Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties of Electrospun Recycled PET Polymeric Fibers Functionalized with Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles
Abstract
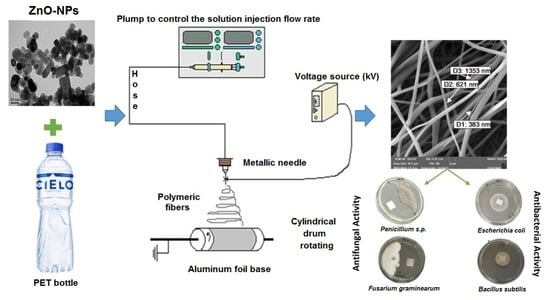
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Synthesis of ZnO-NPs
2.2.2. Characterization of Nanoparticles
2.2.3. Electrospinning Stage
2.2.4. Polymeric Solutions for Electrospinning
2.2.5. Characterization of Electrospun Fibers
2.2.6. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of ZnO-NPs
3.2. Characterization of r-PET Composite Fibers
3.3. Antibacterial and Fungal Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hopewell, J.; Dvorak, R.; Kosior, E. Plastics Recycling: Challenges and Opportunities. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hadi, A.J.; Najmuldeen, G.F.; Ahmed, I. Polyolefins Waste Materials Reconditioning Using Dissolution/Reprecipitation Method. APCBEE Procedia 2012, 3, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Yanful, E.K.; Bassi, A.S. A Review of Plastic Waste Biodegradation. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2005, 25, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilias, D.S.; Karayannidis, G.P. The Chemical Recycling of PET in the Framework of Sustainable Development. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2004, 4, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigail Cedeño, A.; Diaz Barrios, A.; Gallardo Bastidas, J.; Ullaguari Loor, S.; Morales Fuentes, N. Recycled HDPE/PET Clay Nanocomposites. Key Eng. Mater. 2019, 821, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeah, C.; Fazakerley, J.A.; Roberts, C.L. Emerging Trends in Informal Sector Recycling in Developing and Transition Countries. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 2509–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solíz Torre, M.F. Ecología Política y Geografía Crítica de la Basura en el ECUADOR. Let. Verdes. Rev. Latinoam. Estud. Socioambientales 2015, 17, 4–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Salem, S.M.; Lettieri, P.; Baeyens, J. Recycling and Recovery Routes of Plastic Solid Waste (PSW): A Review. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2625–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.T. Waste Recycling. In Waste Treat and Disposal; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2005; Volume 6, pp. 127–170. ISBN 0470849126. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, L.; Worrell, E. Plastic Recycling. In Handbook of Recycling; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 179–190. ISBN 9780123964595. [Google Scholar]
- Aslani, A.; Reza, M.; Babapoor, A.; Amiri, A.; Beyki-shuraki, K. Applied Surface Science Solvothermal Synthesis, Characterization and Optical Properties of ZnO, ZnO–MgO and ZnO–NiO, Mixed Oxide Nanoparticles. Elsevier 2011, 257, 4885–4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, M.; Waser, E.; Würmli, J.C.; Hellweg, S. Is there an environmentally optimal separate collection rate? Waste Manag. 2018, 77, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strain, I.; Wu, Q.; Pourrahimi, A.M.; Hedenqvist, M.S. Electrospinning of Recycled PET to Generate Tough Mesomorphic Fibre Membranes for Smoke Filtration. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benkocká, M.; Lupínková, S.; Matoušek, J.; Kolářová, K.; Kolská, Z. Antimicrobial and Optical Properties of PET Chemically Modified and Grafted with Borane Compounds. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 15001–15008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Issaabadi, Z.; Sajjadi, M.; Sajadi, S.M.; Atarod, M. Types of Nanostructures. In Interface Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 28, pp. 29–80. ISBN 9780128135860. [Google Scholar]
