Preparation and Characterization of Ionic Conductive Poly(acrylic Acid)-Based Silicone Hydrogels for Smart Drug Delivery System
Abstract
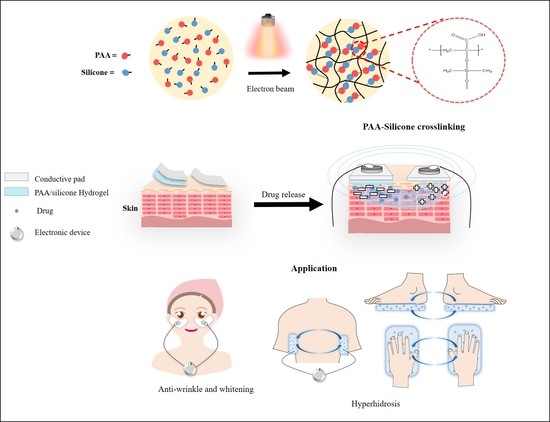
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PAA-Silicone Hydrogel by Electron Beam
2.3. Characterization of the PAA-Silicone Hydrogels
2.4. In Vitro Cell Study
2.5. Drug Release Test
2.6. In Vitro Drug Delivery
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the PAA-Silicone Hydrogels by Electron Beam
3.2. In Vitro Cell Cytocompatibility
3.3. Drug Release Test
3.4. In Vitro Drug Release Using Electrical Device
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- An, Y.H.; Lee, J.; Son, D.U.; Kang, D.H.; Park, M.J.; Cho, K.W.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.H.; Ko, J.; Jang, M.H.; et al. Facilitated Transdermal Drug Delivery Using Nanocarriers-Embedded Electroconductive Hydrogel Coupled with Reverse Electrodialysis-Driven Iontophoresis. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 4523–4535. [Google Scholar]
- Cehn, S.; Matsumoto, H.; Moro-oka, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Miyahara, Y.; Suganami, T.; Matsumoto, A. Smart Microneedle Fabricated with Silk Fibroin Combined Semi-interpenetrating Network Hydrogel for Glucose-Responsive Insulin Delivery. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 5781–5789. [Google Scholar]
- Cerqueira, M.; Millot, S.; Castanheira, M.F.; Félix, A.S.; Silva, T.; Oliveira, G.A.; Oliveira, C.C.; Martins, C.I.M.; Oliveira, R.F. Cognitive appraisal of environmental stimuli induces emotion-like states in fish. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sawy, H.S.; Al-Abd, A.M.; Ahmed, T.A.; El-Say, K.M.; Torchilin, V.P. Stimuli-Responsive Nano-Architecture Drug-Delivery Systems to Solid Tumor Micromilieu: Past, Present, and Future Perspectives. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 10636–10664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senapati, S.; Mahanta, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Maiti, P. Controlled drug delivery vehicles for cancer treatment and their performance. Sig. Transduct. Target Ther. 2018, 3, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiao, Y.; Wan, J.; Zhou, L.; Ma, W.; Yang, Y.; Luo, W.; Yu, Z.; Wang, H. Stimuli-responsive nanotherapeutics for precision drug delivery and cancer therapy. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 11, e1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ganta, S.; Devalapally, H.; Shahiwala, A.; Amiji, M. A review of stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug and gene delivery. J. Control. Release 2008, 126, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Jiang, P.; Li, W.; Guo, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Prausnitz, M.R.; Wang, Z.L. Self-Powered Iontophoretic Transdermal Drug Delivery System Driven and Regulated by Biomechanical Motions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1907378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, P.; Vora, D.; Hemmady, K.; Banga, A.K. Iontophoretic skin delivery systems: Success and failures. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 586, 119584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaid Alkilani, A.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Donnelly, R.F. Transdermal Drug Delivery: Innovative Pharmaceutical Developments Based on Disruption of the Barrier Properties of the stratum corneum. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 438–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cordery, S.F.; Husbands, S.M.; Bailey, C.P.; Guy, R.H.; Delgado-Charro, M.B. Simultaneous Transdermal Delivery of Buprenorphine Hydrochloride and Naltrexone Hydrochloride by Iontophoresis. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 2808–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpiński, T.M. Selected Medicines Used in Iontophoresis. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalia, Y.N.; Naik, A.; Garrison, J.; Guy, R.H. Iontophoretic drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2004, 56, 619–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wang, H.; Hu, J.; Hu, J.J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Y. Smart Hydrogels with Antibacterial Properties Built from All Natural Building Blocks. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 7678–7685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Marchant, R.E. Design properties of hydrogel tissue-engineering scaffolds. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2011, 8, 607–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catoira, M.C.; Fusaro, L.; Francesco, D.D.; Ramella, M.; Boccafoschi, F. Overview of natural hydrogels for regenerative medicine 522 applications. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Med. 2019, 30, 115–523. [Google Scholar]
