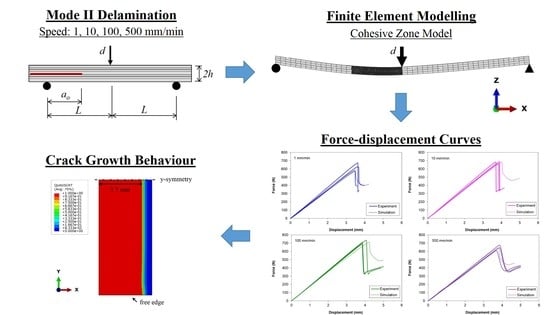
Displacement Rate Effects on the Mode II Shear Delamination Behavior of Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Specimens
2.2. Mode II Interlaminar Fracture Toughness Test
2.3. Morphology Study
2.4. Data Reduction Method
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
3.1. Force-Displacement Curves
3.2. Mode II Interlaminar Fracture Toughness
4. Numerical Modeling
4.1. Cohesive Element
4.2. Finite Element Model
4.3. Cohesive Properties
4.4. Numerical Analyses
5. Conclusions
- Mode II fracture toughness GIIC increases up to 45% at displacement rate 100 mm/min before it drops slightly at 500 mm/min. In general, a higher displacement rate has a positive effect on GIIC of the unidirectional carbon/epoxy composites used in this study.
- Surface morphology analyses show that adhesive failure (fiber/matrix debonding) dominates at displacement rate 1 mm/min. At the cases of 10–500 mm/min, similar rough surfaces with matrix hackles are observed, hence the similar magnitude of GIIC among them. This difference in fracture morphology is postulated to cause the increment in GIIC at higher displacement rates.
- The modified rate dependent model (Equation (4)) proposed in this study is found to fit the data from the current study and literature considerably well. Most of the data has R2 larger than 0.8. So it can be used to describe the mixed effect of loading rate on fracture toughness.
- The GIIC value measured from the experiment or given by Equation (4) can be used as the input parameter in the cohesive element model to predict mode II delamination. Numerical analyses indicate that before the peak load is attained, none of the element has been completely damaged. However, once the peak load is reached, total damage is detected concurrently for all elements leading to an abrupt drop in the load and the crack jumps instantaneously. This explains the occurrence of unstable crack propagation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nash, N.; Ray, D.; Young, T.; Stanley, W. The influence of hydrothermal conditioning on the Mode-I, thermal and flexural properties of Carbon/Benzoxazine composites with a thermoplastic toughening interlayer. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 76, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koloor, S.R.; Tamin, M. Mode-II interlaminar fracture and crack-jump phenomenon in CFRP composite laminate materials. Compos. Struct. 2018, 204, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johar, M.; Israr, H.A.; Low, K.O.; Wong, K.J. Numerical simulation methodology for mode II delamination of quasi-isotropic quasi-homogeneous composite laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 2017, 51, 3955–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koloor, S.S.R.; Karimzadeh, A.; Yidris, N.; Petrů, M.; Ayatollahi, M.R.; Tamin, M.N. An Energy-Based Concept for Yielding of Multidirectional FRP Composite Structures Using a Mesoscale Lamina Damage Model. Polymer 2020, 12, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahdin, A.; Mezeix, L.; Bouvet, C.; Morlier, J.; Gourinat, Y. Monitoring the effects of impact damages on modal parameters in carbon fiber entangled sandwich beams. Eng. Struct. 2009, 31, 2833–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, M.A.A.-S.B.; Laia, W.L.; Saeedipourb, H.; Goha, K.L. Cost-effective and efficient resin-injection device for repairing damaged composites. Reinf. Plast. 2019, 63, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, M. Measuring the rate-dependent mode I fracture toughness of composites—A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 81, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantwell, W.J.; Blyton, M. Influence of loading rate on the interlaminar fracture properties of high performance composites—A review. Appl. Mech. Rev. 1999, 52, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasaee, M.; Mohamed, G.; Pellegrino, A.; Petrinic, N.; Hallett, S.R. Strain rate dependence of mode II delamination resistance in through thickness reinforced laminated composites. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2017, 107, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marzi, S.; Rauh, A.; Hinterhölzl, R.M. Fracture mechanical investigations and cohesive zone failure modelling on automotive com-posites. Compos. Struct. 2014, 111, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantwell, W. The Influence of Loading Rate on the Mode II Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Composite Materials. J. Compos. Mater. 1997, 31, 1364–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusaka, T.; Kurokawa, T.; Hojo, M.; Ochiai, S. Evaluation of Mode II Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Composite Laminates under Impact Loading. Key Eng. Mater. 1997, 141–143, 477–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, J.; Marques, E.; Campilho, R.; da Silva, L.F. Mode II fracture toughness of CFRP as a function of temperature and strain rate. