Eco-Friendly, High-Density Fiberboards Bonded with Urea-Formaldehyde and Ammonium Lignosulfonate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
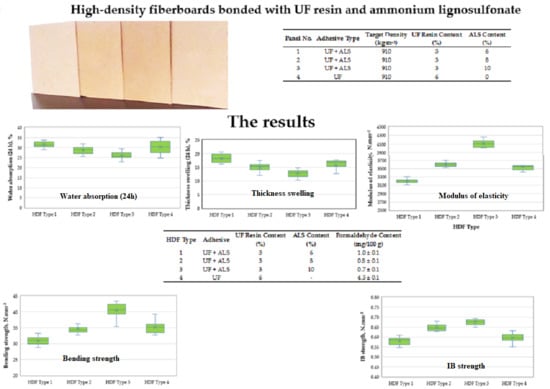
3.1. Physical and Mechanical Properties
3.2. Formaldehyde Content
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pizzi, A. Recent developments in eco-efficient bio-based adhesives for wood bonding: Opportunities and issues. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2006, 20, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzi, A.; Papadopoulos, A.; Policardi, F. Wood Composites and Their Polymer Binders. Polymers 2020, 12, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghiyari, H.R.; Hosseini, S.B.; Ghahri, S.; Ghofrani, M.; Papadopoulos, A.N. Formaldehyde Emission in Micron-Sized Wollastonite-Treated Plywood Bonded with Soy Flour and Urea-Formaldehyde Resin. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdosian, F.; Pan, Z.; Gao, G.; Zhao, B. Bio-based adhesives and evaluation for wood composites application. Polymers 2017, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taghiyari, H.R.; Esmailpour, A.; Majidi, R.; Morrell, J.J.; Mallaki, M.; Militz, H.; Papadopoulos, A.N. Potential Use of Wollastonite as a Filler in UF Resin Based Medium-Density Fiberboard (MDF). Polymers 2020, 12, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antov, P.; Savov, V.; Mantanis, G.I.; Neykov, N. Medium-density fibreboards bonded with phenol-formaldehyde resin and calcium lignosulfonate as an eco-friendly additive. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 1751279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghiyari, H.R.; Tajvidi, M.; Taghiyari, R.; Mantanis, G.I.; Esmailpour, A.; Hosseinpourpia, R. Nanotechnology for Wood Quality Improvement and Protection. In Nanomaterials for Agriculture and Forestry Applications; Husen, A., Jawaid, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 469–489. [Google Scholar]
- Ihnát, V.; Lübke, H.; Balberčák, J.; Kuňa, V. Size Reduction Downcycling of Waste Wood—A Review. Wood Res. 2020, 65, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antov, P.; Mantanis, G.I.; Savov, V. Development of wood composites from recycled fibres bonded with magnesium lignosulfonate. Forests 2020, 11, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iždinský, J.; Vidholdová, Z.; Reinprecht, L. Particleboards from Recycled Wood. Forests 2020, 11, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihnát, V.; Lübke, H.; Russ, A.; Pažitný, A.; Borůvka, V. Waste agglomerated wood materials as a secondary raw material for chipboards and fibreboards. Part II: Preparation and characterization of wood fibres in terms of their reuse. Wood Res. 2018, 63, 431–442. [Google Scholar]
- Mantanis, G.; Athanassiadou, E.; Nakos, P.; Coutinho, A. A New Process for Recycling Waste Fiberboards. In Proceedings of the 38th International Wood Composites Symposium, Washington, DC, USA, 5–8 April 2004; pp. 119–122. [Google Scholar]
- Barbu, M.C.; Sepperer, T.; Tudor, E.M.; Petutschnigg, A. Walnut and Hazelnut Shells: Untapped Industrial Resources and Their Suitability in Lignocellulosic Composites. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kúdela, J. Surface properties of a medium density fibreboard evaluated from the viewpoint of its surface treatment. Acta Facultatis Xylologiae Zvolen 2020, 62, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Lubis, M.A.R.; Hong, M.K.; Park, B.D.; Lee, S.M. Effects of recycled fiber content on the properties of medium density fiberboard. Eur. J. Wood Prod. 2018, 76, 1515–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Buck, D.; Guo, X.; Ekevad, M.; Cao, P.; Wu, Z. Machinability investigation in turning of high density fiberboard. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovatchev, G. Influence of the Belt Type Over Vibration of the Cutting Mechanism in Woodworking Shaper. In Proceedings of the 11th International Science Conference “Chip and Chipless Woodworking Processes”, Zvolen, Slovakia, 13–15 September 2018; pp. 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, K.; Schnabel, T.; Barbu, M.C.; Petutschnigg, A. Analysis of selected properties of fiberboard panels manufactured from wood and leather using the near infrared spectroscopy. Int. J. Spectrosc. 2015, 2015, 691796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tritchkov, N.; Antov, P. Prospects for Developing the Production of Solid Wood Products Taking into Account the Raw-Material Base. In Proceedings of the COST Action E44 Conference “Broad Spectrum Utilisation of Wood”, Vienna, Austria, 14–15 June 2005; pp. 131–139. [Google Scholar]