- Utech, S.; Boccaccini, A.R. A review of hydrogel-based composites for biomedical applications: Enhancement of hydrogel prop-524 erties by addition of rigid inorganic fillers. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 271–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sackett, S.D.; Tremmel, D.M.; Ma, F.; Feeney, A.K.; Maguire, R.M.; Brown, M.E.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; O’Brien, C.; Li, L.; et al. Extracellular matrix scaffold and hydrogel derived from decellularized and delipidized human pancreas. Sci Rep. 2018, 8, 10452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geckil, H.; Xu, F.; Zhang, X.; Moon, S.; Demirci, U. Engineering hydrogels as extracellular matrix mimics. Nanomedicine (UK) 2010, 5, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saldin, L.T.; Cramer, M.C.; Velankar, S.S.; White, L.J.; Badylak, S.F. Extracellular matrix hydrogels from decellularized tissues: Structure and function. Acta Biomater. 2017, 49, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rac, V.; Lević, S.; Balanč, B.; Olalde Graells, B.; Bijelić, G. PVA Cryogel as model hydrogel for iontophoretic transdermal drug delivery investigations. Comparison with PAA/PVA and PAA/PVP interpenetrating networks. Colloid. Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2019, 180, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chansai, P.; Sirivat, A.; Niamlang, S.; Chotpattananont, D.; Viravaidya-Pasuwat, K. Controlled transdermal iontophoresis of sulfosalicylic acid from polypyrrole/poly(acrylic acid) hydrogel. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 381, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.O.; Park, J.S.; Kim, E.J.; Jeong, S.I.; Lee, J.Y.; Lim, Y.M. Preparation of Radiation Cross-Linked Poly(Acrylic Acid) Hydrogel Containing Metronidazole with Enhanced Antibacterial Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nho, Y.C.; Park, J.S.; Lim, Y.M. Preparation of Poly(acrylic acid) Hydrogel by Radiation Crosslinking and Its Application for Mucoadhesives. Polymers 2014, 6, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, P. pH-Sensitive Polyampholyte Microgels of Poly(Acrylic Acid-co-Vinylamine) as Injectable Hydrogel for Controlled Drug Release. Polymers 2019, 11, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khalid, I.; Ahmad, M.; Usman Minhas, M.; Barkat, K.; Sohail, M. Cross-Linked Sodium Alginate-g-poly(Acrylic Acid) Structure: A Potential Hydrogel Network for Controlled Delivery of Loxoprofen Sodium. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Roy, C.K.; Sarkar, S.D.; Roy, H.; Howlader, A.H.; Firoz, S.H. Improvement of the strength of poly(acrylic acid) hydrogels by the incorporation of functionally modified nanocrystalline Cellulose. Mater. Adv. 2020, 1, 2107–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhi, R. Cross-Linked Hydrogel for Pharmaceutical Applications: A Review. Adv Pharm. Bull. 2017, 7, 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehbari, N.; Tavakoli, J.; Khatrao, S.S.; Tang, Y. In situ polymerized hyperbranched polymer reinforced poly(acrylic acid) hydrogels. Mater. Chem. Front. 2017, 1, 1995–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shit, S.C.; Shah, P. A Review on Silicone Rubber. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 2013, 36, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Feng, L.J.; Lei, A.L.; Yan, A.J.; Wang, X.J. Thermal stability and mechanical properties of room temperature vulcanized silicone rubbers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Kang, P.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Yang, J.; Chen, G.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Q. Improved adhesion, heat resistance, anticorrosion properties of epoxy resins/POSS/methyl phenyl silicone coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 135, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Martinez, I.G.; Bachmatiuk, A.; Bezugly, V.; Kunstmann, J.; Gemming, T.; Liu, Z.; Cuniberti, G.; RÜmmeli, M.H. Electron-beam induced synthesis of nanostructures: A review. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 11340–11362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeong, J.O.; Park, J.S.; Kim, Y.A.; Yang, S.J.; Jeong, S.I.; Lee, J.Y.; Lim, Y.M. Gamma Ray-Induced Polymerization and Cross-Linking for Optimization of PPy/PVP Hydrogel as Biomaterial. Polymers 2020, 12, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giri, R.; Sureshkumar, M.S.; Naskar, K.; Bharadwaj, Y.K.; Sarma, K.S.S.; Sabharwal, S.; Nando, G.B. Electron beam irradiation of LLDPE and PDMS rubber blends: Studies on the physicomechanical properties. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2008, 27, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.S.H.; Ashton, M.; Dodou, K. Effect of Crosslinking Agent Concentration on the Properties of Unmedicated Hydrogels. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sienkiewicz, A.; Krasucka, P.; Charmas, B.; Stefaniak, W.; Goworek, J. Swelling effects in cross-linked polymers by thermogravimetry. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 130, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, Y.; Hu, Y. Probing the swelling-dependent mechanical and transport properties of polyacrylamide hydrogels through AFM-based dynamic nanoindentation. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 2619–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Bai, B.; Wang, H.; Suo, Y. Enhanced mechanical stability and sensitive swelling performance of chitosan/yeast hybrid hydrogel beads. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 3350–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullar, J.M.; Carr, A.C.; Vissers, M.C.M. The Roles of Vitamin C in Skin Health. Nutrients 2017, 9, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carr, A.C.; Vissers, M.C.M. Synthetic or Food-Derived Vitamin C—Are They Equally Bioavailable? Nutrients 2013, 5, 4284–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Niaimi, F.; Chiang, N.Y.Z. Topical Vitamin C and the Skin: Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Applications. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2017, 10, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Kaplan, D.L. Biocatalytic Route to Ascorbic Acid-Modified Polymers for Free-Radical Scavenging. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1291–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruppathi, E.; Mani, G. Vitamin-C delivery from CoCr alloy surfaces using polymer-free and polymer-based platforms for cardiovascular stent applications. Langmuir 2014, 30, 6237–6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; He, W.; Peters, E.B.; Ledford, B.T.; Tsihlis, N.D.; Kibbe, M.R. Development of Poly(1,8-octanediol-co-citrate-co-ascorbate) Elastomers with Enhanced Ascorbate Performance for Use as a Graft Coating to Prevent Neointimal Hyperplasia. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 2150–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, S.; Vengurlekar, S.; Rakesh, B.; Jain, S.; Srikarti, G. Transdermal Delivery by Iontophoresis. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 70, 5–10. [Google Scholar]










| PAA (%) | Silicone (%) | Glycerin (%) | Platinum (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si 15 | 82.2 | 15 | 2 | 0.2 |
| Si 20 | 77.8 | 20 | 2 | 0.2 |
| Si 25 | 72.8 | 25 | 2 | 0.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.-A.; Jeong, J.-O.; Park, J.-S. Preparation and Characterization of Ionic Conductive Poly(acrylic Acid)-Based Silicone Hydrogels for Smart Drug Delivery System. Polymers 2021, 13, 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13030406
Kim Y-A, Jeong J-O, Park J-S. Preparation and Characterization of Ionic Conductive Poly(acrylic Acid)-Based Silicone Hydrogels for Smart Drug Delivery System. Polymers. 2021; 13(3):406. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13030406
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Young-Ah, Jin-Oh Jeong, and Jong-Seok Park. 2021. "Preparation and Characterization of Ionic Conductive Poly(acrylic Acid)-Based Silicone Hydrogels for Smart Drug Delivery System" Polymers 13, no. 3: 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13030406
APA StyleKim, Y. -A., Jeong, J. -O., & Park, J. -S. (2021). Preparation and Characterization of Ionic Conductive Poly(acrylic Acid)-Based Silicone Hydrogels for Smart Drug Delivery System. Polymers, 13(3), 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13030406