- Zong, X.; Kim, K.; Fang, D.; Ran, S.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Structure and Process Relationship of Electrospun Bioabsorbable Nanofiber Membranes. Polymers 2002, 43, 4403–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Yao, Z.; Liu, A.; Shi, G. Supercapacitors Based on Flexible Graphene/Polyaniline Nanofiber Composite Films. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 1963–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, P.; Doan, H.; Kinashi, K.; Sakai, W.; Tsutsumi, N.; Huynh, D. Centrifugally Spun Recycled PET: Processing and Characterization. Polymers 2018, 10, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laurenti, M.; Cauda, V. ZnO Nanostructures for Tissue Engineering Applications. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivero, P.J.; Urrutia, A.; Goicoechea, J.; Arregui, F.J. Nanomaterials for Functional Textiles and Fibers. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhou, G.; Huang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X. Electrospinning of Polymeric Nano Fibers for Drug Delivery Applications. J. Control. Release 2014, 185, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Guo, J.; Zhang, W.; Summers, P.A.; Hall, P. From Waste Plastics to Industrial Raw Materials: A Life Cycle Assessment of Mechanical Plastic Recycling Practice Based on a Real-World Case Study Science of the Total Environment from Waste Plastics to Industrial Raw Materials: A Life Cycle Assessment; Elsvier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 601, pp. 1192–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayakron, C.; Namahoot, J.; Saengkiettiyut, K. Progress in Organic Coatings Green Metal Organic Coating from Recycled PETs and Modified Natural Rubber for the Automobile Industry. Prog. Org. Coat. 2015, 86, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, D.; Awaja, F. Recycling of PET Recycling of PET. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 1453–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oromiehie, A.; Mamizadeh, A. Recycling PET Beverage Bottles and Improving Properties. Polym. Int. 2004, 53, 728–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, S.S.; Oliveira, A.M.; Maia, A.; Zanin, M.H.A. Recycled PET Nanofibers Produced by Electrospinning Technique. TechConnect Br. 2016, 335–338. [Google Scholar]
- Cárdenas-Triviño, G.; Cruzat-Contreras, C. Study of Aggregation of Gold Nanoparticles in Chitosan. J. Clust. Sci. 2018, 29, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chircov, C.; Gharbia, S.; Balt, C.; Ros, M.; Holban, A.M.; Ficai, A.; Vasile, B.S.; Andronescu, E. Electrospun Polyethylene Terephthalate Nanofibers Loaded with Silver Nanoparticles: Novel Approach in Anti-Infective Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cárdenas-Triviño, G.; Elgueta, C.; Vergara, L.; Ojeda, J.; Valenzuela, A.; Cruzat, C. Chitosan Doped with Nanoparticles of Copper, Nickel and Cobalt. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cárdenas, G.; Díaz, J.; Meléndrez, M.F.F.; Cruzat, C. Physicochemical Properties of Edible Films from Chitosan Composites Obtained by Microwave Heating. Polym. Bull. 2008, 61, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavilla Lerma, L.; Benomar, N.; Casado Munoz Mdel, C.; Gálvez, A.; Abriouel, H. Correlation between antibiotic and biocide resistance in mesophilic and psychrotrophic Pseudomonas spp. isolated from slaughterhouse surfaces throughout meat chain production. Food Microbiol. 2015, 51, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo, P.S.; Lázár, V.; Papp, B.; Arnoldini, M.; Abel zur Wiesch, P.; Busa-Fekete, R.; Fekete, G.; Pál, C.; Ackermann, M.; Bonhoeffer, S. Antagonism between Bacteriostatic and Bactericidal Antibiotics Is Prevalent. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 4573–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morais, D.S.; Guedes, R.M.; Ascensão Lopes, M. Antimicrobial Approaches for Textiles: From Research to Market. Materials 2016, 9, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, W.; Leitner, D.R.; Zingl, F.G.; Schratter, G.; Prassl, R.; Goessler, W.; Reidl, J.; Schild, S. Antibacterial Activity of Silver and Zinc Nanoparticles against Vibrio Cholerae and Enterotoxic Escherichia Coli. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 305, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raghupathi, K.R.; Koodali, R.T.; Manna, A.C. Size-Dependent Bacterial Growth Inhibition and Mechanism of Antibacterial Activity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2011, 27, 4020–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melaiye, A.; Sun, Z.; Hindi, K.; Milsted, A.; Ely, D.; Reneker, D.H.; Tessier, C.A.; Youngs, W.J. Silver(l)-imidazole cyclophane gem-diol complexes encapsulated by electrospun tecophilic nanofibers: Formation of nanosilver particles and antimicrobial activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 2285–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Bach Truong, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Louis Kyratzis, I. Electrospun antibacterial nanofibers: Production, activity, and in vivo applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Wu, Q.; Qi, Y.; Kärki, T. Electrospun Nanofibers with Antimicrobial Properties. Electrospun Nanofibers 2017, 1, 551–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharaghani, D.; Kee Jo, Y.; Khan, M.Q.; Jeong, Y.; Cha, H.J.; Kim, I.S. Electrospun antibacterial polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membranes functionalized with silver nanoparticles by a facile wetting method. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 108, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Peng, W.; Zare, Y.; Rhee, K.Y. Effects of Size and Aggregation/Agglomeration of Nanoparticles on the Interfacial/Interphase Properties and Tensile Strength of Polymer Nanocomposites. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godavarti, U.; Mote, V.D.; Dasari, M. Precipitated nickel doped ZnO nanoparticles with enhanced low temperature ethanol sensing properties. Mod. Electron. Mater. 2017, 3, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theron, S.A.; Zussman, E.; Yarin, A.L. Experimental investigation of the governing parameters in the electrospinning of polymer solutions. Polymer 2017, 45, 2017–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homaeigohar, S.; Elbahri, M. Nanocomposite Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes for Environmental Remediation. Materials 2014, 7, 1017–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petras, D.; Slobodian, P.; Pavlínek, V.; Sáha, P.; Kimmer, D. The effect of PVAc solution viscosity on diameter of PVAc nanofibres prepared by technology of electrospinning. AIP Conf. Proc. 2011, 1375, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarusuwannapoom, T.; Hongrojjanawiwat, W.; Jitjaicham, S.; Wannatong, L.; Nithitanakul, M.; Pattamaprom, C.; Koombhongse, P.; Rangkupan, R.; Supaphol, P. Effect of solvents on electro-spinnability of polystyrene solutions and morphological appearance of resulting electrospun polystyrene fibers. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannatong, L.; Sirivat, A.; Supaphol, P. Effects of solvents on electrospun polymeric fibers: Preliminary study on polystyrene. Polym. Int. 2004, 1859, 1851–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, K.; Jin, H.J.; Chin, I.-J. Morphological Characterization of Electrospun Nano-Fibrous Membranes of Biodegradable Poly(L-lactide) and Poly(lactide-co-glycolide). Macromol. Symp. 2005, 224, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezarati, R.M.; Eifert, M.B.; Cosgriff-Hernandez, E. Effects of Humidity and Solution Viscosity on Electrospun Fiber Morphology. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2013, 19, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Zeng, L.; Qiao, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ding, J. Fabrication of Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers with Diverse Morphologies. Molecules 2019, 24, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svinterikos, E.; Zuburtikudis, I. Carbon nanofibers from renewable bioresources (lignin) and a recycled commodity polymer [poly(ethylene terephthalate)]. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wen, B.; Wang, F.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yang, M. In situ synthesis of ZnO nanocrystal/PET hybrid nanofibers via electrospinning. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2011, 49, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, P.G.; Morales, N.J.; Candal, R.J.; Hojamberdiev, M.; Rodriguez, J. Influence of zinc acetate content on the photoelectrochemical performance of zinc oxide nanostructures fabricated by electrospinning technique. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2016, 6, 184798041666367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, J.A.; Said, I.A.; Mohamed, M.A.; Yasin, S.A.; Ali, Z.A.; Ahmed, I.H. Electrospinning of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) nanofibers: Optimization study using taguchi design of experiment. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 454, 012130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieh, Y.-T.; Lin, Y.-S.; Twu, Y.-K.; Tsai, H.-B.; Lin, R.-H. Effect of crystallinity on enthalpy recovery peaks and cold-crystallization peaks in PET via TMDSC and DMA studies. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 116, 1334–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanegas, M.E.; Quijada, R.; Serafini, D.; Galland, G.B.; Palza, H. Nonisothermal crystallization and melting behavior of syndiotactic polypropylenes of different microstructure. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2008, 46, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Ryu, Y.; Lee, J.; Cha, S.W. Effect of Aluminum Flakes on Mechanical and Optical Properties of Foam Injection Molded Parts. Polymers 2021, 13, 2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hari, K.D.; Garcia, C.V.; Shin, G.; Kim, J. Improvement of the UV Barrier and Antibacterial Properties of Crosslinked Pectin/Zinc Oxide Bionanocomposite Films. Polymers 2021, 13, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meruvu, H.; Vangalapati, M.; Chaitanya Chippada, S.; Rao Bammidi, S. Syntesis and characterization of znc oxide nanopartcicles and its antimicrobial activity against Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli. Rasayan J. 2011, 4, 217–222. [Google Scholar]
- Kanmani, P.; Rhim, J. Properties and characterization of bionanocomposite films prepared with various biopolymers and ZnO nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 106, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Teng, X.; Li, G.; Rhim, J. Preparation, characterization, and antimicrobial activity of gelatin/ZnO nanocomposite films. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 45, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R. Functionalities of ZnO reinforced thermoplastics composite materials: A state of the art review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirohi, S.; Singh, R.; Jain, N.; Pani, B.; Dutt, K.; Nain, R. Synthesis and characterization of multifunctional ZnO/polyester green composite films. J. Polym. Res. 2017, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, S.L.; Azizi, M.H.; Movahedi, F.; Rahimifard, N.; Tavakolipour, H. Potential perspectives of CMC-PET/ZnO bilayer nanocomposite films for food packaging applications: Physical, mechanical and antimicrobial properties. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 3731–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaf, O.; Anjana, K.; Prasanth, R.; Reshmi, C.R.; Juraij, K.; Rajesh, P.; Chingakham, C.; Sajith, V.; Sujith, A. ZnO decorated anti-bacterial electrospun ABS nanocomposite membrane for oil-water separation. Mater. Lett. 2019, 256, 126626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Wang, L.F.; Rhim, J.W. Incorporation of zinc oxide nanoparticles improved the mechanical, water vapor barrier, UV-light barrier, and antibacterial properties of PLA-based nanocomposite films. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 93, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, E.; Dong, S. Preparation of styrene polymer/ZnO nanocomposite latex via miniemulsion polymerization and its antibacterial property. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2009, 287, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, K.; Canales, D.; Amigo, N.; Montoille, L.; Cament, A.; Rivas, L.M.; Gil-Castell, O.; Reyes, P.; Ulloa, M.T.; Ribes-Greus, A.; et al. Effective antimicrobial materials based on low-density polyethylene (LDPE) with zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 172, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-C.; Li, Y.-N. Mechanical and antibacterial properties of modified nano-ZnO/high-density polyethylene composite films with a low doped content of nano-ZnO. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 2965–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, L.; Mustapha, A.; Li, H.; Hu, Z.Q.; Lin, M. Antibacterial activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles against Escherichia coli O157:H7. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 107, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, A.; Hassan, T.; Jabri, T.; Riaz, S.; Khan, A.; Iqbal, K.M.; Khan, S.U.; Wasim, M.; Shah, M.R.; Khan, M.Q.; et al. Electrospun nanofiber-based viroblock/ZnO/PAN hybrid antiviral nanocomposite for personal protective applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talebian, N.; Amininezhad, S.M.; Doudi, M. Controllable synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their morphology-dependent antibacterial and optical properties. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2013, 120, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palanikumar, L.; Ramasamy, S.N.; Balachandran, C. Size-dependent antimicrobial response of zinc oxide nanoparticles. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2014, 8, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roselli, M.; Finamore, A.; Garaguso, I.; Britti, M.S.; Mengheri, E. Biochemical and Molecular Actions of Nutrients Zinc Oxide Protects Cultured Enterocytes from the Damage Induced by Escherichia Coli 1. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 4077–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Shang, J.K. Antifungal Activity and Mechanism of Palladium-Modified Nitrogen-Doped Titanium Oxide Photocatalyst on Agricultural Pathogenic Fungi Fusarium Graminearum. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 10953–10959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, M.; Geszke-Moritz, M. The newest achievements in synthesis, immobilization and practical applications of antibacterial nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 228, 596–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savi, G.D.; Bortoluzzi, A.J.; Scussel, V.M. Antifungal properties of Zinc-compounds against toxigenic fungi and mycotoxin. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 1834–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Element | r-PET | ZnO-1.5/r-PET | ZnO-3/r-PET | ZnO-6/r-PET | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt% | at.% | wt% | at.% | wt% | at.% | wt% | at.% | |
| Carbon | 63.93 | 70.24 | 56.37 | 64.09 | 62.48 | 70.12 | 54.82 | 64.15 |
| Oxygen | 36.07 | 29.76 | 41.57 | 35.48 | 34.8 | 29.32 | 41.78 | 35.13 |
| Zinc | - | - | 2.06 | 0.43 | 2.72 | 0.56 | 3.4 | 0.72 |
| Sample | Tg (°C) | Tc (°C) | Tm (°C) | Xc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r-PET | 84 | 190 | 249 | 0.25 |
| ZnO-1.5/r-PET | 84 | 186 * | 243 | 0.10 |
| ZnO-3/r-PET | 90 | - | - | - |
| ZnO-6/r-PET | ** | - | - | - |
| Sample | r-PET | ZnO-1.5/r-PET | ZnO-3/r-PET | ZnO-6/r-PET |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 23 | 24 | 31 |
| 2 | 0 | 27 | 23 | 33 |
| 3 | 0 | 25 | 27 | 39 |
| 4 | 0 | 20 | 23 | 34 |
| Zone of inhibition (mm) | 0 | 23.75 ± 2.58 | 24.25 ± 1.63 | 34.25 ± 2.58 |
| Sample | r-PET | ZnO-1.5/r-PET | ZnO-3/r-PET | ZnO-6/r-PET |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 28 | 28 | 40 |
| 2 | 0 | 28 | 30 | 36 |
| 3 | 0 | 27 | 25 | 40 |
| 4 | 0 | 21 | 25 | 38 |
| Zone of inhibition (mm) | 0 | 26 ± 2.91 | 27 ± 2.12 | 38.5 ± 1.65 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vázquez, K.; Vanegas, P.; Cruzat, C.; Novoa, N.; Arrué, R.; Vanegas, E. Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties of Electrospun Recycled PET Polymeric Fibers Functionalized with Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Polymers 2021, 13, 3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213763
Vázquez K, Vanegas P, Cruzat C, Novoa N, Arrué R, Vanegas E. Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties of Electrospun Recycled PET Polymeric Fibers Functionalized with Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Polymers. 2021; 13(21):3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213763
Chicago/Turabian StyleVázquez, Katherine, Paul Vanegas, Christian Cruzat, Néstor Novoa, Ramón Arrué, and Eulalia Vanegas. 2021. "Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties of Electrospun Recycled PET Polymeric Fibers Functionalized with Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles" Polymers 13, no. 21: 3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213763
APA StyleVázquez, K., Vanegas, P., Cruzat, C., Novoa, N., Arrué, R., & Vanegas, E. (2021). Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties of Electrospun Recycled PET Polymeric Fibers Functionalized with Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Polymers, 13(21), 3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213763