- Kulman, S.; Boiko, L.; Gurová, D.H.; Sedliačik, J. The Effect of Temperature and Moisture Changes on Modulus of Elasticity and Modulus of Rupture of Particleboard. Acta Facultatis Xylologiae Zvolen 2019, 61, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Savov, V.; Antov, P. Engineering the Properties of Eco-Friendly Medium Density Fibreboards Bonded with Lignosulfonate Adhesive. Drvna Industrija 2020, 71, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngquist, J.A. Wood-Based Composites and Panel Products. In Wood Handbook: Wood as an Engineering Material; USDA Forest Service, Forest Products Laboratory: Madison, WI, USA, 1999; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wibowo, E.S.; Lubis, M.A.R.; Park, B.D.; Kim, J.S.; Causin, V. Converting crystalline thermosetting urea-formaldehyde resins to amorphous polymer using modified nanoclay. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 87, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantanis, G.I.; Athanassiadou, E.T.; Barbu, M.C.; Wijnendaele, K. Adhesive systems used in the European particleboard, MDF and OSB industries. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 13, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.N.; Pizzi, A. Environmental Aspects of Adhesives–Emission of Formaldehyde. In Adhesives for Wood and Lignocellulosic Materials; Wiley-Scrivener Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 293–312. [Google Scholar]
- Dae, P.B.; Woo, K.J. Dynamic mechanical analysis of urea-formaldehyde resin adhesives with different formaldehyde-to-urea molar ratios. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 108, 2045–2051. [Google Scholar]
- Bekhta, P.; Sedliacik, J.; Saldan, R.; Novak, I. Effect of different hardeners for urea-formaldehyde resin on properties of birch plywood. Acta Fac. Xylologiae Zvolen 2016, 58, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Dunky, M. Adhesives in the Wood Industry. In Handbook of Adhesive Technology; Pizzi, A., Mittal, K.L., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Chapter 47; pp. 872–941. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Ma, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, M.; Chu, F. Preparation and properties of lignin-phenol-formaldehyde resins based on different biorefinery residues of agricultural biomass. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 43, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jivkov, V.; Simeonova, R.; Marinova, A.; Gradeva, G. Study on the Gluing Abilities of Solid Surface Composites with Different Wood Based Materials and Foamed PVC. In Proceedings of the 24th International Scientific Conference Wood Is Good–User Oriented Material, Technology and Design, Zagreb, Croatia, 18 October 2013; pp. 49–55, ISBN 978-953-292-031-4. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.N.; Pizzi, A. Urea-Formaldehyde Resins. In Adhesives for Wood and Lignocellulosic Materials; Wiley-Scrivener Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 61–100. [Google Scholar]
- Tudor, E.M.; Barbu, M.C.; Petutschnigg, A.; Réh, R.; Krišťák, Ľ. Analysis of Larch-Bark Capacity for Formaldehyde Removal in Wood Adhesives. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tudor, E.M.; Dettendorfer, A.; Kain, G.; Barbu, M.C.; Réh, R.; Krišťák, Ľ. Sound-Absorption Coefficient of Bark-Based Insulation Panels. Polymers 2020, 12, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirski, R.; Bekhta, P.; Dziurka, D. Relationships between Thermoplastic Type and Properties of Polymer-Triticale Boards. Polymers 2019, 11, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Łebkowska, M.; Radziwiłł, M.Z.; Tabernacka, A. Adhesives based on formaldehyde—Environmental problems. BioTechnologia 2017, 98, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission. An Update on Formaldehyde (Publication 725); U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2013.