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 114, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabala, H.; Aretxabaleta, L.; Castillo, G.; Aurrekoetxea, J. Dynamic 4 ENF test for a strain rate dependent mode II interlaminar fracture toughness characterization of unidirec-tional carbon fibre epoxy composites. Polym. Test 2016, 55, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, B.R.K.; Dear, J.P.; Kinloch, A.; MacGillivray, H.; Wang, Y.; Williams, J.G.; Yayla, P. The failure of fibre composites and adhesively bonded fibre composites under high rates of test. J. Mater. Sci. 1996, 31, 4467–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Verdiere, M.C.; Skordos, A.; Walton, A.; May, M. Influence of loading rate on the delamination response of untufted and tufted carbon epoxy non-crimp fabric composites/Mode II. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2012, 96, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D7905. Standard Test. Method for Determination of the Mode II Interlaminar Fracture Toughness of Unidirectional Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composites; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, T.P.; Koloor, S.; Djuansjah, J.; Kadir, M.A. Assessment of compressive failure process of cortical bone materials using damage-based model. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 66, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimian Koloor, S.S.; Karimzadeh, A.; Tamin, M.N.; Abd Shukor, M.H. Effects of sample and indenter configurations of nanoindentation experiment on the mechanical behavior and properties of ductile materials. Metals 2018, 8, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koloor, S.; Abdullah, M.; Tamin, M.; Ayatollahi, M. Fatigue damage of cohesive interfaces in fiber-reinforced polymer composite laminates. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 183, 107779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koloor, S.; Abdul-Latif, A.; Tamin, M.N. Mechanics of composite delamination under flexural loading. Key Eng. Mater. 2011, 462–463, 726–731. [Google Scholar]
- Low, K.; Teng, S.; Johar, M.; Israr, H.; Wong, K. Mode I delamination behaviour of carbon/epoxy composite at different displacement rates. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2019, 176, 107293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, G.R.; Kies, J.A. Critical energy rate analysis of fracture strength. Weld. J. Res. Suppl. 1954, 33, 193–198. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, J.J.M.; Marques, E.A.S.; Campilho, R.; da Silva, L.F.M. Mode I fracture toughness of CFRP as a function of temperature and strain rate. J. Compos. Mater. 2016, 51, 3315–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compston, P.; Jar, P.-Y.; Davies, P. Matrix effect on the static and dynamic interlaminar fracture toughness of glass-fibre marine composites. Compos. Part B: Eng. 1998, 29, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compston, P.; Jar, P.-Y.; Burchill, P.; Takahashi, K. The effect of matrix toughness and loading rate on the mode-II interlaminar fracture toughness of glass-fibre/vinyl-ester composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2001, 61, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, B.; Kumar, M.; Soffa, M. Influence of mode ratio and hygrothermal condition on the delamination toughness of a thermoplastic particulate interlayered carbon/epoxy composite. Compos. Part A: Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2009, 40, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maikuma, H.; Gillespie, J.W., Jr.; Wilkins, D.J. Mode II Interlaminar Fracture of the Center Notch Flexural Specimen under Impact Loading. J. Compos. Mater. 1990, 24, 124–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiley, A.; Pipes, R. Rate sensitivity of mode II interlaminar fracture toughness in graphite/epoxy and graphite/PEEK composite materials. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1987, 29, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, W.; Seah, L.K.; Chai, G.B. Delamination growth behavior of a woven E-glass/bismaleimide composite in seawater environment. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2016, 106, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, N.H.; Young, T.M.; Stanley, W.F. The influence of a thermoplastic toughening interlayer and hydrothermal conditioning on the Mode-II interlaminar fracture toughness of Carbon/Benzoxazine composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 81, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purslow, D. Matrix fractography of fibre-reinforced epoxy composites. Composites 1986, 17, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, L.; Cantwell, W.J. Temperature and loading rate effects in the mode II interlaminar fracture behavior of carbon fiber rein-forced PEEK. Polym. Compos. 2001, 22, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camanho, P.; Davila, C.G.; De Moura, M.F. Numerical Simulation of Mixed-Mode Progressive Delamination in Composite Materials. J. Compos. Mater. 2003, 37, 1415–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, B.F.; Goutianos, S.; Jacobsen, T.K. Strength scaling of adhesive joints in polymer–matrix composites. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2009, 46, 741–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mollón, V.; Bonhomme, J.; Elmarakbi, A.; Argüelles, A.; Vina-Olay, J.A. Finite element modelling of mode I delamination specimens by means of implicit and explicit solvers. Polym. Test. 2012, 31, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turon, A.; Dávila, C.; Camanho, P.; Costa, J. An engineering solution for mesh size effects in the simulation of delamination using cohesive zone models. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2007, 74, 1665–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, P.W.; Hallett, S.R. Cohesive zone length in numerical simulations of composite delamination. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2008, 75, 4774–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harper, P.W.; Sun, L.; Hallett, S.R. A study on the influence of cohesive zone interface element strength parameters on mixed mode behaviour. Compos. Part A: Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2012, 43, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soto, A.; González, E.; Maimí, P.; Turon, A.; De Aja, J.S.; De La Escalera, F. Cohesive zone length of orthotropic materials undergoing delamination. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2016, 159, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, D.; Clyne, T.W. An Introduction to Composite Materials, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Fei, B. Simulation of delamination growth in multidirectional laminates under mode I and mixed mode I/II loadings using cohe-sive elements. Compos. Struct. 2014, 116, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turon, A.; Camanho, P.P.; Costa, J.; Renart, J. Accurate simulation of delamination growth under mixed-mode loading using cohesive elements: Definition of inter-laminar strengths and elastic stiffness. Compos. Struct. 2010, 92, 1857–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, L.; Botsis, J.; Gmür, T.; Humbert, L. Bridging tractions in mode I delamination: Measurements and simulations. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 2350–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johar, M.; Wong, K.J.; Tamin, M.N. Mixed-mode delamination failures of quasi-isotropic quasi-homogeneous carbon/epoxy laminated composite. In Failure Analysis and Prevention; Ali, A., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia; pp. 33–45. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johar, M.; Chong, W.; Kang, H.; Wong, K. Effects of moisture absorption on the different modes of carbon/epoxy composites delamination. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2019, 165, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannathan, N.; Chandra, A.R.A.; Manjunatha, C.M. Onset-of-growth behavior of mode II delamination in a carbon fiber compo-site under spectrum fatigue loads. Compos. Struct. 2015, 132, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, B.N.J. A simple model for viscoelastic crack propagation. Eur. Phys. J. E 2021, 44, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manikkavel, A.; Kumar, V.; Lee, D.-J. Simple fracture model for an electrode and interfacial crack in a dielectric elastomer under tensile loading. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2020, 108, 102626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| E11 (GPa) | E2 (GPa) | G12 (GPa) | G13 (GPa) | G23 (GPa) | ν12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 103 | 6.7 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 2.5 | 0.34 |
| v (mm/min) | 1 | 10 | 100 | 500 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GIIC (N/mm) | 1.35 ± 0.17 | 1.80 ± 0.07 | 1.96 ± 0.14 | 1.62 ± 0.17 |
| Label (Figure 5) | m | ζ | R2 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current study | 3.29 × 10−1 | 1.36 × 10−4 | 0.7210 | / |
| Yasaee (Control) | 1.72 × 10−3 | 2.08 | 0.8095 | [9] |
| Yasaee (Z-pin) | 3.68 × 10−9 | 7.53 | 0.9570 | [9] |
| Colin de Verdiere (Tufted) | 2.14 × 10−3 | 1.88 | 0.8448 | [16] |
| Cantwell (AS4 C/PEEK) | 9.14 × 10−2 | 0.56 | 0.9061 | [11] |
| Cantwell (PW C/E) | 3.27 × 10−1 | 9.10 × 10−2 | 0.8384 | [11] |
| Cantwell (UD C/E) | 4.72 × 10−2 | 0.64 | 0.6883 | [11] |
| Blackman (AS4 C/PEEK) | −5.79 × 10−9 | 6.76 | 0.5117 | [15] |
| v (mm/min) | GIC (N/m) a | GIIC (N/m) | tu,n (MPa) a | tu,s (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 245.03 | 1349.26 | 35 | 82 |
| 10 | 202.59 | 1795.78 | 35 | 104 |
| 100 | 275.06 | 1962.69 | 35 | 93 |
| 500 | 258.59 | 1623.85 | 35 | 88 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Low, K.O.; Johar, M.; Israr, H.A.; Gan, K.W.; Rahimian Koloor, S.S.; Petrů, M.; Wong, K.J. Displacement Rate Effects on the Mode II Shear Delamination Behavior of Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111881
Low KO, Johar M, Israr HA, Gan KW, Rahimian Koloor SS, Petrů M, Wong KJ. Displacement Rate Effects on the Mode II Shear Delamination Behavior of Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Composites. Polymers. 2021; 13(11):1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111881
Chicago/Turabian StyleLow, Kean Ong, Mahzan Johar, Haris Ahmad Israr, Khong Wui Gan, Seyed Saeid Rahimian Koloor, Michal Petrů, and King Jye Wong. 2021. "Displacement Rate Effects on the Mode II Shear Delamination Behavior of Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Composites" Polymers 13, no. 11: 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111881
APA StyleLow, K. O., Johar, M., Israr, H. A., Gan, K. W., Rahimian Koloor, S. S., Petrů, M., & Wong, K. J. (2021). Displacement Rate Effects on the Mode II Shear Delamination Behavior of Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Composites. Polymers, 13(11), 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111881