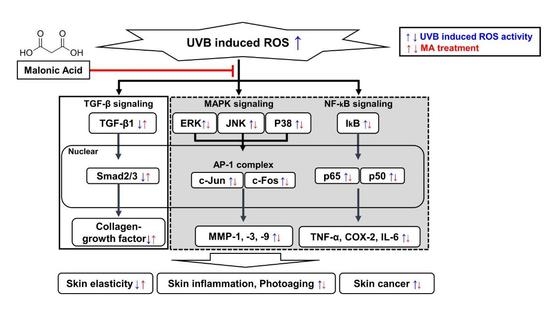
Malonic Acid Isolated from Pinus densiflora Inhibits UVB-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in HaCaT Keratinocytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents
2.2. Plant Materials and Extraction of MA
2.3. Cell Culture and UVB Irradiation
2.4. Cell Viability
2.5. Evaluation of ROS Generation (DCF-DA Assay)
2.6. RNA Isolation, cDNA Synthesis, and Real-time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of MA on Oxidative Stress and Viability in UVB-induced HaCaT Cells
3.2. Effects of MA on UVB-induced Antioxidant Enzyme Expression through Activation of Nrf2 in HaCaT Cells
3.3. Effects of MA on UVB-induced NF-κB Activation and Proinflammatory Factors in HaCaT Cells
3.4. Effects of MA on Phosphorylation during MAPK/AP-1signaling and MMP Expression in UVB-Induced HaCaT Cells
3.5. Effects of MA on the Transforming Growth Factor-β (TGF-β) Signaling Pathway and Collagen Synthesis Factors in UVB-Induced HaCaT Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parrado, C.; Mercado-Saenz, S.; Perez-Davo, A.; Gilaberte, Y.; Gonzalez, S.; Juarranz, A. Environmental stressors on skin aging. Mechanistic insights. Front. Pharm. 2019, 10, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, R.M.; Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Steffen, V.S.; Caviglione, C.V.; Vignoli, J.A.; Barbosa, D.S.; Baracat, M.M.; Georgetti, S.R.; Verri, W.A., Jr.; Casagrande, R. Naringenin inhibits uvb irradiation-induced inflammation and oxidative stress in the skin of hairless mice. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1647–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, R.; Morelli, S.; Tomaino, A.; Pellegrino, M.; Saija, A.; Grumetto, L.; Puglia, C.; Ventura, D.; Bonina, F. Antioxidant and photoprotective activity of a crude extract of culcitium reflexum h.B.K. Leaves and their major flavonoids. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2002, 79, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, K.M.; Clegg, R.M. Observation and quantification of ultraviolet-induced reactive oxygen species in ex vivo human skin. Photochem. Photobiol. 2002, 76, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K. Protective effect of garlic on cellular senescence in uvb-exposed hacat human keratinocytes. Nutrients 2016, 8, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karin, M.; Greten, F.R. Nf-kappab: Linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, S.; Oresajo, C.; Hayward, J. Ultraviolet radiation and skin aging: Roles of reactive oxygen species, inflammation and protease activation, and strategies for prevention of inflammation-induced matrix degradation—A review. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2005, 27, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Park, Y.G.; Lee, H.J.; Lim, S.J.; Nho, C.W. Youngiasides a and c isolated from youngia denticulatum inhibit uvb-induced mmp expression and promote type i procollagen production via repression of mapk/ap-1/nf-kappab and activation of ampk/nrf2 in hacat cells and human dermal fibroblasts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 5428–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Fisher, G.J. Ultraviolet (uv) light irradiation induced signal transduction in skin photoaging. J. Dermatol. Sci. Suppl. 2005, 1, S1–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, T.; Qin, Z.; Xia, W.; Shao, Y.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. Matrix-degrading metalloproteinases in photoaging. J. Investig. Derm. Symp. Proc. 2009, 14, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Lee, C.W.; Kim, E.K.; Lee, S.J.; Park, N.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, H.K.; Char, K.; Jang, Y.P.; Kim, J.W. Inhibition effect of gynura procumbens extract on uv-b-induced matrix-metalloproteinase expression in human dermal fibroblasts. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittayapruek, P.; Meephansan, J.; Prapapan, O.; Komine, M.; Ohtsuki, M. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in photoaging and photocarcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venkatesan, T.; Choi, Y.W.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.K. Pinus densiflora needle supercritical fluid extract suppresses the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators inos, il-6 and il-1beta, and activation of inflammatory stat1 and stat3 signaling proteins in bacterial lipopolysaccharide-challenged murine macrophages. Daru 2017, 25, 18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jung, H.Y.; Shin, J.C.; Park, S.M.; Kim, N.R.; Kwak, W.; Choi, B.H. Pinus densiflora extract protects human skin fibroblasts against uvb-induced photoaging by inhibiting the expression of mmps and increasing type i procollagen expression. Toxicol. Rep. 2014, 1, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Yang, L.; Yang, P.; Jiang, S.