Synthesis Characterization of Platinum (IV) Complex Curcumin Backboned Polyprodrugs: In Vitro Drug Release Anticancer Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.3. Synthesis of Isocyanate Functionalized Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Monomethyl Ether (mPEG5k-NCO)
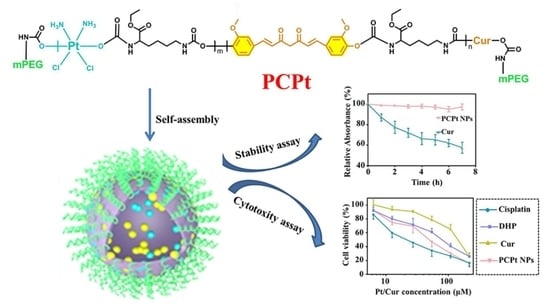
2.4. Synthesis of Cur and Pt(IV)-Backbone Prodrug Polymer [mPEG-poly(platinum-co-Cur)-mPEG (PCPt)]
2.5. Preparation and Characterization of PCPt Nanoparticles (PCPt NPs)
2.6. PCPt NPs Stability
2.7. In Vitro Drug Release Profiles
2.8. Cell Culture
2.9. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.10. In Vitro Cellular Uptake
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Synthesis of PCPt
3.2. Self-Assembly Behaviors
3.3. Stability Characterization
3.4. Pt and Cur Release Profile
3.5. In Vitro Cytotoxicity and Cellular Uptake
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Chang, Y.; Jian, H.; Zheng, R.; Wu, X.; Xu, K.; Wang, L.; Ma, X.; Li, X.; et al. Time-staggered delivery of erlotinib and doxorubicin by gold nanocages with two smart polymers for reprogrammable release and synergistic with photothermal therapy. Biomaterials 2019, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Han, J.; Shin, H.; Han, H.; Na, K.; Kim, H. Combination of chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy for cancer treatment with sonoporation effects. J. Control. Release 2018, 283, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, S.Y.; Cheng, Y.J.; Lei, Q.; Zhang, A.Q.; Zhang, X.Z. Combinational strategy for high-performance cancer chemotherapy. Biomaterials 2018, 171, 178–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, G.; Kim, M.G.; Kim, D.; Park, J.Y.; Oh, Y.K. Nanoformulation-based sequential combination cancer therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 115, 57–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.; Guo, S.; Lin, C.M.; Liu, Q.; Huang, L. Nanoformulations for combination or cascade anticancer therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 115, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawal, S.; Patel, M.M. Threatening cancer with nanoparticle aided combination oncotherapy. J. Control. Releas. 2019, 301, 76–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Ding, B.; Zhang, X.; Deng, X.; Deng, K.; Cheng, Z.; Xing, B.; Jin, D.; Ma, P.; Lin, J. Targeted iron nanoparticles with platinum-(IV) prodrugs and anti-EZH2 siRNA show great synergy in combating drug resistance in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials 2018, 155, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Sun, W.; Zhong, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y. Multistage Nanovehicle Delivery System Based on Stepwise Size Reduction and Charge Reversal for Programmed Nuclear Targeting of Systemically Administered Anticancer Drugs. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 4101–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, L.L.; Xu, X.D.; Bertrand, N.; Choi, W.I.; Yameen, B.; Shi, J.J.; Shah, V.; Mulvale, M.; MacLean, J.L.; et al. Hydrophobic Cysteine Poly(disulfide)-based Redox-Hypersensitive Nanoparticle Platform for Cancer Theranostics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 9218–9223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Q.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yan, D. A small molecule nanodrug consisting of amphiphilic targeting ligand-chemotherapy drug conjugate for targeted cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2016, 230, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qu, X.; Payne, G.F.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Ren, J.; Hong, H.; Liu, C. Biospecific Self-Assembly of a Nanoparticle Coating for Targeted and Stimuli-Responsive Drug Delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 1404–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Chen, H.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, L.; Trepout, S.; Guo, J.; Li, M.H. Fluorescent Polymersomes with Aggregation-Induced Emission. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 4025–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, P.; He, Z.; He, H.; Rong, W.; Li, J.; Zhou, D.; Huang, Y. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles with lactose-mediated targeting effect to deliver platinum(iv) prodrug for liver cancer therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 7591–7597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Deng, Q.; Kang, L.; Sun, Y.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. A Smart Nanoparticle-Laden and Remote-Controlled Self-Destructive Macrophage for Enhanced Chemo/Chemodynamic Synergistic Therapy. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 13894–13904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Lin, Y.; Yin, M.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Biomineralization inspired surface engineering of nanocarriers for pH-responsive, targeted drug delivery. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 1364–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wen, D.; Gu, Z. Cargo-encapsulated cells for drug delivery. Sci. Chin. Life Sci. 2020, 63, 599–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Gu, Z. Bioinspired and Biomimetic Nanomedicines. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltantabar, P.; Calubaquib, E.L.; Mostafavi, E.; Biewer, M.C.; Stefan, M.C. Enhancement of Loading Efficiency by Coloading of Doxorubicin and Quercetin in Thermoresponsive Polymeric Micelles. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Sun, M.; Cheng, X.; Xu, Y.; Lv, X.; Wang, X.; Tang, R. pH/redox dual-sensitive platinum (IV)-based micelles with greatly enhanced antitumor effect for combination chemotherapy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 541, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Chen, J.; Lin, L.; Wu, J.; Tian, H.; Chen, X. Pulmonary delivery by exploiting doxorubicin and cisplatin co-loaded nanoparticles for metastatic lung cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2019, 295, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Kuang, H.; Xie, Z.; Chen, X.; Jing, X.; Huang, Y. Novel hydroxyl-containing reduction-responsive pseudo-poly(aminoacid) via click polymerization as an efficient drug carrier. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 4488–4498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Wu, S.; Hu, C.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Fan, F.; Qin, Y.; Wang, C.; Sun, H.; Leng, X.; et al. Folate-targeted polymersomes loaded with both paclitaxel and doxorubicin for the combination chemotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Acta Biomater. 2017, 58, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hou, H.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z. Co-delivery of doxorubicin and paclitaxel by reduction/pH dual responsive nanocarriers for osteosarcoma therapy. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vossen, L.I.; Wedepohl, S.; Calderon, M. A Facile, One-Pot, Surfactant-Free Nanoprecipitation Method for the Preparation of Nanogels from Polyglycerol(-)Drug Conjugates that Can Be Freely Assembled for Combination Therapy Applications. Polymers 2018, 10, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baabur-Cohen, H.; Vossen, L.I.; Kruger, H.R.; Eldar-Boock, A.; Yeini, E.; Landa-Rouben, N.; Tiram, G.; Wedepohl, S.; Markovsky, E.; Leor, J.; et al. In vivo comparative study of distinct polymeric architectures bearing a combination of paclitaxel and doxorubicin at a synergistic ratio. J. Control. Release 2017, 257, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wu, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Luan, Y. Precise ratiometric loading of PTX and DOX based on redox-sensitive mixed micelles for cancer therapy. Colloids Surf. B 2017, 155, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Weitzhandler, I.; Bhattacharyya, J.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Qi, Y.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Chilkoti, A. Ring-Opening Polymerization of Prodrugs: A Versatile Approach to Prepare Well-Defined Drug-Loaded Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, H.; Murphy, C.J.; Zhang, B.; Shen, Y.; Van Kirk, E.A.; Murdoch, W.J.; Radosz, M. Curcumin polymers as anticancer conjugates. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 7139–7149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Liu, H.-Y.; Zha, J.-C.; Mao, X.