Synthesis and Characterization of Exopolysaccharide Encapsulated PCL/Gelatin Skin Substitute for Full-Thickness Wound Regeneration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
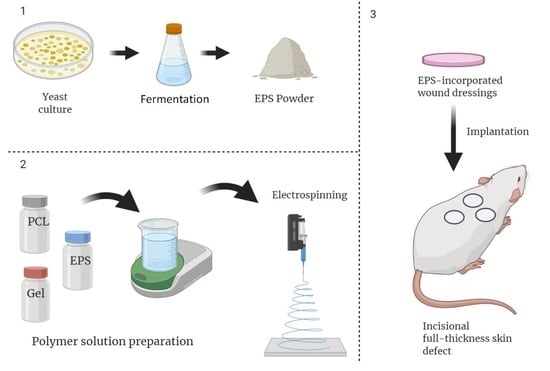
2.2. Production and Isolation of EPS
2.3. Polymer Solution Preparation and Electrospinning
2.4. Characterizations
2.4.1. Morphological Studies
2.4.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy
2.4.3. Dynamic Light Scattering
2.4.4. Thermal Analysis
2.4.5. Tensile Properties
2.4.6. Water Contact Angle Measurement
2.4.7. Cell Viability
2.5. In Vivo Assessments
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. EPS Characterization
3.2. Nanofiber Characterization
3.2.1. Morphological Studies
3.2.2. FTIR Spectroscopy
3.2.3. Tensile Properties
3.2.4. Water Contact Angle
3.2.5. Cell Viability
3.3. In Vivo Assessments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Research Ethical Approval
References
- Clark, R.A.F.; Ghosh, K.; Tonnesen, M.G. Tissue Engineering for Cutaneous Wounds. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 1018–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yousef, H.; Miao, J.H.; Alhajj, M.; Badri, T. Histology, Skin Appendages; StatPearls Internet: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Murphrey, M.B.; Miao, J.H.; Zito, P.M. Histology, Stratum Corneum; StatPearls Internet: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao-Wu, W.; Herndon, D.N.; Spies, M.; Sanford, A.P.; Wolf, S.E. Effects of Delayed Wound Excision and Grafting in Severely Burned Children. Arch. Surg. 2002, 137, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schofield, J.K.; Fleming, D.; Grindlay, D.; Williams, H. Skin Conditions are the Commonest New Reason People Present to General Practitioners in England and Wales. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 165, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cañedo-Dorantes, L.; Cañedo-Ayala, M. Skin Acute Wound Healing: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Inflam. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundar, G.; Joseph, J.; C, P.; John, A.; Abraham, A. Natural Collagen Bioscaffolds for Skin Tissue Engineering Strategies in Burns: A Critical Review. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargozar, S.; Mozafari, M.; Hill, R.G.; Milan, P.B.; Joghataei, M.T.; Hamzehlou, S.; Baino, F. Synergistic Combination of Bioactive Glasses and Polymers for Enhanced Bone Tissue Regeneration. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 15532–15539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Shih, S.; Khachemoune, A. Skin Substitutes for Acute and Chronic Wound Healing: An Updated Review. J. Derm. Treat. 2020, 31, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milan, P.B.; Amini, N.; Joghataei, M.T.; Ebrahimi, L.; Amoupour, M.; Sarveazad, A.; Kargozar, S.; Mozafari, M. Decellularized Human Amniotic Membrane: From Animal Models to Clinical Trials. Methods 2020, 171, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, H.; Shin, Y.M.; Terai, H.; Vacanti, J.P. A Biodegradable Nanofiber Scaffold by Electrospinning and Its Potential for Bone Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 2077–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadi, P.S.; Hivechi, A.; Bahrami, H.; Hemmatinegad, N.; Milan, P.B. Antibacterial and Biological Properties of Coconut Oil Loaded Poly (ε-caprolactone)/Gelatin Electrospun Membranes. J. Ind. Text. 2021, 0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hivechi, A.; Bahrami, S.H.; Siegel, R.A.; Siehr, A.; Sahoo, A.; Milan, P.B.; Joghataei, M.T.; Amoupour, M.; Simorgh, S. Cellulose Nanocrystal Effect on Crystallization Kinetics and Biological Properties of Electrospun Polycaprolactone. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2021, 121, 111855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, Y.K.; Kim, K.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B.; Hadjiargyrou, M. Development of a Nanostructured DNA Delivery Scaffold via Electrospinning of PLGA and PLA–PEG Block Copolymers. J. Control. Release 2003, 89, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorasani, M.T.; Joorabloo, A.; Adeli, H.; Milan, P.B.; Amoupour, M. Enhanced Antimicrobial and Full-thickness Wound Healing Efficiency of Hydrogels Loaded with Heparinized ZnO Nanoparticles: In vitro and in vivo Evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 166, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, A.G.; Chauhan, G. Nanofiber Alignment for Biomedical Applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keirouz, A.; Chung, M.; Kwon, J.; Fortunato, G.; Radacsi, N. 2D and 3D Electrospinning Technologies for the Fabrication of Nanofibrous Scaffolds for Skin Tissue Engineering: A Review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. 