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. Polydopamine free radical scavengers. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 4940–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Xu, Z.; Liu, G.; Wu, J. Polyphenols as a versatile component in tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2021, 119, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Gu, Z.; Zhu, F.; Li, Y. Structural and functional tailoring of melanin-like polydopamine radical scavengers. CCS Chem. 2020, 2, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Gu, Z.; Li, Y. Ultrasmall nanoparticle ros scavengers based on polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 38, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, K.; Chiba, T.; Takahashi, S.; Ishii, T.; Igarashi, K.; Katoh, Y.; Oyake, T.; Hayashi, N.; Satoh, K.; Hatayama, I.; et al. An nrf2/small maf heterodimer mediates the induction of phase ii detoxifying enzyme genes through antioxidant response elements. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 236, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, A.; Kawachi, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Koga, T.; Hamada, K.; Otsuka, F. Acceleration of uvb-induced photoageing in nrf2 gene-deficient mice. Exp. Derm. 2011, 20, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, P.M.; Piao, M.J.; Kang, K.A.; Ryu, Y.S.; Hewage, S.R.; Chae, S.W.; Hyun, J.W. Rosmarinic acid attenuates cell damage against uvb radiation-induced oxidative stress via enhancing antioxidant effects in human hacat cells. Biomol. Ther. (Seoul) 2016, 24, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bosch, R.; Philips, N.; Suarez-Perez, J.A.; Juarranz, A.; Devmurari, A.; Chalensouk-Khaosaat, J.; Gonzalez, S. Mechanisms of photoaging and cutaneous photocarcinogenesis, and photoprotective strategies with phytochemicals. Antioxidants 2015, 4, 248–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, B.Y.; Wu, Y.M.; Chang, K.J.; Pan, T.M. Dimerumic acid inhibits sw620 cell invasion by attenuating h(2)o(2)-mediated mmp-7 expression via jnk/c-jun and erk/c-fos activation in an ap-1-dependent manner. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.R.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, M.K.; Kim, I.H.; Choi, Y.H.; Nam, T.J. Pyropia yezoensis peptide promotes collagen synthesis by activating the tgf-beta/smad signaling pathway in the human dermal fibroblast cell line hs27. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quan, T.; He, T.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. Ultraviolet irradiation blocks cellular responses to transforming growth factor-beta by down-regulating its type-ii receptor and inducing smad7. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 26349–26356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quan, T.; He, T.; Kang, S.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. Solar ultraviolet irradiation reduces collagen in photoaged human skin by blocking transforming growth factor-beta type ii receptor/smad signaling. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 165, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massague, J. How cells read tgf-beta signals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 1, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macias, M.J.; Martin-Malpartida, P.; Massague, J. Structural determinants of smad function in tgf-beta signaling. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015, 40, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.Y.; Chung, H.J. Flavor compounds of pine sprout tea and pine needle tea. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1269–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.J.; Lee, K.S.; Ahn, Y.J. Growth-inhibiting effects of constituents of pinus densiflora leaves on human intestinal bacteria. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2001, 10, 403–407. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.S.; Jeon, M.H.; Hwang, H.J.; Park, M.R.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, M. Antioxidant activity and analysis of proanthocyanidins from pine (pinus densiflora) needles. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2011, 5, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, J.L.; Gao, Y. Protective effects of lindera coreana on uvb-induced oxidative stress in human hacat keratinocytes. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Rigo, L.A.; Da Silva, C.R.; De Oliveira, S.M.; Cabreira, T.N.; De Bona da Silva, C.; Ferreira, J.; Beck, R.C. Nanoencapsulation of rice bran oil increases its protective effects against uvb radiation-induced skin injury in mice. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikiaris, N.D.; Michailidou, G.; Lazaridou, M.; Christodoulou, E.; Gounari, E.; Ofrydopoulou, A.; Lambropoulou, D.A.; Vergkizi-Nikolakaki, S.; Lykidou, S.; Nikolaidis, N. Innovative skin product emulsions with enhanced antioxidant, antimicrobial and uv protection properties containing nanoparticles of pure and modified chitosan with encapsulated fresh pomegranate juice. Polymers 2020, 12, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimino, F.; Cristani, M.; Saija, A.; Bonina, F.P.; Virgili, F. Protective effects of a red orange extract on uvb-induced damage in human keratinocytes. Biofactors 2007, 30, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, M.; Bhatti, H.; Nerusu, K.C.; Bhagavathula, N.; Kang, S.; Fisher, G.J.; Varani, J.; Voorhees, J.J. Matrix metalloproteinase-1 is the major collagenolytic enzyme responsible for collagen damage in uv-irradiated human skin. Photochem. Photobiol. 2003, 78, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fisher, G.J.; Quan, T.; Purohit, T.; Shao, Y.; Cho, M.K.; He, T.; Varani, J.; Kang, S.; Voorhees, J.J. Collagen fragmentation promotes oxidative stress and elevates matrix metalloproteinase-1 in fibroblasts in aged human skin. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rittie, L.; Fisher, G.J. Uv-light-induced signal cascades and skin aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2002, 1, 705–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, M.; Baker, A.H.; Newby, A.C. Nuclear factor kappab activity is essential for matrix metalloproteinase-1 and -3 upregulation in rabbit dermal fibroblasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 264, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.J.; Cobb, M.H. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997, 9, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, S.A.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, E.S.; Eun, S.Y.; Kim, G.H.; Park, M.H.; Woo, I.S.; Kim, H.J.; Chang, K.C.; et al. Ppardelta promotes wound healing by up-regulating tgf-beta1-dependent or -independent expression of extracellular matrix proteins. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 1747–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.J.; Yuan, W.; Mori, Y.; Levenson, A.; Trojanowska, M.; Varga, J. Stimulation of type i collagen transcription in human skin fibroblasts by tgf-beta: Involvement of smad 3. J. Investig. Derm. 1999, 112, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, M.S.; Yoo, M.S.; Son, D.J.; Jung, H.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Jung, J.K.; Lee, B.C.; Yun, Y.P.; Pyo, H.B.; Hong, J.T. Increase of collagen synthesis by obovatol through stimulation of the tgf-beta signaling and inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase in uvb-irradiated human fibroblast. J. Derm. Sci. 2007, 46, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, C.; Park, J.; Kim, W.-J.; Kim, W.; Cheong, H.; Kim, S.-J. Malonic Acid Isolated from Pinus densiflora Inhibits UVB-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in HaCaT Keratinocytes. Polymers 2021, 13, 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050816
Park C, Park J, Kim W-J, Kim W, Cheong H, Kim S-J. Malonic Acid Isolated from Pinus densiflora Inhibits UVB-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in HaCaT Keratinocytes. Polymers. 2021; 13(5):816. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050816
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Cheolwoo, Jaeyoung Park, Won-Jin Kim, Woong Kim, Hyeonsook Cheong, and Seok-Jun Kim. 2021. "Malonic Acid Isolated from Pinus densiflora Inhibits UVB-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in HaCaT Keratinocytes" Polymers 13, no. 5: 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050816
APA StylePark, C., Park, J., Kim, W. -J., Kim, W., Cheong, H., & Kim, S. -J. (2021). Malonic Acid Isolated from Pinus densiflora Inhibits UVB-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in HaCaT Keratinocytes. Polymers, 13(5), 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050816