-X.; Yin, J. Completely degradable backbone-type hydrogen peroxide responsive curcumin copolymer: Synthesis and synergistic anticancer investigation. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 4305–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Kuang, G.; He, S.; Lu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, D.; Huang, Y. Photoactivatable Prodrug-Backboned Polymeric Nanoparticles for Efficient Light-Controlled Gene Delivery and Synergistic Treatment of Platinum-Resistant Ovarian Cancer. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 3039–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, M.; Peng, H.; Hua, Q.; Ma, L.; Wang, B.; Wei, H. Facile Fabrication of 10-Hydroxycamptothecin-Backboned Amphiphilic Polyprodrug with Precisely Tailored Drug Loading Content for Controlled Release. Bioconjug. Chem. 2018, 29, 2239–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, Q.; Yin, L.; Ma, L.; Tang, L.; Cheng, J. Chain-shattering polymeric therapeutics with on-demand drug-release capability. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 6435–6439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, S.; Zhou, S.; Chen, S.; Lu, Q. Polyphosphazene-Based Drug Self-Framed Delivery System as a Universal Intelligent Platform for Combination Therapy against Multidrug-Resistant Tumors. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 2284–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, W.; Sui, M.; Tang, J.; Shen, Y. Platinum (IV)-coordinate polymers as intracellular reduction-responsive backbone-type conjugates for cancer drug delivery. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9136–9143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamae, I.; Morimoto, T.; Shima, H.; Shionyu, M.; Fujiki, H.; Yoneda-Kato, N.; Yokoyama, T.; Kanaya, S.; Kakiuchi, K.; Shirai, T.; et al. Curcumin Derivatives Verify the Essentiality of ROS Upregulation in Tumor Suppression. Molecules 2019, 24, 4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, H.; Guo, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Cisar, J.; Skoda, D.; Kuritka, I.; Guo, L.; et al. Structure-based design of charge-conversional drug self-delivery systems for better targeted cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2020, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, N.; Rawat, K.; Bohidar, H.B. Self-assembly of synthetic liposome-like curcumin nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 73677–73682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Gheybi, F.; Zamani, P.; Mashreghi, M.; Golmohammadzadeh, S.; Darban, S.A.; Badiee, A.; Jaafari, M.R. Preparation and characterization of stable nanoliposomal formulations of curcumin with high loading efficacy: In vitro and in vivo anti-tumor study. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y.; Cao, Y.X.; Zhou, X.; Wei, B. Delivery of folic acid-modified liposomal curcumin for targeted cervical carcinoma therapy. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 2205–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhao, P.; Wu, S.; Yang, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; He, C.; Zheng, C.; Li, K.; Ma, X.; et al. Cisplatin and curcumin co-loaded nano-liposomes for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 545, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.P.; Alvi, S.B.; Pemmaraju, D.B.; Singh, A.D.; Manda, S.V.; Srivastava, R.; Rengan, A.K. NIR triggered liposome gold nanoparticles entrapping curcumin as in situ adjuvant for photothermal treatment of skin cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 110, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, Y.; Xiao, H.; Xiong, H.; Wang, Z.; Ding, J.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Liang, X.J.; Zhou, D.; Huang, Y. Dual Drug Backboned Shattering Polymeric Theranostic Nanomedicine for Synergistic Eradication of Patient-Derived Lung Cancer. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, J.; Liang, X.J.; Chen, X.; Xiao, H.; Zhou, D.; Huang, Y. Tailoring Platinum(IV) Amphiphiles for Self-Targeting All-in-One Assemblies as Precise Multimodal Theranostic Nanomedicine. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 7272–7281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, H.; Chen, C.; Ren, K.