveness, and Biodegradability. Polymers 2019, 11, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]












| Composition. | Notation of Membranes | Membrane Appearance. | Composition | Notation of Membranes | Membrane Appearance. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium alginate, Glycerol | A |  | Sodium alginate, Glycerol, PVP | AGP |  |
| Sodium alginate, Glycerol + MTX | A-MTX |  | Sodium alginate, Glycerol, PVP + MTX | AGP-MTX |  |
| Sodium alginate, Glycerol, Tween 20 | AGT |  | Sodium alginate, Glycerol, Carbopol | AGC |  |
| Sodium alginate, Glycerol, Tween 20 + MTX | AGT-MTX |  | Sodium alginate, Glycerol, Carbopol+ MTX | AGC-MTX |  |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bajas, D.; Vlase, G.; Mateescu, M.; Grad, O.A.; Bunoiu, M.; Vlase, T.; Avram, C. Formulation and Characterization of Alginate-Based Membranes for the Potential Transdermal Delivery of Methotrexate. Polymers 2021, 13, 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010161
Bajas D, Vlase G, Mateescu M, Grad OA, Bunoiu M, Vlase T, Avram C. Formulation and Characterization of Alginate-Based Membranes for the Potential Transdermal Delivery of Methotrexate. Polymers. 2021; 13(1):161. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010161
Chicago/Turabian StyleBajas, Dorothea, Gabriela Vlase, Mădălina Mateescu, Oana Alexandra Grad, Mădălin Bunoiu, Titus Vlase, and Claudiu Avram. 2021. "Formulation and Characterization of Alginate-Based Membranes for the Potential Transdermal Delivery of Methotrexate" Polymers 13, no. 1: 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010161
APA StyleBajas, D., Vlase, G., Mateescu, M., Grad, O. A., Bunoiu, M., Vlase, T., & Avram, C. (2021). Formulation and Characterization of Alginate-Based Membranes for the Potential Transdermal Delivery of Methotrexate. Polymers, 13(1), 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010161