Tuning the Adhesive Properties of Soy Protein Wood Adhesives with Different Coadjutant Polymers, Nanocellulose and Lignin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
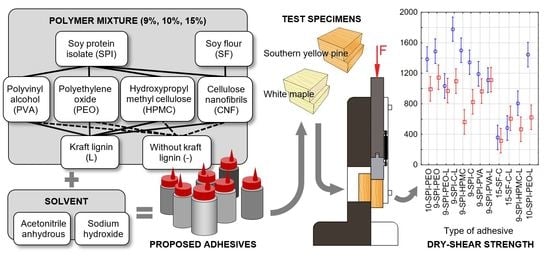
2.2. Preparation of Protein Adhesives
2.3. Basic Properties
2.4. Preparation of Testing Specimens
2.5. Preparation of Control Adhesive: Commercial Urea Formaldehyde Adhesive
2.6. Moisture and Density of Wood Specimens
2.7. Shear Strength Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rheology of Adhesive Formulations
3.2. Effect of Type of Wood Species
3.3. Effect of Protein Type and Total Solid Content
3.4. Performance of Soy-Based Adhesives: Effect of Coadjutant Polymer
3.5. Effect of Kraft Lignin Addition
3.6. Stability and Bond Line Color of Proposed Protein Adhesives
3.7. Performance of Proposed Adhesives with Relation to UF Adhesive
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wood Adhesives Market Size, Share & Trend Analysis Report, Grand View Research. 2019. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/wood-adhesives-market (accessed on 15 October 2020).
- Solt, P.; Konnerth, J.; Gindl-altmutter, W.; Kantner, W. Technological performance of formaldehyde-free adhesive alternatives for particleboard industry. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2019, 94, 99–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzi, A.; Papadopoulos, A.N.; Policardi, F. Wood composites and their polymer binders. Polymers 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Agency. Formaldehyde Emission Standards for Composite Wood Products. 2016. Available online: https://beta.regulations.gov/document/EPA-HQ-OPPT-2016-0461-0001 (accessed on 15 October 2020).
- Bekhta, P.; Sedliačik, J.; Noshchenko, G.; Kačík, F.; Bekhta, N. Characteristics of beech bark and its effect on properties of UF adhesive and on bonding strength and formaldehyde emission of plywood panels. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2021, 79, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, J.F.; Erhan, S.Z.; Sharma, B.K.; Johnson, L.A.; Myers, D.J. Biobased products from Soybeans. In Soybeans: Chemistry, Production Processing, and Utilization; Johnson, L.A., White, P.J., Galloway, R., Eds.; AOCS Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 2008; pp. 539–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frihart, C.R. Wood adhesives: Past, present, and future. For. Prod. J. 2015, 65, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keimel, F.A. Historical Development of Adhesives and Adhesive Bonding. In Handbook of Adhesive Technology; Pizzi, A., Mittal, K.L., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 1–12. ISBN 0-8247-0986-1. [Google Scholar]
- Salas, C.; Rojas, O.J.; Lucia, L.A.; Hubbe, M.A.; Genzer, J. Adsorption of Glycinin and β-Conglycinin on Silica and Cellulose: Surface Interactions as a Function of enaturation, pH, and Electrolytes. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frihart, C.R.; Hunt, C.G.; Birkeland, M.J. Soy Proteins as Wood Adhesives. In Recent Advances in Adhesion Science and Technology; Gutowski, W.V., Dodiuk, H., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 277–291. ISBN 978-90-04-20173-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz, L.; Birkeland, M.; Daurio, C.; Frihart, C.R. Soy Flour Adhesive Strength Compared with That of Purified Soy Proteins. For. Prod. J. 2015, 65, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodaran, S.; Zhu, D. A Formaldehyde-Free Water-Resistant Soy Flour-Based Adhesive for Plywood. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2016, 93, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frihart, C.R. Influence of Soy Type on Wood Bonding Performance. In Proceedings of the 34th Annual Meeting of the Adhesion Society; Adhesion Society: Savannah, GA, USA, 2011; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.H.; Li, X.P.; Zhang, X.Q. A Soy-based Adhesive from Basic Modification. Pigment Resin Technol. 2008, 37, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vnučec, D.; Kutnar, A.; Goršek, A. Soy-based adhesives for wood-bonding—A review. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2017, 31, 910–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiarachchy, N.S.; Kalapathy, U.; Myers, D.J. Alkali-Modified Soy Protein with Improved Adhesive and Hydrophobic Properties. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1995, 72, 1461–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambuth, A.L. Protein Adhesives for Wood. In Handbook of Adhesive Technology; Pizzi, A., Mittal, K.L., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 457–477. ISBN 0-8247-0986-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kalapathy, U.; Hettiarachchy, N.S.; Myers, D.; Hanna, M.A. Modification of Soy Proteins and their Ahesives Properties on Woods. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1995, 72, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Sun, X.S. Thermal Properties and Adhesiveness of Soy Protein Modified with Cationic Detergent. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2005, 82, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frihart, C.R.; Coolidge, T.; Mock, C.; Valle, E. High Bonding Temperatures Greatly Improve Soy Adhesive Wet Strength. Polymers 2016, 8, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.S. Soy Protein Adhesives. In Bio-Based Polymers and Composites; Wool, R.P., Sun, X.S., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2005; pp. 327–368. ISBN 978-0-12-763952-9. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.T.; Netravali, A.N. Performance of protein-based wood bioadhesives and development of small-scale test method for characterizing properties of adhesive-bonded wood specimens. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2013, 27, 2083–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Sun, X. Adhesive Properties of Soy Proteins Modified by Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate and Sodium Dodecylbenzene Sulfonate. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2000, 77, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wescott, J.M.; Frihart, C.R. Competitive Soybean Flour/Adhesives for Oriented Strandboard. In Proceedings of the 38th International Wood Composites Symposium; Pullman, Wash: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; pp. 199–206. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Luo, J.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Gao, Q.; Chen, H. An eco-friendly wood adhesive from soy protein and lignin: Performance properties. R. Soc. Chem. 2015, 5, 100849–100855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradyawong, S.; Qi, G.; Li, N.; Sun, X.S.; Wang, D. Adhesion properties of soy protein adhesives enhanced by biomass lignin. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2017, 75, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dongre, P.; Driscoll, M.; Amidon, T.; Bujanovic, B. Lignin-Furfural Based Adhesives. Energies 2015, 8, 7897–7914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Kelley, S.S.; Venditti, R.A. Lignin-Based Thermoplastic Materials. ChemSusChem 2016, 9, 770–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younesi-Kordkheili, H.; Kazemi-Najafi, S.; Eshkiki, R.B.; Pizzi, A. Improving urea formaldehyde resin properties by glyoxalated soda bagasse lignin. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2015, 73, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arias, A.; González-García, S.; González-Rodríguez, S.; Feijoo, G.; Moreira, M.T. Cradle-to-gate Life Cycle Assessment of bio-adhesives for the wood panel industry. A comparison with petrochemical alternatives. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 140357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dababi, I.; Gimello, O.; Elaloui, E.; Quignard, F. Organosolv Lignin-Based Wood Adhesive. Influence of the Lignin Extraction Conditions on the Adhesive Performance. Polymers 2016, 8, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Gupta, A.; Beg, M.D.H.; Chua, G.K.; Kumar, A. Fabrication of medium density fibreboard from enzyme treated rubber wood (Hevea brasiliensis) fibre and modified organosolv lignin. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2013, 44, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domínguez, J.C.; Oliet, M.; Alonso, M.V.; Rojo, E.; Rodríguez, F. Structural, thermal and rheological behavior of a bio-based phenolic resin in relation to a commercial resol resin. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 42, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmilä, V.; Adamopoulos, S.; Hosseinpourpia, R.; Ahmed, S.A. Ammonium lignosulfonate adhesives for particleboards with pMDI and furfuryl alcohol as crosslinkers. Polymers 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antov, P.; Savov, V.; Krišt’ák, L.; Réh, R.; Mantanis, G.I. Eco-friendly, high-density fiberboards bonded with urea-formaldehyde and ammonium lignosulfonate. Polymers 2021, 13, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antov, P.; Krišt’ák, L.; Réh, R.; Savov, V.; Papadopoulos, A.N. Eco-friendly fiberboard panels from recycled fibers bonded with calcium lignosulfonate. Polymers 2021, 13, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahendran, A.R.; Wuzella, G.; Kandelbauer, A. Thermal Characterization of Kraft Lignin Phenol-Formaldehyde Resin for Paper Impregnation. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2010, 24, 1553–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Zhang, P.; Wolcott, M.P.; Zhang, J.; Hiscox, W.C.; Zhang, X. A Novel and Formaldehyde-Free Preparation Method for Lignin Amine and Its Enhancement for Soy Protein Adhesive. J. Polym. Environ. 2017, 25, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Peshkova, S.; Geng, X. Investigation of soy protein-kymene® adhesive systems for wood composites. JAOCS J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2004, 81, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mansouri, N.E.; Pizzi, A.; Salvadó, J. Lignin-based wood panel adhesives without formaldehyde. Holz Roh Werkst. 2007, 65, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xi, X.; Pizzi, A.; Fredon, E.; Du, G.; Gerardin, C.; Amirou, S. Oxidized demethylated lignin as a bio-based adhesive for wood bonding. J. Adhes. 2020, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.N.; Kilgore, K.; Ford, C.; Fortier, C.; Dowd, M.K.; He, Z. Cottonseed protein-based wood adhesive reinforced with nanocellulose. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2019, 33, 1357–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilbao-Sáinz, C.; Avena-Bustillos, R.J.; Wood, D.F.; Williams, T.G.; Mchugh, T.H. Composite edible films based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose reinforced with microcrystalline cellulose nanoparticles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3753–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega-Lugo, A.C.; Lim, L.T. Electrospinning of Soy Protein Isolate Nanofibers. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 2008, 2, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, C.; Ago, M.; Lucia, L.A.; Rojas, O.J. Synthesis of soy protein-lignin nanofibers by solution electrospinning. React. Funct. Polym. 2014, 85, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorpade, V.M.; Hanna, M.A.; Weller, C.L. Soy Protein Isolate/Poly (ethylene oxide) Films. Cereal Chem. 1995, 72, 559–563. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, J.; Li, B.; Wand, Z. An Ultraelastic Poly (ethylene oxide)/Soy Protein Film with Fully Amorphous Structure. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasek, J. Poly (ethylene glycol) interactions with proteins Poly (ethylene glycol) interactions with proteins. Z. Krist. Suppl. 2006, 23, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Min, B.G.; Kumar, S. Solution spinning and characterization of poly(vinyl alcohol)/soybean protein blend fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, J.; Chen, K.; Yang, F.; Yang, R. Heat-sealing properties of soy protein isolate/polyvinyl alcohol film made compatible by glycerol. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Zhang, C.; Du, Z.; Zou, W.; Li, H. Structure and Properties of Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Soy Protein Isolate Blend Film Fabricated Through Melt Processing. J. Polym. Environ. 2015, 23, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallmeyer, I.; Ko, F.; Kadla, J.F. Electrospinning of Technical Lignins for the Production of Fibrous Networks. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2010, 30, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ago, M.; Okajima, K.; Jakes, J.E.; Park, S.; Rojas, O.J. Lignin-based electrospun nanofibers reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ago, M.; Jakes, J.E.; Johansson, L.S.; Park, S.; Rojas, O.J. Interfacial properties of lignin-based electrospun nanofibers and films reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 6849–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veigel, S.; Rathke, J.; Weigl, M.; Gindl-Altmutter, W. Particle board and oriented strand board prepared with nanocellulose- reinforced adhesive. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heon Kwon, J.; Lee, S.H.; Ayrilmis, N.; Hyung Han, T. Tensile shear strength of wood bonded with urea-formaldehyde with different amounts of microfibrillated cellulose. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2015, 60, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrdt, E.; Pinkl, S.; Schmidberger, C.; van Herwijnen, H.W.G.; Veigel, S.; Gindl-Altmutter, W. Effect of addition of microfibrillated cellulose to urea-formaldehyde on selected adhesive characteristics and distribution in particle board. Cellulose 2016, 23, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Antorrena, G.; Freire, M.S.; Pizzi, A.; González-Álvarez, J. Environmentally friendly wood adhesives based on chestnut (Castanea sativa) shell tannins. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2017, 75, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndiwe, B.; Pizzi, A.; Tibi, B.; Danwe, R.; Konai, N.; Amirou, S. African tree bark exudate extracts as biohardeners of fully biosourced thermoset tannin adhesives for wood panels. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 132, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristri, M.A.; Adly, M.; Lubis, R.; Yadav, S.M.; Antov, P.; Papadopoulos, A.N.; Pizzi, A.; Fatriasari, W.; Ismayati, M.; Iswanto, A.H. Recent Developments in Lignin- and Tannin-Based Non-Isocyanate Polyurethane Resins for Wood Adhesives—A Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahri, S.; Chen, X.; Pizzi, A.; Hajihassani, R.; Papadopoulos, A.N. Natural tannins as new cross-linking materials for soy-based adhesives. Polymers 2021, 13, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Lu, X.; Zhou, X.; Chrusciel, L.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, S.; Brosse, N. Enhancement of mechanical strength of particleboard using environmentally friendly pine (Pinus pinaster L.) tannin adhesives with cellulose nanofibers. Ann. For. Sci. 2015, 72, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghahri, S.; Pizzi, A.; Mohebby, B.; Mirshokraie, A.; Mansouri, H.R. Soy-based, tannin-modified plywood adhesives. J. Adhes. 2018, 94, 218–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Han, Y.; Shi, S.Q.; Gao, Q.; Li, J. Preparation of a moderate viscosity, high performance and adequately-stabilized soy protein-based adhesive via recombination of protein molecules. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Pizzi, A.; Gerardin, C.; Chen, X.; Amirou, S. Soy protein isolate-based polyamides as wood adhesives. Wood Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Chu, F.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Fan, D. Preparation and characterization of a soy protein based bio-adhesive crosslinked by waterborne epoxy resin and polyacrylamide. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 35273–35279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, L.; Meng, Z.; Yi, Z.; Gao, Q.; Mao, A.; Li, J. Effects of different denaturants on properties and performance of soy protein-based adhesive. Polymers 2019, 11, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, Y.; Xu, P.; Yang, W.; Chu, H.; Wang, W.; Dong, W.; Chen, M.; Bai, H.; Ma, P. Soy protein-based adhesive with superior bonding strength and water resistance by designing densely crosslinking networks. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 142, 110128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siró, I.; Plackett, D. Microfibrillated cellulose and new nanocomposite materials: A review. Cellulose 2010, 17, 459–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.P.S.A.; Davoudpour, Y.; Islam, N.; Mustapha, A.; Sudesh, K.; Dungani, R.; Jawaid, M. Production and modification of nanofibrillated cellulose using various mechanical processes: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naderi, A. Nanofibrillated cellulose: Properties reinvestigated. Cellulose 2017, 24, 1933–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Chun, S.; Kang, I.; Park, J. Preparation of cellulose nanofibrils by high-pressure homogenizer and cellulose-based composite films. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2009, 15, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM. ASTM D905-08, Standard Test Method for Strength Properties of Adhesive Bonds in Shear by Compression Loading; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM. ASTM D4442-20, Standard Test Methods for Direct Moisture Content Measurement of Wood and Wood-Based Materials; ASTM Internationa: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM. ASTM D2395-17, Standard Test Methods for Density and Specific Gravity (Relative Density) of Wood and Wood-Based Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Khabbaz, B.; Solouk, A.; Mirzadeh, H. Polyvinyl alcohol/soy protein isolate nanofibrous patch for wound-healing applications. Prog. Biomater. 2019, 8, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- River, B. Fracture of Adhesive-Bonded Wood Joints. Handb. Adhes. Technol. Revis. Expand. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.; Park, B.D. Effect of molecular weight of urea–formaldehyde resins on their cure kinetics, interphase, penetration into wood, and adhesion in bonding wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 665–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frihart, C.R.; Birkeland, M.J.; Allen, A.J.; Wescott, J.M. Soy Adhesives that Can Form Durable Bonds for Plywood, Laminated Wood Flooring, and Particleboard. In Proceedings of the International Convention of Society of Wood Science and Technology and United Nations Economic Commission for Europe, Geneva, Switzerland, 11–14 October 2010; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Bove, J.I.; Ma, C.Y.; Harwalkar, V.R. Coagulation of Proteins. In Food Proteins and Their Applications; Damodaran, S., Paraf, A., Eds.; M. Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1997; ISBN 0-8247-9820-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hamarneh, A.I.M. Novel Wood Adhesives from Bio-Based Materials and Polyketones; University of Groningen: Groningen, The Netherlands, 2010; ISBN 978-90-367-4356-3. [Google Scholar]









| Proposed Adhesives | Commercial Adhesive | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lignin Addition | Non-Lignin | With Lignin | UF | ||||||||||
| Protein Type | SPI | SF | SPI | SF | |||||||||
| Concentration | 9% | 10% | 15% | 9% | 10% | 15% | |||||||
| Coadjutant Polymer | PEO | HPMC | CNF | PVA | PEO | CNF | PEO | HMPC | CNF | PVA | PEO | CNF | |
| Mean (psi) | 1488 a,b | 1501 a,b | 1345 a,b,c | 1193 b,c,d | 1386 a,b,c | 359 e | 1035 c,d | 808 d,e | 1777 a | 1111 b,c,d | 1445 a,b,c | 483 e | 808 d,e |
| Mean (MPa) | 10.26 | 10.35 | 9.27 | 8.23 | 9.56 | 2.48 | 7.14 | 5.57 | 12.25 | 7.66 | 9.96 | 3.33 | 5.57 |
| Median (psi) | 1444 | 1547 | 1358 | 1300 | 1335 | 392 | 1103 | 707 | 1758 | 1088 | 1479 | 485 | 808 |
| Standard Deviation (psi) | 408 | 207 | 215 | 261 | 379 | 90 | 493 | 367 | 255 | 281 | 243 | 99 | 296 |
| Minimum (psi) | 904 | 1139 | 1009 | 670 | 641 | 211 | 435 | 377 | 1481 | 672 | 1074 | 328 | 299 |
| Maximum (psi) | 2130 | 1756 | 1789 | 1487 | 2048 | 456 | 1846 | 1362 | 2102 | 1524 | 1801 | 638 | 1253 |
| Coefficient of Variation (%) | 27% | 14% | 16% | 22% | 27% | 25% | 48% | 45% | 14% | 25% | 17% | 20% | 37% |
| Proposed Adhesives | Commercial Adhesive | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lignin Addition | Non-Lignin | With Lignin | UF | ||||||||||
| Protein Type | SPI | SF | SPI | SF | |||||||||
| Concentration | 9% | 10% | 15% | 9% | 10% | 15% | |||||||
| Coadjutant | PEO | HPMC | CNF | PVA | PEO | CNF | PEO | HMPC | CNF | PVA | PEO | CNF | |
| Mean (psi) | 1148 a | 564 c,d,e | 826 b,c | 967 a,b | 995 a,b | 318 d,e | 973 a,b | 468 d,e | 1098 a,b | 1115 a,b | 624 c,d | 610 c,d | 281 e |
| Mean (MPa) | 7.92 | 3.89 | 5.70 | 6.67 | 6.86 | 2.19 | 6.71 | 3.23 | 7.57 | 7.69 | 4.30 | 4.21 | 1.94 |
| Median (psi) | 1185 | 557 | 805 | 858 | 976 | 323 | 895 | 443 | 1069 | 1125 | 626 | 546 | 269 |
| Standard Deviation (psi) | 338 | 154 | 248 | 320 | 124 | 97 | 225 | 98 | 216 | 320 | 133 | 125 | 84 |
| Minimum (psi) | 654 | 321 | 415 | 507 | 834 | 175 | 744 | 318 | 690 | 399 | 376 | 496 | 180 |
| Maximum (psi) | 1881 | 893 | 1229 | 1484 | 1227 | 435 | 1522 | 679 | 1459 | 1494 | 825 | 865 | 466 |
| Coefficient of Variation (%) | 29% | 27% | 30% | 33% | 12% | 30% | 23% | 21% | 20% | 29% | 21% | 20% | 30% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Podlena, M.; Böhm, M.; Saloni, D.; Velarde, G.; Salas, C. Tuning the Adhesive Properties of Soy Protein Wood Adhesives with Different Coadjutant Polymers, Nanocellulose and Lignin. Polymers 2021, 13, 1972. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13121972
Podlena M, Böhm M, Saloni D, Velarde G, Salas C. Tuning the Adhesive Properties of Soy Protein Wood Adhesives with Different Coadjutant Polymers, Nanocellulose and Lignin. Polymers. 2021; 13(12):1972. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13121972
Chicago/Turabian StylePodlena, Milan, Martin Böhm, Daniel Saloni, Guillermo Velarde, and Carlos Salas. 2021. "Tuning the Adhesive Properties of Soy Protein Wood Adhesives with Different Coadjutant Polymers, Nanocellulose and Lignin" Polymers 13, no. 12: 1972. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13121972
APA StylePodlena, M., Böhm, M., Saloni, D., Velarde, G., & Salas, C. (2021). Tuning the Adhesive Properties of Soy Protein Wood Adhesives with Different Coadjutant Polymers, Nanocellulose and Lignin. Polymers, 13(12), 1972. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13121972