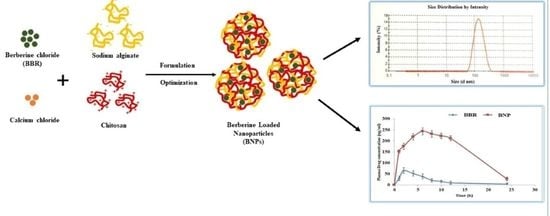
Development of Natural Polysaccharide–Based Nanoparticles of Berberine to Enhance Oral Bioavailability: Formulation, Optimization, Ex Vivo, and In Vivo Assessment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Berberine-Loaded Nanoparticles (BNPs)
- 10 mL solution of calcium chloride was added dropwise to the 50 mL alginate solution with stirring (Pregelation step).
- At pregelation step: added BBR (5 mg was dissolved in 1 mL of DMSO)
- Kept it on magnetic stirrer for 30 min
- Gelation step: added 20 mL of chitosan solution drop by drop
- Continue stirring for 60 min
- Sonicated for 15 min
- Finally homogenized for 30 min at 22,360 g-forces
- Kept the formulation for 24 h
2.3. HPLC Method of Analysis
2.4. Characterization of BNPs
2.4.1. PS, PDI, and ZP Measurement
2.4.2. Determination of Entrapment Efficiency (EE) and Drug-Loading (DL) Efficiency
2.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry Analysis
2.6. FTIR Spectroscopy Analysis
2.7. Microscopic Evaluation of BNPs
2.8. In Vitro Drug-Release Study
2.9. Stability Studies
2.10. Ex Vivo Gut-Permeation Study
2.11. In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Study
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Formation and Characterization of BNPs
3.2. BBR loading and Entrapment in BNPs
3.3. DSC Analysis
3.4. FTIR Spectroscopy Analysis
3.5. Nanoparticle Morphology
3.6. In Vitro Drug-Release Kinetics
3.7. Stability Studies
3.8. Ex Vivo Gut-Permeation Study
3.9. Pharmacokinetic Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ortiz, L.M.G.; Lombardi, P.; Tillhon, M.; Scovassi, A.I. Berberine, an Epiphany Against Cancer. Molecules 2014, 19, 12349–12367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, S.-H.; Lu, F.-E.; Xu, L.-J. Therapeutic effects of berberine in impaired glucose tolerance rats and its influence on insulin secretion. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2004, 25, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tillhon, M.; Ortiz, L.M.G.; Lombardi, P.; Scovassi, A.I. Berberine: New perspectives for old remedies. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujtaba, A.; Akhter, H.; Alam, S.; Ali, M.D.; Hussain, A. An updated review on therapeutic potential and recent advances in drug delivery of Berberine: Current status and future prospect. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2021, 22, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-T.; Hao, H.-P.; Xie, H.-G.; Lai, L.; Wang, Q.; Liu, C.-X.; Wang, G.-J. Extensive Intestinal First-Pass Elimination and Predominant Hepatic Distribution of Berberine Explain Its Low Plasma Levels in Rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2010, 38, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Miao, Y.-Q.; Fan, D.-J.; Yang, S.-S.; Lin, X.; Meng, L.-K.; Tang, X. Bioavailability Study of Berberine and the Enhancing Effects of TPGS on Intestinal Absorption in Rats. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.-S.; Zheng, Y.-R.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Long, X.-Y. Research progress on berberine with a special focus on its oral bioavailability. Fitoterapia 2016, 109, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, R.; Shou, J.-W.; Zhao, Z.-X.; He, C.-Y.; Ma, C.; Huang, M.; Fu, J.; Tan, X.-S.; Li, X.-Y.; Wen, B.-Y.; et al. Transforming berberine into its intestine-absorbable form by the gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, Y.-L.; Gao, L.-N.; Jiang, H.-L. Effects of β-cyclodextrin on the intestinal absorption of berberine hydrochloride, a P-glycoprotein substrate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 59, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.Z.; Ahmad, J.R.; Alasmary, M.Y.; Akhter, H.; Abdel-Wahab, B.A.; Warsi, M.H.; Haque, A. Rizwanullah Progress in nanomedicine-based drug delivery in designing of chitosan nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2021, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, H.; Kumar, S.; Nomani, S. Sonication tailored enhance cytotoxicity of naringenin nanoparticle in pancreatic cancer: Design, optimization, and in vitro studies. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2020, 46, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Loquercio, A.; Castell-Perez, E.; Gomes, C.; Moreira, R.G. Preparation of Chitosan-Alginate Nanoparticles forTrans-cinnamaldehyde Entrapment. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, N2305–N2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katuwavila, N.P.; Perera, A.D.L.C.; Samarakoon, S.R.; Soysa, P.; Karunaratne, V.; Amaratunga, G.A.J.; Karunaratne, D.N. Chitosan-alginate nanoparticle system efficiently delivers doxorubicin to MCF-7 Cells. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 3178904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.-J.; Hu, X.-B.; Lu, X.-L.; Liao, D.-H.; Tang, T.-T.; Wu, J.-Y.; Xiang, D.-X. Nanoemulsion-based delivery system for enhanced oral bioavailability and Caco-2 cell monolayers permeability of berberine hydrochloride. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 1868–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yadav, K.; Sawant, K.K. Formulation Optimization of Etoposide Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles by Double Factorial Design and their Evaluation. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujtaba, M.A.; Hassan, K.A.M.; Imran, M. Chitosan-alginate nanoparticles as a novel drug delivery system for rutin. Int. J. Adv. Biotechnol. Res. 2018, 9, 1895–1903. [Google Scholar]
- Akhter, M.H.; Ahmad, A.; Ali, J. Formulation and Development of CoQ10-Loaded s-SNEDDS for Enhancement of Oral Bioavailability. J. Pharm. Innov. 2014, 9, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Neupane, Y.R.; Shafi, S.; Mangla, B.; Kohli, K. PEGylated liposomes as an emerging therapeutic platform for oral nanomedicine in cancer therapy: In vitro and in vivo assessment. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 303, 112649. [Google Scholar]
- Soni, K.; Mujtaba, A.; Kohli, K. Lipid drug conjugate nanoparticle as a potential nanocarrier for the oral delivery of pemetrexed diacid: Formulation design, characterization, ex vivo, and in vivo assessment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujtaba, M.A.; Alotaibi, N.M. Chitosan-sodium alginate nanoparticle as a promising approach for oral delivery of rosuvastatin calcium: Formulation, optimization and in vitro characterization. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2020, 32, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorasitthiyanukarn, F.N.; Muangnoi, C.; Na Bhuket, P.R.; Rojsitthisak, P.; Rojsitthisak, P. Chitosan/alginate nanoparticles as a promising approach for oral delivery of curcumin diglutaric acid for cancer treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 93, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujtaba, A.; Ali, M.; Kohli, K. Statistical optimization and characterization of pH-independent extended-release drug delivery of cefpodoxime proxetil using Box–Behnken design. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2014, 92, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai, H.; Nguyen, C.T.; Thach, L.T.; Tran, M.T.; Mai, H.D.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Le, G.D.; Van Can, M.; Tran, L.D.; Bach, G.L.; et al. Characterization of chitosan/alginate/lovastatin nanoparticles and investigation of their toxic effects in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, K.L.; Tabrizian, M. Effect of experimental parameters on the formation of alginate–chitosan nanoparticles and evaluation of their potential application as DNA carrier. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2005, 16, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujtaba, A.; Ali, M.; Kohli, K. Formulation of extended release cefpodoxime proxetil chitosan–alginate beads using quality by design approach. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 69, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, Y.; Park, K. Control of encapsulation efficiency and initial burst in polymeric microparticle systems. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2004, 27, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Battu, S.K.; Repka, M.A.; Maddineni, S.; Chittiboyina, A.; Avery, M.; Majumdar, S. Physicochemical Characterization of Berberine Chloride: A Perspective in the Development of a Solution Dosage Form for Oral Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2010, 11, 1466–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khuroo, T.; Verma, D.; Talegaonkar, S.; Padhi, S.; Panda, A.K.; Iqbal, Z. Topotecan–tamoxifen duple PLGA polymeric nanoparticles: Investigation of in vitro, in vivo and cellular uptake potential. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 473, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujtaba, A.; Kohli, K. In vitro/in vivo evaluation of HPMC/alginate based extended-release matrix tablets of cefpodoxime proxetil. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 89, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Werle, M. Natural and Synthetic Polymers as Inhibitors of Drug Efflux Pumps. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vuddanda, P.R.; Chakraborty, S.; Singh, S. Berberine: A potential phytochemical with multispectrum therapeutic activities. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2010, 19, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Pan, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, R.; Zhu, Y.; Pan, W. Developments in Methods for Measuring the Intestinal Absorption of Nanoparticle-Bound Drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Ahmad, I.; Akhter, S.; Jain, G.K.; Iqbal, Z.; Talegaonkar, S.; Ahmad, F.J. Nanocarrier based formulation of Thymoquinone improves oral delivery: Stability assessment, in vitro and in vivo studies. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Wang, N.; Song, H.; Xi, X.; Wang, J.; Hao, A.; Li, T. Preparation of an anhydrous reverse micelle delivery system to enhance oral bioavailability and anti-diabetic efficacy of berberine. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 44, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Ao, M.; Zheng, X.; Li, N.; Xia, J.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Hou, Z.; Qi, Z.; Chen, X.D. PEG–lipid–PLGA hybrid nanoparticles loaded with berberine–phospholipid complex to facilitate the oral delivery efficiency. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Formulation Code | Factors Combinations at Different Levels | Response Variables | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 = Chitosan (% w/v) | X2= Sodium Alginate (% w/v) | X3 = Calcium Chloride (% w/v) | Y1 = Particle Size (nm) | Y2 = Polydispersity Index (%) | Y3 = Zeta Potential (mV) | |
| BNP1 | 0.02 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 248.3 ± 0.02 | 0.541 ± 0.02 | −20.8 ± 2.3 |
| BNP2 | 0.04 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 270 ± 3.3 | 0.414 ± 0.05 | −20.9 ± 2.3 |
| BNP3 | 0.06 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 314 ± 6.5 | 0.621 ± 0.03 | −25.4 ± 2.6 |
| BNP4 | 0.05 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 314.2 ± 9.9 | 0.568 ± 0.01 | −13.6 ± 3.1 |
| BNP5 | 0.08 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 341.2 ± 2.3 | 0.761 ± 0.08 | −30.8 ± 2.3 |
| BNP6 | 0.02 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 278.2 ± 4.6 | 0.496 ± 0.06 | −21.8 ± 2.7 |
| BNP7 | 0.04 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 341.2 ± 5.7 | 0.521 ± 0.05 | −22.8 ± 2.9 |
| BNP8 | 0.02 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 347.5 ± 4.8 | 0.376 ± 0.04 | −27.8 ± 1.6 |
| BNP9 | 0.02 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 246.1 ± 5.3 | 0.295 ± 0.07 | −25.8 ± 1.9 |
