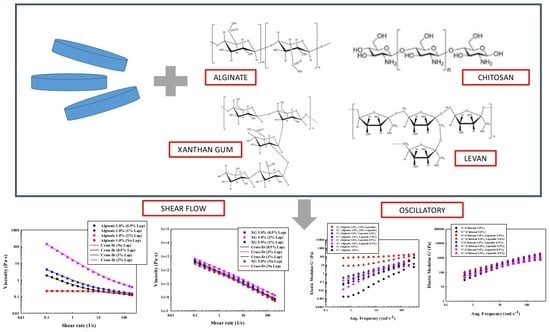
Steady and Oscillatory Shear Flow Behavior of Different Polysaccharides with Laponite®
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Polysaccharides
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Levan Obtention
3.3. Rheological Analysis
3.4. Gel Formation
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Laponite® Effect on Polysaccharides Solutions
4.1.1. Steady Flow Test for Solutions of Polysaccharides
4.1.2. Oscillatory Flow Tests for Solutions of Polysaccharides
4.2. Alginate and Chitosan Gels
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guggenheim, S.; Martin, R.T.; Alietti, A.; Drits, V.A.; Formoso, M.L.L.; Galán, E.; Köster, H.M.; Morgan, D.J.; Paquet, H.; Watanabe, T.; et al. Definition of clay and clay mineral: Joint report of the AIPEA nomenclature and CMS nomenclature committees. Clays Clay Miner. 1995, 4, 255–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretero, M.I.; Pozo, M. Clay and non-clay minerals in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries Part II: Active ingredients. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 47, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawari, S.L.; Koch, D.L.; Cohen, C. Electrical double-layer effects on the Brownian diffusivity and aggregation rate of Laponite clay particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 240, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felbeck, T.; Lezhnina, M.M.; Resch-Genger, U.; Kynast, U.H. Red emissive nanoclay hybrids in transparent aqueous dispersion—Towards optical applications in biophotonics. J. Lumin. 2016, 19, 728–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzicka, B.; Zaccarelli, E. A fresh look at the Laponite phase diagram. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 1268–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapasin, R.; Grassi, M.; Abrami, M.; Sebenik, U. Structural evolution of salt-free aqueous Laponite dispersions: A study based on low-field NMR relaxometry and rheological investigations. Colloids Surf. A 2020, 602, 125126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.W.; Huang, T.K.; Wang, Y.C.; Alamani, B.G.; Lin, J.J. Intercalation strategies in clay/polymer hybrids. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 443–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidou, S.; Papaspyrides, C.D. A review on polymer-layered silicate nanocomposites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 1119–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, H.; Alves, C.S.; Rodrigues, J. Laponite®: A key nanoplatform for biomedical applications, Nanomed: Nanotech. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 2407–2420. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.K.; Choi, Y.B.; Oh, J.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Hwang, S.J.; Choy, J.H. Controlled release of donezepil intercalated in smectite clays. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 359, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Kim, H.M.; Bin Choy, Y.; Hwang, S.J.; Choy, J.H. Itraconazole–Laponite: Kinetics and mechanism of drug release. Appl. Clay Sci. 2008, 40, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.W.; Butterworth, J.T. The nature of laponite and its aqueous dispersions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1992, 151, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaharwar, A.K.; Mihaila, S.M.; Swami, A.; Patel, A.; Sant, S.; Reis, R.L.; Marques, A.P.; Gomes, M.E.; Khademhosseini, A. Bioactive silicate nanoplatelets for osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3329–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, F.; Alves, V.D.; Reis, M.A.M. Advances in bacterial exopolysaccharides: From production to biotechnological applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsen-Nygaard, J.; Strand, S.P.; Varum, K.M.; Draget, K.I.; Nordgard, C.T. Chitosan: Gels and interfacial properties. Polymers 2015, 7, 552–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Guo, R.; Huang, Y.; Wen, S.; Shen, M.; Wang, J.; Shi, X. Laponite nanodisks as an efficient platform for doxorubicin delivery to cancer cells. Langmuir 2013, 29, 5030–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzaga, V.A.M.; Poli, A.L.; Gabriel, J.S.; Tezuka, D.Y.; Valdes, T.A.; Leitao, A.; Rodero, C.F.; Bauab, T.M.; Chorilli, M.; Schmitt, C.C. Chitosan-laponite nanocomposites scaffolds for wound dressing application. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2020, 108, 1388–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacelli, S.; Paolicelli, P.; Dreesen, I.; Kobayashi, S.; Vitalone, A.; Casadei, M.A. Injectable and photocross-linkable gels based on gellan gum methacrylate: A new tool for biomedical application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 72, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dávila, J.L.; D’Ávila, M.A. Laponite as a rheological modifier of alginate solutions: Physical gelation and aging evolution. Carbohyd. Polym. 2017, 57, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapasin, R. Propietá reologiche di dispersioni di laponite in matrice acquose di xantano. Boll. Panta Rei 2016, 14, 7–19. [Google Scholar]
- Lapasin, R.; Abrami, M.; Grassi, M.; Sebenik, U. Rheology of Laponite-scleroglucan hydrogels. Carbohyd. Polym. 2017, 168, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, B.M.; Lessa, V.L.; Silva, B.M.; Carvalho Filho, M.A.S.; Schnitzler, E.; Lacerda, L.G. Xanthan gum: Properties, production conditions, quality and economic perspective. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2015, 54, 185–194. [Google Scholar]
- Petri, D.F.S. Xanthan gum: A versatile biopolymer for biomedical and technological applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 42035–42048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Tan, H. Alginate-based biomaterials for regenerative medicine applications. Materials 2013, 6, 1285–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öner, E.T.; Hernández, L.; Combie, J. Review of Levan polysaccharide: From a century of past experiences to future prospects. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 827–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Garcinuño, A.; Tabernero, A.; Marcelo, G.; Sebastián, V.; Arruebo, M.; Santamaría, J.; Martín del Valle, E.M. Differences in levan nanoparticles depending on their synthesis route: Microbial vs. cell-free systems. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvidson, S.A.; Rinehart, B.D.; Gadala-Maria, F. Concentration regimes of solutions of levan polysaccharide from Bacillus sp. Carbohyd. Polym. 2006, 65, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, M.M. Rheology of non-Newtonian fluids: A new flow equation for pseudoplastic systems. J. Colloid Sci. 1965, 20, 417–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porkodi, P.; Abhilash, J.K.; Shukla, H.K.; Rawat, J. Rheological properties of concentrated polyacrylonitrile co-polymer and lignin blend solution. Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 3937–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabernero, A.; Baldino, L.; Misol, A.; Cardea, S.; Martín del Valle, E.M. Role of rheological properties on physical chitosan aerogels obtained by supercritical drying. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 233, 115850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Chang, G.S. Rheology of concentrated xanthan gum solutions: Steady shear flow behavior. Fibers Polym. 2006, 7, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Solution | Zero-Rate Viscosity (Pa·s) | Consistency (s) | Critical Strain (s−1) | Rate Index | Standard Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate (1.0% w/w) | 0.22 | 3.10 × 10−3 | 333.33 | 0.84 | 14.43 |