- Bekhta, P.; Sedliačik, J.; Noshchenko, G.; Kačík, F.; Bekhta, N. Characteristics of Beech Bark and its Effect on Properties of UF Adhesive and on Bonding Strength and Formaldehyde Emission of Plywood Panels. Eur. J. Wood Prod. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Formaldehyde, 2–Butoxyethanol and 1–tert–Butoxypropan–2–ol. In Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risk to Humans; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2006; Volume 88. [Google Scholar]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. IARC Classifies Formaldehyde as Carcinogenic to Humans; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kawalerczyk, J.; Siuda, J.; Mirski, R.; Dziurka, D. Hemp Flour as a Formaldehyde Scavenger for Melamine-Urea-Formaldehyde Adhesive in Plywood Production. Bioresources 2020, 15, 4052–4064. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulou, E. Adhesives from renewable resources for binding wood-based panels. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2009, 10, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Nordström, E.; Demircan, D.; Fogelström, L.; Khabbaz, F.; Malmström, E. Green Binders for Wood Adhesives. In Applied Adhesive Bonding in Science and Technology; Interhopen Books: London, UK, 2017; pp. 47–71. [Google Scholar]
- Hemmilä, V.; Adamopoulos, S.; Karlsson, O.; Kumar, A. Development of sustainable bio-adhesives for engineered wood panels-A review. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 38604–38630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpourpia, R.; Adamopoulos, S.; Mai, C.; Taghiyari, H.R. Properties of medium-density fiberboards bonded with dextrin-based wood adhesives. Wood Res. 2019, 64, 185–194. [Google Scholar]
- Antov, P.; Savov, V.; Neykov, N. Sustainable Bio-based Adhesives for Eco-Friendly Wood Composites—A Review. Wood Res. 2020, 65, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunky, M. Wood Adhesives Based on Natural Resources: A Critical Review Part II. Carbohydrate-Based Adhesives, In Reviews of Adhesion and Adhesives; Scrivener Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; Volume 8, pp. 333–378. [Google Scholar]
- Sarika, P.R.; Nancarrow, P.; Khansaheb, A.; Ibrahim, T. Bio-Based Alternatives to Phenol and Formaldehyde for the Production of Resins. Polymers 2020, 12, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.D.; Kang, E.C.; Park, J.Y. Thermal curing behavior of modified urea-formaldehyde resin adhesives with two formaldehyde scavengers and their influence on adhesion performance. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, N.; Pereira, J.; Ferra, J.; Cruz, P.; Martins, J.; Magalhāes, F.; Mendes, A.; Carvalho, L.H. Scavengers for achieving zero formaldehyde emission of wood-based panels. Wood Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1261–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, N.; Pereira, J.; Martins, J.; Ferra, J.; Cruz, P.; Magalhāes, F.; Mendes, A.; Carvalho, L. Alternative to latent catalysts for curing UF resins used in the production of low formaldehyde emission wood-based panels. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2012, 33, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Cademartori, P.H.G.; Artner, M.A.; de Freitas, R.A.; Magalhaes, W.L.E. Alumina nanoparticles as formaldehyde scavenger for urea-formaldehyde resin: Rheological and in-situ cure performance. Compos. B Eng. 2019, 176, 107281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medved, S.; Gajsek, U.; Tudor, E.M.; Barbu, M.C.; Antonovic, A. Efficiency of bark for reduction of formaldehyde emission from particleboards. Wood Res. 2019, 64, 307–315. [Google Scholar]
- Réh, R.; Igaz, R.; Krišt’ák, Ľ.; Ružiak, I.; Gajtanska, M.; Božíková, M.; Kučerka, M. Functionality of beech bark in adhesive mixtures used in plywood and its effect on the stability associated with material systems. Materials 2019, 12, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirski, R.; Kawalerczyk, J.; Dziurka, D.; Siuda, J.; Wieruszewski, M. The Application of Oak Bark Powder as a Filler for Melamine-Urea-Formaldehyde Adhesive in Plywood Manufacturing. Forests 2020, 11, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boran, S.; Usta, M.; Ondaral, S.; Gümüskaya, E. The efficiency of tannin as a formaldehyde scavenger chemical in medium density fiberboard. Compos. B Eng. 2012, 43, 2487–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekhta, P.; Sedliacik, J.; Kacik, F.; Noshchenko, G.; Kleinova, A. Lignocellulosic waste fibers and their application as a component of urea-formaldehyde adhesive composition in the manufacture of plywood. Eur. J. Wood Prod. 2019, 77, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antov, P.; Savov, V.; Neykov, N. Reduction of Formaldehyde Emission from Engineered Wood Panels by Formaldehyde Scavengers—A Review. In Proceedings of the 13th International Scientific Conference Wood EMA 2020 and 31st International Scientific Conference ICWST 2020 Sustainability of Forest-Based Industries in the Global Economy, Vinkovci, Croatia, 28–30 September 2020; pp. 7–11, ISBN 978-953-57822-8-5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Pang, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Developing eco-friendly high-strength soy adhesives with improved ductility through multiphase core–shell hyperbranchedpolysiloxane. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 7784–7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frihart, C.; Birkeland, M. Soy Properties and Soy Wood Adhesives; American Chemical Society: Midland, MI, USA, 2014; pp. 167–192. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, F.; Wu, L.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, L. Assessment of soybean protein-based adhesive formulations, prepared by different liquefaction technologies for particleboard applications. Wood Sci. Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Weng, X. Preparation of the Plywood Using Starch-based Adhesives Modified with blocked isocyanates. Procedia Eng. 2011, 15, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Gu, Z.; Cheng, L.; Hong, Y. Effects of montmorillonite addition on the performance of starch-based wood adhesive. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndiwe, B.; Pizzi, A.; Tibi, B.; Danwe, R.; Konai, N.; Amirou, S. African tree bark exudate extracts as biohardeners of fully biosourced thermoset tannin adhesives for wood panels. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 132, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Antorrena, G.; Freire, M.S.; Pizzi, A.; Álvarez, J.G. Environmentally friendly Wood adhesives based on chestnut (Castanea sativa) shell tannins. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2017, 75, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konai, N.; Pizzi, A.; Danwe, R.; Lucien, M.; Lionel, K.T. Thermomechanical analysis of African tannins resins and biocomposite characterization. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2020, 1850611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mansouri, N.E.; Pizzi, A.; Salvadó, J. Lignin-based wood panel adhesives without formaldehyde. Holz Roh Werkst. 2006, 65, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.J.; Gutierrez, J.; Chung, Y.; Frank, C.W.; Billington, S.L.; Sattely, E.S. A lignin-epoxy resin derived from biomass as an alternative to formaldehyde-based wood adhesives. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadhave, R.V.; Srivastava, S.; Mahanwar, P.A.; Gadekar, P.T. Lignin: Renewable Raw Material for Adhesive. Open J. Polym. Chem. 2019, 9, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antov, P.; Jivkov, V.; Savov, V.; Simeonova, R.; Yavorov, N. Structural Application of Eco-Friendly Composites from Recycled Wood Fibres Bonded with Magnesium Lignosulfonate. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lora, J.H.; Glasser, W.G. Recent industrial applications of lignin: A sustainable alternative to nonrenewable materials. J. Polym. Environ. 2002, 10, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lignin: Biosynthesis and Transformation for Industrial Applications; Sharma, S.; Kumar, A. (Eds.) Springer Series on Polymer and Composite Materials, Switzerland AG; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bajwa, D.S.; Pourhashem, G.; Ullah, A.H.; Bajwa, S.G. A concise review of current lignin production, applications, products and their environmental impact. Ind. Crop Prod. 2019, 139, 111526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapiszewski, Ł.; Oliwa, R.; Oleksy, M.; Jesionowski, T. Calcium lignosulfonate as eco-friendly additive of crosslinking fibrous composites with phenol-formaldehyde resin matrix. Polymers 2018, 63, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zheng, Z. Preparation and characterization of phenol–formaldehyde adhesives modified with enzymatic hydrolysis lignin. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 2046–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmilä, V.; Adamopoulos, S.; Hosseinpourpia, R.; Sheikh, A.A. Ammonium lignosulfonate adhesives for particleboards with pMDI and furfuryl alcohol as cross-linkers. Polymers 2019, 11, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vázquez, G.; González, J.; Freire, S.; Antorrena, G. Effect of chemical modification of lignin on the gluebond performance of lignin-phenolic resins. Bioresour. Technol. 1997, 60, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lora, J. Industrial Commercial Lignins: Sources, Properties and Applications. In Monomers, Polymers and Composites from Renewable Resources; Belgacem, M.N., Gandini, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 225–241. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, A.; Kaushik, N.; Biswas, S. Derivatives and applications of lignin—An insight. SciTech J. 2014, 1, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Berlin, A.; Balakshin, M. Industrial Lignins: Analysis, Properties, and Applications. In Bioenergy Research: Advances and Applications; Gupta, V.K., Tuohy, M., Kubicek, C., Saddler, J., Xu, F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Chapter 18; pp. 315–336. [Google Scholar]
