Affordable Magnetic Hydrogels Prepared from Biocompatible and Biodegradable Sources
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. FTIR Analysis
2.2.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.2.3. Scanning Electron Spectroscopy (SEM)
2.2.4. Thermogravimetric (TG) Analyses
2.2.5. Magnetic Properties
2.2.6. Test of Swelling Properties
2.2.7. Hydrogels Stability Studies
2.3. Cellulose Oxidation
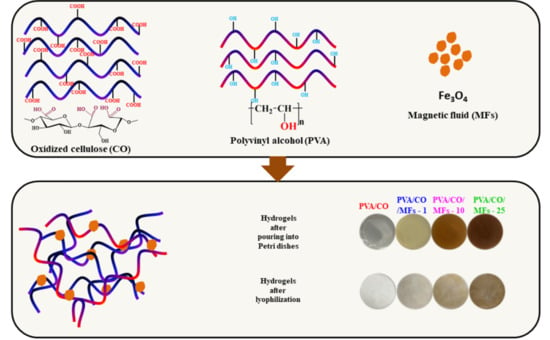
2.4. Fabrication of PVA/CO/MFs Hydrogels
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FTIR Analysis
3.2. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
3.3. Morphology of Magnetic Hydrogels
3.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TG)
3.5. Hydrogels Stability under Various Environments
3.6. Magnetic Properties (VSM) of the as Prepared Magnetic Hydrogels
3.7. Swelling Properties of Magnetic Hydrogels
4. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, C.; Zhang, L. Cellulose-based hydrogels: Present status and application prospects. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Lu, T.; Zhang, P.; Jing, X. Preparation and antibacterial effects of PVA-PVP hydrogels containing silver nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 103, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abobatta, W. Impact of hydrogel polymer in agricultural sector. Adv. Agric. Environ. Sci. Open Access 2018, 1, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Tang, X.; Liu, S.; Yang, Y.; Shen, X.; Gao, C. Laponite crosslinked starch/polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels by freezing/thawing process and studying their cadmium ion absorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.; Peng, B.; Shen, C. Synthesis of F127/PAA hydrogels for removal of heavy metal ions from organic wastewater. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2018, 167, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuai, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Yang, W.; Peng, S.; Feng, P. Surface modification of nanodiamond: Toward the dispersion of reinforced phase in poly-L-lactic acid scaffolds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Wu, P.; Gao, C.; Yang, Y.; Guo, W.; Yang, W.; Shuai, C. A Multimaterial Scaffold With Tunable Properties: Toward Bone Tissue Repair. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, C.; Xu, Y.; Feng, P.; Wang, G.; Xiong, S.; Peng, S. Antibacterial polymer scaffold based on mesoporous bioactive glass loaded with in situ grown silver. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 374, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; He, J.; Peng, S.; Gao, C.; Zhao, Z.; Xiong, S.; Shuai, C. Characterizations and interfacial reinforcement mechanisms of multicomponent biopolymer based scaffold. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 100, 809–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liao, J.; Wang, T.; Sun, W.; Tong, Z. Polyampholyte Hydrogels with pH Modulated Shape Memory and Spontaneous Actuation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1707245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biliuta, G.; Coseri, S. Magnetic cellulosic materials based on TEMPO-oxidized viscose fibers. Cellulose 2016, 23, 3407–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.I.; Bercea, M.; Avadanei, M.; Lisa, G.; Biliuta, G.; Coseri, S. Green route for the fabrication of self-healable hydrogels based on tricarboxy cellulose and poly(vinyl alcohol). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, R.I.; Culica, M.E.; Biliuta, G.; Bercea, M.; Gherman, S.; Zavastin, D.; Ochiuz, L.; Avadanei, M.; Coseri, S. Physical hydrogels of oxidized polysaccharides and poly(vinyl alcohol) forwound dressing applications. Materials (Basel). 2019, 12, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coseri, S.; Biliuta, G.; Zemljič, L.F.; Srndovic, J.S.; Larsson, P.T.; Strnad, S.; Kreže, T.; Naderi, A.; Lindström, T. One-shot carboxylation of microcrystalline cellulose in the presence of nitroxyl radicals and sodium periodate. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 85889–85897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, T.; Pöhler, E.; Geiger, T. Cellulose Fibrils for Polymer Reinforcement. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Peng, Y. Research of a PVA composite ultrafiltration membrane used in oil-in-water. Desalination 2007, 204, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieger, M.; Kantorová, M.; Prell, A.; Řezanka, T.; Votruba, J. Biodegradable plastics from renewable sources. Folia Microbiol. (Praha). 2003, 48, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Liu, H. Cellulose nanofiber reinforced poly(vinyl alcohol) composite film with high visible light transmittance. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 1638–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, T.; Drzal, L.T. Preparation and properties of microfibrillated cellulose polyvinyl alcohol composite materials. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodkate, N.; Rutnakornpituk, M. Multi-responsive magnetic microsphere of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/carboxymethylchitosan hydrogel for drug controlled release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, A.; Sohrabi, A.; Poole, K.; Seidlits, S.; Di Carlo, D. A 3D Magnetic Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel for Magnetomechanical Neuromodulation of Primary Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowser, D.A.; Moore, M.J. Biofabrication of neural microphysiological systems using magnetic spheroid bioprinting. Biofabrication 2019, 12, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Wei, X.; Wan, Y.; Lin, X.; Wang, Z.; Huang, P. 3D printing of hydrogel scaffolds for future application in photothermal therapy of breast cancer and tissue repair. Acta Biomater. 2019, 92, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alammar, A.; Park, S.H.; Ibrahim, I.; Deepak, A.; Holtzl, T.; Dumée, L.F.; Lim, H.N.; Szekely, G. Architecting neonicotinoid-scavenging nanocomposite hydrogels for environmental remediation. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 21, 100878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Song, Z.; Li, S.; Tat Thang, N.; Gao, X.; Gong, X.; Guo, M. Facile one-pot synthesis of self-assembled nitrogen-doped carbon dots/cellulose nanofibril hydrogel with enhanced fluorescence and mechanical properties. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 3296–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lu, H.; Chu, J.; Ma, J.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ni, Y. Lignin-Directed Control of Silver Nanoparticles with Tunable Size in Porous Lignocellulose Hydrogels and Their Application in Catalytic Reduction. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 12655–12663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, D.; Vékás, L.; Avdeev, M.V.; Marinicǎ, O.; Socoliuc, V.; Bǎlǎsoiu, M.; Garamus, V.M. Sterically stabilized water based magnetic fluids: Synthesis, structure and properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 311, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serkis, M.; Špírková, M.; Poręba, R.; Hodan, J.; Kredatusová, J.; Kubies, D. Hydrolytic stability of polycarbonate-based polyurethane elastomers tested in physiologically simulated conditions. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 119, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel-da-Silva, A.L.; Moreira, J.; Neto, R.; Estrada, A.C.; Gil, A.M.; Trindade, T. Impact of magnetic nanofillers in the swelling and release properties of k-carrageenan hydrogel nanocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 328–335. [Google Scholar]
- Ritger, P.L.; Peppas, N.A. A simple equation for description of solute release II. Fickian and anomalous release from swellable devices. J. Control. Release 1987, 5, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sample | DTG Peak (°C) | Residual Mass (%) |
|---|---|---|
| PVA/CO | 296.5 | 9.13 |
| PVA/CO/MFs-1 | 296.6 | 8.29 |
| PVA/CO/MFs-10 | 294.3 | 9.39 |
| PVA/CO/MFs-25 | 291.7 | 13.21 |
| MFs | 67.20 |
| Magnetic Hydrogels | Initial MF Load [wt %] | Sample Mass [g] | Msat [emu/g] | μsat [memu] | MNP Organosol Load [wt %] | MNP Load [wt %] | Final MF Load [wt %] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVA/CO/MFs-1 | 1 | 0.0064 | 0.0539 | 0.345 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.85 |
| PVA/CO/MFs-10 | 10 | 0.0068 | 0.3646 | 2.479 | 0.93 | 0.64 | 6.05 |
| PVA/CO/MFs-25 | 25 | 0.0079 | 0.9147 | 7.226 | 2.37 | 1.36 | 16.70 |
| MNP Organosol | - | 0.1175 | 39.4939 | 4633.740 | - | - | - |
| Hydrogels | R2 | k | n | Swelling Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVA/CO | 0.9962 | 0.1736 | 0.2649 | Fickian diffusion |
| PVA/CO/MFs-1 | 0.9951 | 0.1780 | 0.2898 | Fickian diffusion |
| PVA/CO/MFs-10 | 0.9951 | 0.2231 | 0.2293 | Fickian diffusion |
| PVA/CO/MFs-25 | 0.9934 | 0.2758 | 0.2095 | Fickian diffusion |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baron, R.I.; Biliuta, G.; Socoliuc, V.; Coseri, S. Affordable Magnetic Hydrogels Prepared from Biocompatible and Biodegradable Sources. Polymers 2021, 13, 1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111693
Baron RI, Biliuta G, Socoliuc V, Coseri S. Affordable Magnetic Hydrogels Prepared from Biocompatible and Biodegradable Sources. Polymers. 2021; 13(11):1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111693
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaron, Raluca Ioana, Gabriela Biliuta, Vlad Socoliuc, and Sergiu Coseri. 2021. "Affordable Magnetic Hydrogels Prepared from Biocompatible and Biodegradable Sources" Polymers 13, no. 11: 1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111693
APA StyleBaron, R. I., Biliuta, G., Socoliuc, V., & Coseri, S. (2021). Affordable Magnetic Hydrogels Prepared from Biocompatible and Biodegradable Sources. Polymers, 13(11), 1693. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111693