| Alginate (3.0% w/w) | 3.42 | 1.20 × 10−2 | 83.33 | 0.86 | 6.59 |
| Alginate (5.0% w/w) | 12.66 | 2.80 × 10−2 | 35.71 | 0.73 | 5.35 |
| Chitosan (1.0% w/w) | 0.29 | 7.80 × 10−3 | 128.20 | 0.25 | 83.36 |
| Chitosan (3.0% w/w) | 20.34 | 0.31 | 3.22 | 0.55 | 7.06 |
| Chitosan (5.0% w/w) | 314.80 | 2.09 | 0.48 | 0.65 | 11.06 |
| Xanthan Gum (1.0% w/w) | 199.60 | 13.69 | 0.07 | 0.96 | 5.30 |
| Xanthan Gum (3.0% w/w) | 399.01 | 14.01 | 0.07 | 0.96 | 8.12 |
| Xanthan Gum (5.0% w/w) | 517.20 | 11.36 | 0.09 | 0.88 | 14.16 |
| Solution | Laponite® Concentration % w/w | Zero-Rate Viscosity (Pa·s) | Consistency (s) | Critical Strain (s−1) | Rate Index | Standard Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate (1.0% w/w) | 0.5 | 4.43 × 103 | 3.11 × 106 | 3.21 × 10−7 | 0.62 | 20.09 |
| 1.0 | 21.39 × 103 | 3.59 × 106 | 2.80 × 10−7 | 0.67 | 16.17 | |
| 2.0 | 1.25 × 106 | 2.00 × 105 | 5.00 × 10−6 | 0.92 | 8.55 | |
| Alginate (3.0% w/w) | 0.5 | 5.39 | 1.60 × 10−2 | 62.50 | 0.82 | 4.69 |
| 1.0 | 5.82 | 2.20 × 10−2 | 45.45 | 0.65 | 8.12 | |
| 2.0 | 11.06 | 0.17 | 5.88 | 0.45 | 25.92 | |
| Alginate (5.0% w/w) | 0.5 | 22.92 | 4.22 × 10−2 | 23.81 | 0.72 | 5.76 |
| 1.0 | 22.82 | 5.21 × 10−2 | 19.23 | 0.69 | 8.29 | |
| 2.0 | 23.62 | 5.96 × 10−2 | 16.77 | 0.68 | 8.08 | |
| Chitosan (1.0% w/w) | 0.5 | 0.30 | 7.30 × 10−3 | 136.98 | 0.39 | 44.12 |
| 1.0 | 0.37 | 9.60 × 10−3 | 104.17 | 0.61 | 28.02 | |
| 2.0 | 0.49 | 1.20 × 10−2 | 83.33 | 0.71 | 22.17 | |
| Chitosan (3.0% w/w) | 0.5 | 69.11 | 0.99 | 1.01 | 0.63 | 3.03 |
| 1.0 | 89.41 | 1.39 | 0.72 | 0.63 | 5.36 | |
| 2.0 | 126.10 | 1.77 | 0.56 | 0.64 | 2.75 | |
| Chitosan (5.0% w/w) | 0.5 | 888.30 | 10.56 | 0.09 | 0.66 | 5.53 |
| 1.0 | 1.38 × 103 | 14.48 | 0.07 | 0.68 | 5.63 | |
| 2.0 | 1.53 × 103 | 9.19 | 0.10 | 0.75 | 8.67 | |
| Xanthan Gum (1.0% w/w) | 0.5 | 298.40 | 14.31 | 0.07 | 0.98 | 4.20 |
| 1.0 | 666.10 | 55.55 | 1.80 × 10−2 | 0.98 | 23.00 | |
| 2.0 | 1.15 × 103 | 62.75 | 1.60 × 10−2 | 0.84 | 8.15 | |
| Xanthan Gum (3.0% w/w) | 0.5 | 1.09 × 103 | 24.18 | 0.04 | 0.93 | 10.20 |
| 1.0 | 1.17 × 103 | 102.60 | 0.01 | 0.85 | 11.80 | |
| 2.0 | 1.16 × 103 | 50.84 | 0.02 | 1.00 | 25.38 | |
| Xanthan Gum (5.0% w/w) | 0.5 | 1.20 × 103 | 27.32 | 0.04 | 0.87 | 7.19 |
| 1.0 | 1.35 × 103 | 24.44 | 0.04 | 0.87 | 19.41 | |
| 2.0 | 1.84 × 103 | 23.62 | 0.04 | 0.85 | 6.78 | |
| Levan (2.0% w/w Laponite®) | 3.0%w/w Levan | 258.90 | 21.88 | 0.05 | 0.89 | 21.95 |
| 5.0%w/w Levan | 509.30 | 13.55 | 0.07 | 0.90 | 8.88 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blanco-López, M.; González-Garcinuño, Á.; Tabernero, A.; Martín del Valle, E.M. Steady and Oscillatory Shear Flow Behavior of Different Polysaccharides with Laponite®. Polymers 2021, 13, 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060966
Blanco-López M, González-Garcinuño Á, Tabernero A, Martín del Valle EM. Steady and Oscillatory Shear Flow Behavior of Different Polysaccharides with Laponite®. Polymers. 2021; 13(6):966. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060966
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlanco-López, Marcos, Álvaro González-Garcinuño, Antonio Tabernero, and Eva M. Martín del Valle. 2021. "Steady and Oscillatory Shear Flow Behavior of Different Polysaccharides with Laponite®" Polymers 13, no. 6: 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060966
APA StyleBlanco-López, M., González-Garcinuño, Á., Tabernero, A., & Martín del Valle, E. M. (2021). Steady and Oscillatory Shear Flow Behavior of Different Polysaccharides with Laponite®. Polymers, 13(6), 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060966