| BNP10 | 0.02 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 323.3 ± 6.2 | 0.504 ± 0.03 | −19.8 ± 2.1 |
| BNP11 | 0.02 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 260.4 ± 2.9 | 0.491 ± 0.02 | −18.4 ± 1.6 |
| BNP12 | 0.02 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 361.5 ± 4.2 | 0.594 ± 0.04 | −30.8 ± 1.8 |
| BNP13 | 0.10 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 290.2 ± 8.2 | 0.435 ± 0.03 | −18.6 ± 3.0 |
| BNP14 | 0.04 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 220.52 ± 3.1 | 0.311 ± 0.01 | −15.1 ± 1.6 |
| BNP15 | 0.08 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 218.6 ± 5.1 | 0.672 ± 0.012 | −16.1 ± 1.8 |
| BNP16 | 0.06 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 334.1 ± 2.9 | 0.446 ± 0.06 | −11.9 ± 2.9 |
| BNP17 | 0.02 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 253.8 ± 6.1 | 0.582 ± 0.02 | −12.7 ± 3.5 |
| Optimized BNPs Formulation Composition (X1:X2:X3) | Response Variable | Experimental Value | Predicted Value | Percentage Prediction Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.04:0.5:0.1 | Y1 | 202.2 | 209.5 | −2.272 |
| Y2 | 0.236 | 0.241 | −2.075 | |
| Y3 | −14.8 | −15.1 | −1.987 |
| Formulation | Zero-Order | First Order | Higuchi | Korsmeyer–Peppas | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | k | R2 | k | R2 | k | n | R2 | |
| BNPs | 0.8050 | 3.113 | 0.9232 | 0.0258 | 0.9636 | 17.290 | 0.3907 | 0.9554 |
| BBR suspension | 0.283 | 2.372 | 0.4017 | 0.0535 | 0.5667 | 17.045 | 0.2401 | 0.6767 |
| BNPs Formulation (5 ± 2 °C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Time (Days) | Change in Physical Appearance | Particle Size ± SD nm | Drug Content |
| 0 30 60 90 | No No No No | 202.2 ± 1.60 203.5 ± 1.56 203.9 ± 3.21 205.9 ± 1.95 | 85.54 ± 2.10 84.89 ± 1.46 83.76 ± 1.67 83.23 ± 1.69 |
| BNPs formulation (25 ± 2 °C) | |||
| 0 30 60 90 | No No No No | 202.2 ± 1.60 203.7 ± 2.32 205.6 ± 3.29 206.4 ± 3.11 | 85.54 ± 2.10 84.23 ± 1.26 83.53 ± 1.37 82.98 ± 1.83 |
| Pharmacokinetic Parameters | BBR Suspension | BNPs |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax(ng/mL) | 67.54 ± 3.90 | 230.57 ± 8.30 |
| Tmax(h) | 2.00 ± 0.12 | 6.00 ± 0.02 |
| AUC0ߝ24 (ng·h/mL) | 910.87 ± 28.30 | 3758.14 ± 199.89 |
| Kel (h−1) | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.003 |
| t1/2 (h) | 5.42 ± 0.99 | 9.04 ± 0.17 |
| Bioavailability enhancement (F) | - | 4.13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kohli, K.; Mujtaba, A.; Malik, R.; Amin, S.; Alam, M.S.; Ali, A.; Barkat, M.A.; Ansari, M.J. Development of Natural Polysaccharide–Based Nanoparticles of Berberine to Enhance Oral Bioavailability: Formulation, Optimization, Ex Vivo, and In Vivo Assessment. Polymers 2021, 13, 3833. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213833
Kohli K, Mujtaba A, Malik R, Amin S, Alam MS, Ali A, Barkat MA, Ansari MJ. Development of Natural Polysaccharide–Based Nanoparticles of Berberine to Enhance Oral Bioavailability: Formulation, Optimization, Ex Vivo, and In Vivo Assessment. Polymers. 2021; 13(21):3833. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213833
Chicago/Turabian StyleKohli, Kanchan, Ali Mujtaba, Rozina Malik, Saima Amin, Md Sarfaraz Alam, Abuzer Ali, Md. Abul Barkat, and Mohammad Javed Ansari. 2021. "Development of Natural Polysaccharide–Based Nanoparticles of Berberine to Enhance Oral Bioavailability: Formulation, Optimization, Ex Vivo, and In Vivo Assessment" Polymers 13, no. 21: 3833. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213833
APA StyleKohli, K., Mujtaba, A., Malik, R., Amin, S., Alam, M. S., Ali, A., Barkat, M. A., & Ansari, M. J. (2021). Development of Natural Polysaccharide–Based Nanoparticles of Berberine to Enhance Oral Bioavailability: Formulation, Optimization, Ex Vivo, and In Vivo Assessment. Polymers, 13(21), 3833. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213833