Removal of Oily Contaminants from Water by Using the Hydrophobic Ag Nanoparticles Incorporated Dopamine Modified Cellulose Foam
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
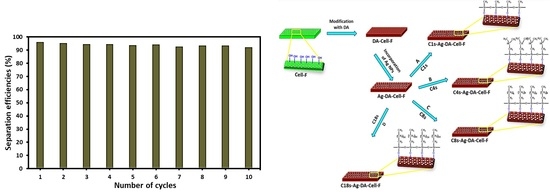
2.3. Development of Functionalized Cellulose Foam
2.4. Functionalized Cellulose Foam for Oil/Water Separation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FTIR
3.2. Morphological and Elemental Characterization of the Functionalized Cell-F
3.3. Surface Wettability Analysis
3.4. Separation of the Oil/Water Mixture
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Q.; Wang, C.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J. Novel porous oil-water separation material with super-hydrophobicity and super-oleophilicity prepared from beeswax, lignin, and cotton. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Quan, X.; Feng, W.; Wang, Q. Fluorine-free and hydrophobic hexadecyltrimethoxysilane-TiO2 coated mesh for gravity-driven oil/water separation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 586, 124189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Fu, B.; Cao, Q.; Hang, T.; Hu, A.; Ling, H.; Li, M. Robust CuO micro-cone decorated membrane with superhydrophilicity applied for oil–water separation and anti-viscous-oil fouling. Mater. Charact. 2021, 179, 111387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Lu, J.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Cheng, H. Facile fabrication of acid-resistant and hydrophobic Fe3O4@SiO2@C magnetic particles for valid oil-water separation application. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 21, 100651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Peng, C.; Dai, M.; Lin, D.; Ali, I.; Alhewairini, S.S.; Zheng, X.; Chen, G.; Li, J.; Naz, I. Recent development of super-wettable materials and their applications in oil-water separation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 266, 121624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, C.H.; Sow, P.K.; Zahiri, B.; Mérida, W. Assessment and Interpretation of Surface Wettability Based on Sessile Droplet Contact Angle Measurement: Challenges and Opportunities. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1900839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhai, J. A Lotus-Leaf-like Superhydrophobic Surface: A Porous Microsphere/Nanofiber Composite Film Prepared by Electrohydrodynamics. Angew. Chemie 2004, 116, 4438–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, L.; Ma, X.; Peng, Y.; Hu, J.; Ruan, S. Self-cleaning poly(L-dopa)-based coatings with exceptional underwater oil repellency for crude oil/water separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 510, 145402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Kang, Z. Spray deposition process to fabricate Cu2O superhydrophobic surfaces on brass mesh for efficient oil-water separation. Mater. Lett. 2018, 210, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhang, T.; Xu, Z.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y. A single covalently grafted fluorolayer imparts intrinsically hydrophilic foams with simultaneous oleophobicity and hydrophilicity for removing water from oils. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 605, 125380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan, S.; Lakshmi, D.S.; Vivekanandhan, S.; Ngamcharussrivichai, C. Biocarbons as emerging and sustainable hydrophobic/oleophilic sorbent materials for oil/water separation. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2021, 28, e00268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, J.; Huang, X.-J.; Xu, Z.-K. Wettability Switchable Membranes for Separating Both Oil-in-water and water-in-oil emulsions. J. Memb. Sci. 2021, 624, 118976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, M.; Xu, H.; Guo, K.-Y.; Zhang, J.-W.; Xia, Q.-Q.; Zhang, G.-D.; Zhao, L.; Gao, J.-F.; Tang, L.-C. Mechanically flexible, super-hydrophobic and flame-retardant hybrid nano-silica/graphene oxide wide ribbon decorated sponges for efficient oil/water separation and fire warning response. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 140, 106191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Grishkewich, N.; Tam, K.C.; Yuan, J.; Mao, Z.; Sui, X. CO2-Responsive Cellulose Nanofibers Aerogels for Switchable Oil–Water Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 9367–9373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Luo, Q.; Xu, J.; Li, K.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, H. A Novel Freeze-Drying-Free Strategy to Fabricate a Biobased Tough Aerogel for Separation of Oil/Water Mixtures. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 3779–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiari, N.; Azizian, S.; Mohazzab, B.F.; Jaleh, B. One-step fabrication of brass filter with reversible wettability by nanosecond fiber laser ablation for highly efficient oil/water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 259, 118139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, N. Recent Progress on the Development of Superhydrophobic and Superoleophilic Meshes for Oil and Water Separation: A Review. In ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; Volume 1352, pp. 175–196. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Z.S.; Taylor, S.E. Facile preparation of superhydrophobic melamine sponge for efficient underwater oil-water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 247, 116996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Raza, S.; Wang, P.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Huang, W.; Liang, L.; Hu, H.; Deng, L.; Liu, C. Robust super hydrophobic cotton fabrics functionalized with Ag and PDMS for effective antibacterial activity and efficient oil–water separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Li, Y.; Shi, J.; Wang, Q. Functionalization of cellulose via ATRP and “click” chemistry to construct hydrophobic filter paper for oil/water separation. Cellulose 2021, 28, 9413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Wu, W.; Huang, Z.; Lei, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, S. Preparation and characterization of a novel fluorine-free and pH-sensitive hydrophobic porous diatomite ceramic as highly efficient sorbent for oil–water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhao, X.; Wahid, F.; Zhao, X.; Qin, X.; Bai, H.; Xie, Y.; Zhong, C.; Jia, S. Sustainable, superhydrophobic membranes based on bacterial cellulose for gravity-driven oil/water separation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 253, 117220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, S.; Singh, R.K.; Kumar, A. Oil-water separation through an ultrahydrophobic filter paper developed by sol-gel dip-coating technique. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 26, 2495–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.-Y.; Liu, M.-C.; Li, Y.-D.; Zhu, J.; Du, A.-K.; Zeng, J.-B. Biobased super-hydrophobic coating on cotton fabric fabricated by spray-coating for efficient oil/water separation. Polym. Test. 2018, 66, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, J.; Du, A. Hydrophobic Silica Nanorod Arrays Vertically Grown on Melamine Foams for Oil/Water Separation. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 1479–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Han, F.; Liang, B.; Geng, G. Hydrothermal fabrication of robustly superhydrophobic cotton fibers for efficient separation of oil/water mixtures and oil-in-water emulsions. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 54, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Zeng, X.; Li, H.; Lai, X. Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic and flame-retardant coatings on cotton fabrics via layer-by-layer assembly. Cellulose 2018, 25, 3135–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, H.; Liu, S.; Peng, B.; Deng, Z. Composite polydopamine-based TiO2 coated mesh with restorable superhydrophobic surfaces for wastewater treatment. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 7321–7333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Jiang, C.; Liu, W.; Liang, L.; Xie, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhang, F.; Pi, K. A water-rich system of constructing durable and fluorine-free superhydrophobic surfaces for oil/water separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 507, 145165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Y.; Li, S.H.; Ge, M.Z.; Wang, L.N.; Xing, T.L.; Chen, G.Q.; Liu, X.F.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Zhang, K.Q.; Chen, T.; et al. Robust superhydrophobic TiO 2 @fabrics for UV shielding, self-cleaning and oil–water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 2825–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Lin, H.; Chen, K.; Zeng, R.; Lin, Y.; Xu, Y. Robust and Durable Superhydrophobic Polythiophene/SiO2 Coated Cotton Fabric for Versatile Oil–Water Separation. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2100725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, M.; Ge, B.; Ren, G.; Li, W.; Zhao, L. Application of superhydrophobic ZnO rod composites with environmentally-friendly and photodegradation properties in water environment treatment. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 618, 126437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, M.R.; Taylor, A.; Serwinowski, N.; Parkerson, Z.J.; Confer, M.P.; Kammakakam, I.; Bara, J.E.; Esfahani, A.R.; Mahmoodi, S.N.; Koutahzadeh, N.; et al. Sustainable Novel Bamboo-Based Membranes for Water Treatment Fabricated by Regeneration of Bamboo Waste Fibers. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 4225–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.W.; Wei, H.; Gauthier, A.C.; Song, J.; Jin, Y.; Xiao, H. Superhydrophobic modification of cellulose and cotton textiles: Methodologies and applications. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2020, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, N.; Kammakakam, I.; Falath, W. Nanomaterials: A review of synthesis methods, properties, recent progress, and challenges. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 1821–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, G.Y.; Min, B.G.; Jeong, Y.G.; Lee, S.C.; Jang, J.H.; Koo, G.H. Superhydrophobicity of cotton fabrics treated with silica nanoparticles and water-repellent agent. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 337, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venyaminov, S.Y.; Prendergast, F.G. Water (H2O and D2O) Molar Absorptivity in the 1000–4000 cm−1 Range and Quantitative Infrared Spectroscopy of Aqueous Solutions. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 248, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-L.; Johnston, C.T.; Bish, D.L.; White, J.L.; Hem, S.L. Water-vapor adsorption and surface area measurement of poorly crystalline boehmite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 260, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.Y.; Yoo, D.I.; Shin, Y.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, H.Y.; Chung, Y.S.; Park, W.H.; Youk, J.H. Crystalline structure analysis of cellulose treated with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide by means of X-ray diffraction and FTIR spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 2376–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, T.; Sawatari, C. A Fourier transform infra-red spectroscopic analysis of the character of hydrogen bonds in amorphous cellulose. Polymer 1996, 37, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharudin, K.A.; Sreekantan, S.; Basiron, N.; Chun, L.K.; Kumaravel, V.; Abdullah, T.K.; Ahmad, Z.A. Improved super-hydrophobicity of eco-friendly coating from palm oil fuel ash (POFA) waste. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2018, 337, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Pan, Q. Mussel-Inspired Direct Immobilization of Nanoparticles and Application for Oil–Water Separation. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 1402–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Karde, V.; Cheng, T.N.H.; Ramli, S.S.; Heng, J.Y.Y. Surface hydrophobicity: Effect of alkyl chain length and network homogeneity. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2021, 15, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marczak, J.; Kargol, M.; Psarski, M.; Celichowski, G. Modification of epoxy resin, silicon and glass surfaces with alkyl- or fluoroalkylsilanes for hydrophobic properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 380, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Fan, T.; Bai, H.; Guan, H.; Ning, X.; Yu, M.; Long, Y. Bioinspired superhydrophobic and superlipophilic nanofiber membrane with pine needle-like structure for efficient gravity-driven oil/water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 274, 119098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baig, N.; Kammakakam, I. Removal of Oily Contaminants from Water by Using the Hydrophobic Ag Nanoparticles Incorporated Dopamine Modified Cellulose Foam. Polymers 2021, 13, 3163. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183163
Baig N, Kammakakam I. Removal of Oily Contaminants from Water by Using the Hydrophobic Ag Nanoparticles Incorporated Dopamine Modified Cellulose Foam. Polymers. 2021; 13(18):3163. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183163
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaig, Nadeem, and Irshad Kammakakam. 2021. "Removal of Oily Contaminants from Water by Using the Hydrophobic Ag Nanoparticles Incorporated Dopamine Modified Cellulose Foam" Polymers 13, no. 18: 3163. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183163
APA StyleBaig, N., & Kammakakam, I. (2021). Removal of Oily Contaminants from Water by Using the Hydrophobic Ag Nanoparticles Incorporated Dopamine Modified Cellulose Foam. Polymers, 13(18), 3163. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183163