2020, 12, e1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmadi, S.; Hivechi, A.; Bahrami, S.H.; Milan, P.B.; Ashraf, S.S. Cinnamon Extract Loaded Electrospun Chitosan/Gelatin Membrane with Antibacterial Activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 173, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Hung, K.-C.; Hsieh, M.-J.; Chang, S.-H.; Juang, J.-H.; Hsieh, I.C.; Wen, M.-S.; Liu, S.-J. Core-shell Insulin-loaded Nanofibrous Scaffolds for Repairing Diabetic Wounds. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2020, 24, 102123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natta, F.J.v.; Hill, J.W.; Carothers, W.H. Studies of Polymerization and Ring Formation. XXIII. 1 ε-Caprolactone and its Polymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1934, 56, 455–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, G.G.; Gratzl, M.M.; Kimmel, G.L.; Surles, J.; Sohindler, A. Aliphatic Polyesters II. The Degradation of Poly (DL-lactide), Poly (ε-caprolactone), and Their Copolymers in vivo. Biomaterials 1981, 2, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdal-hay, A.; Taha, M.; Mousa, H.M.; Bartnikowski, M.; Hassan, M.L.; Dewidar, M.; Ivanovski, S. Engineering of Electrically-conductive Poly(ε-caprolactone)/ Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes Composite Nanofibers for Tissue Engineering Applications. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 15736–15740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janmohammadi, M.; Nourbakhsh, M.J.I.J.o.P.M.; Biomaterials, P. Electrospun Polycaprolactone Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering: A Review. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Po. 2019, 68, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosworth, L.; Downes, S. Biocompatible Three-dimensional Scaffolds for Tendon Tissue Engineering Using Electrospinning. In Cellular Response to Biomaterials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Fu, M.; Li, F.; Fu, W.; Zhao, Z.; Xia, H.; Niu, Y. Tissue-engineered PLLA/Gelatine Nanofibrous Scaffold Promoting the Phenotypic Expression of Epithelial and Smooth Muscle Cells for Urethral Reconstruction. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2020, 111, 110810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, F.R.; Maia, R.C.A.P.; Rannier, L.; Andrade, L.N.; V Chaud, M.; da Silva, C.F.; Corrêa, C.B.; de Albuquerque, R.L.C., Jr.; P da Costa, L.; Shin, S.R. Silver Nanoparticles-composing Alginate/Gelatine Hydrogel Improves Wound Healing in vivo. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenberg, E.; DeLong, E.F.; Lory, S.; Stackebrandt, E.; Thompson, F. The Prokaryotes: Applied Bacteriology and Biotechnology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Donot, F.; Fontana, A.; Baccou, J.C.; Schorr-Galindo, S. Microbial Exopolysaccharides: Main Examples of Synthesis, Excretion, Genetics and Extraction. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, I.W. Novel and Established Applications of Microbial Polysaccharides. Trends Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hivechi, A.; Bahrami, S.H.; Siegel, R.A.; Milan, P.B.; Amoupour, M. In vitro and in vivo Studies of Biaxially Electrospun Poly(caprolactone)/Gelatin Nanofibers, Reinforced with Cellulose Nanocrystals, for Wound Healing Applications. Cellulose 2020, 27, 5179–5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashtchian, M.; Hivechi, A.; Bahrami, S.H.; Milan, P.B.; Simorgh, S. Fabricating Alginate/Poly(caprolactone) Nanofibers with Enhanced Bio-mechanical Properties via Cellulose Nanocrystal Incorporation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 233, 115873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghersad, S.; Hajir Bahrami, S.; Mohammadi, M.R.; Mojtahedi, M.R.M.; Milan, P.B. Development of Biodegradable Electrospun Gelatin/Aloe-vera/Poly(ε-caprolactone) Hybrid Nanofibrous Scaffold for Application as Skin Substitutes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 93, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar-Mohammadi, M.; Rabbani, S.; Bahrami, S.H.; Joghataei, M.T.; Moayer, F. Antibacterial Performance and in vivo Diabetic Wound Healing of Curcumin Loaded Gum Tragacanth/Poly(ε-caprolactone) Electrospun Nanofibers. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 69, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, M.; Gholipour, A.R.; Delattre, C.; Sesdighi, F.; Seveiri, R.M.; Pasdaran, A.; Kheirandish, S.; Pierre, G.; Safarzadeh Kozani, P.; Safarzadeh Kozani, P.; et al. Production, Characterization and Biological Activities of Exopolysaccharides from a New Cold-adapted Yeast: Rhodotorula mucilaginosa sp. GUMS16. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hivechi, A.; Bahrami, S.H.; Siegel, R.A. Drug Release and Biodegradability of Electrospun Cellulose Nanocrystal Reinforced Polycaprolactone. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 94, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hivechi, A.; Bahrami, H.S.; Siegel, R.A. Investigation of Morphological, Mechanical and Biological Properties of Cellulose Nanocrystal Reinforced Electrospun Gelatin Nanofibers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehdizadehkashi, A.; Tahermanesh, K.; Anvari-Yazdi, A.F.; Chaichian, S.; Azarpira, N.; Nobakht, M.; Abed, S.M.; Hashemi, N. Ultrastructural Investigation of Pelvic Peritoneum in Patients with Chronic Pelvic Pain and Subtle Endometriosis in Association with Chromoendoscopy. J. Minim. Invasive. Gynecol. 2017, 24, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Cui, H.; Li, C.; Lin, L. A Novel Polyethylene Oxide/Dendrobium Officinale Nanofiber: Preparation, Characterization and Application in Pork Packaging. Food Packag. 2019, 21, 100329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Patra, P.K.; Warner, S.B.; Bhowmick, S. Role of Fiber Diameter in Adhesion and Proliferation of NIH 3T3 Fibroblast on Electrospun Polycaprolactone Scaffolds. Tissue Eng. 2007, 13, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.; Zhu, D.-H.; Wu, H.; Zong, M.-H.; Jing, Y.-R.; Han, S.-Y. Encapsulation of Cinnamon Essential Oil in Electrospun Nanofibrous Film for Active Food Packaging. Food Control. 2016, 59, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zhu, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, L.; Surendhiran, D.; Cui, H. Antibacterial Activity of PEO Nanofibers Incorporating Polysaccharide from Dandelion and Its Derivative. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.-M.; Yoon, G.H.; Lee, H.C.; Shin, H.S. Chitosan Nanoparticle/PCL Nanofiber Composite for Wound Dressing and Drug Delivery. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. 2015, 26, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheradvar, S.A.; Nourmohammadi, J.; Tabesh, H.; Bagheri, B. Starch Nanoparticle as a Vitamin E-TPGS Carrier Loaded in Silk Fibroin-poly(Vinyl Alcohol)-Aloe Vera Nanofibrous Dressing. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 166, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Zhong, A.; Zhou, M.; Sun, Y.; Guo, L.; Yang, Y. Sustained Release of N-Acetylcysteine by Sandwich Structured Polycaprolactone/Collagen Scaffolds for Wound Healing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 2019, 107, 1414–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.-W.; Yu, Y.-L.; Hsu, F.-Y. Fabrication of Polycaprolactone Tubular Scaffolds with an Orthogonal-bilayer Structure for Smooth Muscle Cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 100, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Liu, L.; Pan, J.; Mei, J.; Li, C.; Zheng, Y.J. Biomimetic Composite Scaffold of Hydroxyapatite/Gelatin-chitosan Core-shell Nanofibers for Bone Tissue Engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2019, 97, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joodaki, H.; Panzer, M.B. Skin Mechanical Properties and Modeling: A Review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H. 2018, 232, 323–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, A.; Lowe, A.; Al-Jumaily, A.M. Mechanical Behaviour of Skin: A Review. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 5, 1000254. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Khor, E.; Wee, A.; Lim, L.Y. Chitosan–alginate PEC Membrane as a Wound Dressing: Assessment of Incisional Wound Healing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 63, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, A.; Ní Annaidh, A.; Bruyère, K. Dynamic Tensile Properties of Human Skin. In Proceedings of the IRCOBI Conference 2012, Dublin, Ireland, 12–14 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zahedi, P.; Karami, Z.; Rezaeian, I.; Jafari, S.H.; Mahdaviani, P.; Abdolghaffari, A.H.; Abdollahi, M. Preparation and Performance Evaluation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride Loaded Wound Dressing Mats Based on Electrospun Nanofibrous Poly (lactic acid)/poly (ϵ-caprolactone) Blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 4174–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganya, S.; Venugopal, J.; Mary, S.A.; Ramakrishna, S.; Lakshmi, B.S.; Dev, V.R.G. Aloe Vera Incorporated Biomimetic Nanofibrous Scaffold: A Regenerative Approach for Skin Tissue Engineering. Iran. Polym. J. 2014, 23, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, M.K.; Tiwari, A.P.; Pant, H.R.; Shrestha, B.K.; Kim, H.J.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. In Situ Generation of Cellulose Nanocrystals in Polycaprolactone Nanofibers: Effects on Crystallinity, Mechanical Strength, Biocompatibility, and Biomimetic Mineralization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2015, 7, 19672–19683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, E.; Salaberria, A.M.; Herrera, R.; Fernandes, S.C.M.; Labidi, J. Self-bonded Composite Films Based on Cellulose Nanofibers and Chitin Nanocrystals as Antifungal Materials. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 144, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Xu, Q.; Li, C.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, D.; Wang, Z. Engineering 3D Aligned Nanofibers for Regulation of Cell Growth Behavior. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1600448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, F.; Alves, V.D.; Reis, M.A.M. Advances in Bacterial Exopolysaccharides: From Production to Biotechnological Applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Carmona, E.; Villaverde, A. Nanostructured Bacterial Materials for Innovative Medicines. Trends Microbiol. 2010, 18, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Kuroyanagi, Y. Development of a Wound Dressing Composed of Hyaluronic Acid Sponge Containing Arginine and Epidermal Growth Factor. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. 2010, 21, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbar Saadat, Y.; Yari Khosroushahi, A.; Pourghassem Gargari, B. A Comprehensive Review of Anticancer, Immunomodulatory and Health Beneficial Effects of the Lactic Acid Bacteria Exopolysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 217, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, B.; Lou, W.; Chen, X.; Hua, J.; Sun, Y.j.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, T. Characterization, Antioxidativity, and Anti-carcinoma Activity of Exopolysaccharide Extract from Rhodotorula Mucilaginosa CICC 33013. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insulkar, P.; Kerkar, S.; Lele, S.S. Purification and Structural-functional Characterization of an Exopolysaccharide from Bacillus licheniformis PASS26 with in-vitro Antitumor and Wound Healing Activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.L.; Zhao, F.; Chen, X.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Song, X.Y.; Sun, C.Y.; Yang, J. Promotion of Wound Healing and Prevention of Frostbite Injury in Rat Skin by Exopolysaccharide from the Arctic Marine Bacterium Polaribacter sp. SM1127. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sahana, T.G.; Rekha, P.D. A Novel Exopolysaccharide from Marine Bacterium Pantoea sp. YU16-S3 Accelerates Cutaneous Wound Healing through Wnt/β-catenin Pathway. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 238, 116191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trabelsi, I.; Slima, S.B.; Chaabane, H.; Riadh, B.S. Purification and Characterization of a Novel Exopolysaccharides Produced by Lactobacillus sp. Ca6. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 74, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, I.; Ktari, N.; Ben Slima, S.; Triki, M.; Bardaa, S.; Mnif, H.; Ben Salah, R. Evaluation of Dermal Wound Healing Activity and in vitro Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities of a New Exopolysaccharide Produced by Lactobacillus sp.Ca6. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Sample | Modulus (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCL/Gel | 135 ± 10 | 6.23 ± 0.20 | 28.2 ± 3.0 |
| PCL/Gel + 1% EPS | 116 ± 12 | 6.01 ± 0.69 | 19.6 ± 5.1 |
| PCL/Gel + 2% EPS | 137 ± 13 | 6.17 ± 0.20 | 14.0 ± 3.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hivechi, A.; Milan, P.B.; Modabberi, K.; Amoupour, M.; Ebrahimzadeh, K.; Gholipour, A.R.; Sedighi, F.; Amini, N.; Bahrami, S.H.; Rezapour, A.; et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Exopolysaccharide Encapsulated PCL/Gelatin Skin Substitute for Full-Thickness Wound Regeneration. Polymers 2021, 13, 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060854
Hivechi A, Milan PB, Modabberi K, Amoupour M, Ebrahimzadeh K, Gholipour AR, Sedighi F, Amini N, Bahrami SH, Rezapour A, et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Exopolysaccharide Encapsulated PCL/Gelatin Skin Substitute for Full-Thickness Wound Regeneration. Polymers. 2021; 13(6):854. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060854
Chicago/Turabian StyleHivechi, Ahmad, Peiman Brouki Milan, Khashayar Modabberi, Moein Amoupour, Kaveh Ebrahimzadeh, Amir Reza Gholipour, Faezeh Sedighi, Naser Amini, S. Hajir Bahrami, Alireza Rezapour, and et al. 2021. "Synthesis and Characterization of Exopolysaccharide Encapsulated PCL/Gelatin Skin Substitute for Full-Thickness Wound Regeneration" Polymers 13, no. 6: 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060854
APA StyleHivechi, A., Milan, P. B., Modabberi, K., Amoupour, M., Ebrahimzadeh, K., Gholipour, A. R., Sedighi, F., Amini, N., Bahrami, S. H., Rezapour, A., Hamidi, M., & Delattre, C. (2021). Synthesis and Characterization of Exopolysaccharide Encapsulated PCL/Gelatin Skin Substitute for Full-Thickness Wound Regeneration. Polymers, 13(6), 854. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060854