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; He, L. Curcumin enhances cisplatin sensitivity of human NSCLC cell lines through influencing Cu-Sp1-CTR1 regulatory loop. Phytomedicine 2018, 48, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Zhou, D.; Huang, Y.; Li, J. Light-stimulus Dual-drug Responsive Nanoparticles for Photoactivated Therapy Using Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2018, 34, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolic, M.S.; Krack, M.; Aleksandrovic, V.; Kornowski, A.; Forster, S.; Weller, H. Tailor-made ligands for biocompatible nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 6577–6580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Kuang, G.; Liu, S.; Zhou, D.; Chen, X.; Jing, X.; Huang, Y. Pt(iv) prodrug-backboned micelle and DCA loaded nanofibers for enhanced local cancer treatment. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 2115–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Asghar, S.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, M.; Huang, L.; Ye, J.; Ping, Q.; Xiao, Y. The effect of the molecular weight of hyaluronic acid on the physicochemical characterization of hyaluronic acid-curcumin conjugates and in vitro evaluation in glioma cells. Colloids Surf. B 2018, 165, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Zhao, C.; Yan, L.; Qi, R.; Jing, X.; Wang, Z. Sensitizing nanoparticle based platinum(IV) drugs by curcumin for better chemotherapy. Colloids Surf. B 2016, 145, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wen, W.; Jia, Y.G.; Liu, S.; Guo, J. pH-Responsive Micelles Assembled by Three-Armed Degradable Block Copolymers with a Cholic Acid Core for Drug Controlled-Release. Polymers 2019, 11, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, X. Binding, stability, and antioxidant activity of curcumin with self-assembled casein–dextran conjugate micelles. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 3295–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sauraj Kumar, S.U.; Kumar, V.; Priyadarshi, R.; Gopinath, P.; Negi, Y.S. pH-responsive prodrug nanoparticles based on xylan-curcumin conjugate for the efficient delivery of curcumin in cancer therapy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 188, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Polymer | Number-Average Molecular Weight (kDa) | Molecular Weight Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| PCPt | 17.4 | 1.51 |
| Nanoparticles (NP) | Average Diameter (nm) | PDI |
|---|---|---|
| PCPt NPs incubated in PBS 7.4 for 0 h | 103 | 0.19 |
| PCPt NPs incubated in PBS 7.4 for 72 h | 112 | 0.20 |
| PCPt NPs incubated in PBS 5.0 for 0 h | 127 | 0.22 |
| PCPt NPs incubated in PBS 5.0 for 72 h | 297 | 034 |
| PCPt NPs incubated with 10 mM SA for 0 h | 118 | 0.22 |
| PCPt NPs incubated with 10 mM SA for 72 h | 195 | 0.53 |
| Cell Line | Cisplatin | DHP | Cur | PCPt NPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 of (μM) | IC50 of (μM) | IC50 of (μM) | IC50 of (μM) | |
| HeLa | 27.1 | 54.1 | 108.2 | 53.9 |
| A549 | 26.7 | 84.8 | 125.1 | 54.2 |
| A549/DDP | >216 | >216 | >216 | 55.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, C.; Xue, X.; Xu, B.; Li, T.; Chen, Z. Synthesis Characterization of Platinum (IV) Complex Curcumin Backboned Polyprodrugs: In Vitro Drug Release Anticancer Activity. Polymers 2021, 13, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010067
Zhang H, Wu Y, Xu X, Chen C, Xue X, Xu B, Li T, Chen Z. Synthesis Characterization of Platinum (IV) Complex Curcumin Backboned Polyprodrugs: In Vitro Drug Release Anticancer Activity. Polymers. 2021; 13(1):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010067
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Honglei, Yanjuan Wu, Xiao Xu, Chen Chen, Xiukun Xue, Ben Xu, Tianduo Li, and Zhaowei Chen. 2021. "Synthesis Characterization of Platinum (IV) Complex Curcumin Backboned Polyprodrugs: In Vitro Drug Release Anticancer Activity" Polymers 13, no. 1: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010067
APA StyleZhang, H., Wu, Y., Xu, X., Chen, C., Xue, X., Xu, B., Li, T., & Chen, Z. (2021). Synthesis Characterization of Platinum (IV) Complex Curcumin Backboned Polyprodrugs: In Vitro Drug Release Anticancer Activity. Polymers, 13(1), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010067