- Vishtal, A.G.; Kraslawski, A. Challenges in industrial applications of technical lignins. BioResources 2011, 6, 3547–3568. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, M.V.; Oliet, M.; Rodríguez, F.; Astarloa, G.; Echeverría, J.M. Use of a methylolated softwood ammonium lignosulfonate as partial substitute of phenol in resol resins manufacture. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 94, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.V.; Oliet, M.; Rodríguez, F.; García, J.; Gilarranz, M.A.; Rodríguez, J.J. Modification of ammonium lignosulfonate by phenolation for use in phenolic resins. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EN 310. Wood-Based Panels-Determination of Modulus of Elasticity in Bending and of Bending Strength; European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- EN 317. Particleboards and Fibreboards-Determination of Swelling in Thickness after Immersion in Water; European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- EN 322. Wood-Based Panels-Determination of Moisture Content; European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- EN 323. Wood-Based Panels-Determination of Density; European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- EN ISO 12460-5. Wood-Based Panels-Determination of Formaldehyde Release—Part 5. Extraction Method (Called the Perforator Method); European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kordkheili, H.Y.; Najafi, S.K.; Eshkiki, R.B.; Pizzi, A. Improving urea formaldehyde resin properties by glyoxalated soda bagasse lignin. Eur. J. Wood. Prod. 2015, 73, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.W.; Carlbom, K.; Matuana, L.; Heiden, P. Thermoplastic modification of urea-formaldehyde wood adhesives to improve moisture resistance. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 101, 4222–4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihajlova, J.; Savov, V. Physical Indicators of High-Density Fibreboards (HDF) Manufactured from Wood of Hard Broadleaved Species. In Proceedings of the 8th Hardwood Conference, Sopron, Hungary, 25–26 October 2018; pp. 142–144, ISBN 978-963-359-096-6. [Google Scholar]
- EN 622-2. Fibreboards–Specifications—Part 2: Requirements for Hardboard; European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.Q.; Gardner, D.J. Hygroscopic thickness swelling rate of compression molded wood fiberboard and wood fiber/polymer composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Khali, D.P.; Jawaid, M.; Tahir, P.M.; Siakeng, R.; Asim, M.; Khan, T.A. Recent development in binderless fiber-board fabrication from agricultural residues: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 211, 502–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.P.; Guo, M.H. Influence of ammonium lignosulfonate on the mechanical and dimensional properties of wood fiber biocomposites reinforced with polyactic acid. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 78, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.V.; Rodriguez, J.J.; Oliet, M.; Rodriguez, F.; Garcia, J.; Gilarranz, M.A. Characterization and Structural Modification of Ammonic Lignosulfonate by Methylolation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 82, 2661–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roffael, E. Volatile organic compounds and formaldehyde in nature, wood and wood based panels. Holz Roh Werkst. 2006, 64, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanassiadou, E.; Roffael, E.; Mantanis, G. Medium Density Fiberboards (MDF) from Recycled Fibres. In Proceedings of the Conference “Towards a Higher Technical, Economical and Environmental Standard in Europe” COST Action E31, Bordeaux, France, 29 September–1 October 2005; pp. 248–261. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, M.Z.M.; Böhm, M. Understanding of formaldehyde emissions from solid wood: An overview. BioResources 2013, 8, 4775–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Panel No. | Adhesive Type | Target Density (kg·m−3) | UF Resin Content (%) | Ammonium Lignosulfonate Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | UF + ALS | 910 | 3 | 6 |
| 2 | UF + ALS | 910 | 3 | 8 |
| 3 | UF + ALS | 910 | 3 | 10 |
| 4 | UF | 910 | 6 | 0 |
| HDF Type | Adhesive | UF Resin Content (%) | Ammonium Lignosulfonate Content (%) | Formaldehyde Content (mg/100 g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | UF + ALS | 3 | 6 | 1.0 ± 0.1 |
| 2 | UF + ALS | 3 | 8 | 0.8 ± 0.1 |
| 3 | UF + ALS | 3 | 10 | 0.7 ± 0.1 |
| 4 | UF | 6 | - | 4.3 ± 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antov, P.; Savov, V.; Krišťák, Ľ.; Réh, R.; Mantanis, G.I. Eco-Friendly, High-Density Fiberboards Bonded with Urea-Formaldehyde and Ammonium Lignosulfonate. Polymers 2021, 13, 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13020220
Antov P, Savov V, Krišťák Ľ, Réh R, Mantanis GI. Eco-Friendly, High-Density Fiberboards Bonded with Urea-Formaldehyde and Ammonium Lignosulfonate. Polymers. 2021; 13(2):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13020220
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntov, Petar, Viktor Savov, Ľuboš Krišťák, Roman Réh, and George I. Mantanis. 2021. "Eco-Friendly, High-Density Fiberboards Bonded with Urea-Formaldehyde and Ammonium Lignosulfonate" Polymers 13, no. 2: 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13020220
APA StyleAntov, P., Savov, V., Krišťák, Ľ., Réh, R., & Mantanis, G. I. (2021). Eco-Friendly, High-Density Fiberboards Bonded with Urea-Formaldehyde and Ammonium Lignosulfonate. Polymers, 13(2), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13020220