Influence of Salt on the Self-Organization in Solutions of Star-Shaped Poly-2-alkyl-2-oxazoline and Poly-2-alkyl-2-oxazine on Heating
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Polymer Star Synthesis
2.2. Solution Investigation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Behavior of Star-Shaped Six-Arm Pseudo-Polypeptoids in Water-Salt Solutions at Low Temperatures
3.2. Temperature Dependences of Characteristics of Star-Shaped Pseudo-Dendrimers Water-Salt Solutions
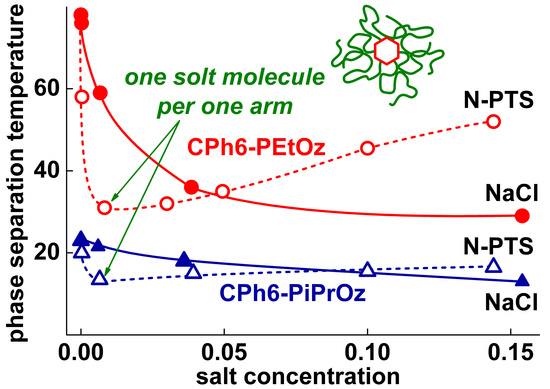
3.3. Influence of Salt Content on Phase Separation Temperatures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zahoranova, A.; Luxenhofer, R. Poly(2-oxazoline)-and poly(2-oxazine)-based self-assemblies, polyplexes, and drug nanoformulations—an update. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2001382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, I.; Trzebicka, B.; Müller, A.H.E.; Dworak, A.; Tsvetanov, C.B. Thermosensitive water-soluble copolymers with doubly responsive reversibly interacting entities. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 1275–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aseyev, V.; Tenhu, H.; Winnik, F. Non-ionic thermoresponsive polymers in water. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2011, 242, 29–89. [Google Scholar]
- Seuring, J.; Agarwal, S. Polymers with upper critical solution temperature in aqueous solution. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2012, 33, 1898–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancoillie, G.; Frank, D.; Hoogenboom, R. Thermoresponsive poly(oligo ethylene glycol acrylates). Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1074–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangloff, N.; Ulbricht, J.; Lorson, T.; Schlaad, H.; Luxenhofer, R. Peptoids and polypeptoids at the frontier of supr- and mcromolecular engineering. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 1753–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, G.; Suwa, S.; Yokoyama, M.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y.; Kataoka, K. Enhanced tumor accumulation and prolong circulation times of micelle-forming poly(ethylene-oxide-aspartate)block copolymer-adriamycin conjugates. J. Control. Release 1994, 29, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.; Maysinger, D.; Eisenberg, A. Nano-engineering block copolymer aggregates for drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B. 1999, 16, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, K.; Harada, A.; Nagasaki, Y. Block copolymer micelles for drug delivery: Design, characterization and biological significance. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 47, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Lu, Z.Z.; Li, X.; Sarker, A.K.; Hu, L.; Choi, P.; Li, X.; Hakobyan, N.; Serpe, M.J. Responsive polymers for analytical applications: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 789, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, A.; Paul, A.; Sen, S.O.; Sen, K.K. Studies on thermoresponsive polymers: Phase behaviour, drug delivery and biomedical applications. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 10, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.; Wang, W.; Li, J. Star polymers: Advances in biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 46, 55–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vdovchenko, A.A.; Hubina, A.V.; Vlakh, E.G.; Tennikova, T.B. Self-assembled polymer particles based on thermoresponsive biodegradable copolymers of amino acids. Mendeleev Commun. 2017, 27, 153–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlacek, O.; Hoogenboom, R. Drug delivery systems based on poly(2-oxazoline)s and poly(2-oxazine)s. Adv. Therap. 2020, 3, 1900168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomalia, D.A.; Sheetz, D.P. Homopolymerization of 2-alkyl- and 2-aryl-2-oxazolines. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1966, 4, 2253–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeliger, W.; Aufderhaar, E.; Diepers, W.; Feinauer, R.; Nehring, R.; Thier, W.; Hellmann, H. Recent syntheses and reactions of cyclic imidic esters. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1966, 5, 875–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagiya, T.; Narisawa, S.; Maeda, T.; Fukui, K. Ring-opening polymerization of 2-substituted 2-oxazolines. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Lett. 1966, 4, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassiri, T.G.; Levy, A.; Litt, M. Polymerization of cyclic imino ethers. I. Oxazolines. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Lett. 1967, 5, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, A.J.; Litt, M.H. Polymerization of cyclic imino ethers. II. Oxazines. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Lett. Ed. 1967, 5, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Igarashi, T.; Moriuchi, Y.; Saegusa, T. Block copolymers from cyclic imino ethers: A new class of nonionic polymer surfactant. Macromolecules 1986, 19, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambermont-Thijs, H.M.L.; Fijten, M.W.M.; van der Linden, A.J.T.; van Lankvelt, B.M.; Bloksma, M.M.; Schubert, U.S.; Hoogenboom, R. Efficient cationic ring-opening polymerization of diverse cyclic imino ethers: Unexpected copolymerization behavior. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 4320–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kempe, K. Chain and step growth polymerizations of cyclic imino ethers: From poly(2-oxazoline)s to poly(ester amide)s. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2017, 218, 1700021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.; Wagner, M.; Baykal, D.; Hoeppener, S.; Paulus, R.M.; Festag, G.; Altuntas, E.; Schacher, F.H.; Schubert, U.S. Easy access to amphiphilic heterografted poly(2-oxazoline) comb copolymers. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 5107–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luxenhofer, R.; Bezen, M.; Jordan, R. Kinetic investigations on the polymerization of 2-oxazolines using pluritriflate initators. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2008, 29, 1509–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogenboom, R.; Schlaad, H. Thermoresponsive poly(2-oxazoline)s, polypeptoids, and polypeptides. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 24–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dworak, A.; Trzebicka, B.; Kowalczuk, A.; Tsvetanov, C.; Rangelov, S. Polyoxazolines–mechanism of synthesis and solution properties. Polymery 2014, 59, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glassner, M.; D’hooge, D.R.; Park, J.; van Steenberge, P.H.; Monnery, B.D.; Reyniers, M.-F.; Hoogenboom, R. Systematic investigation of alkyl sulfonate initiators for the cationic ring-opening polymerization of 2-oxazolines revealing optimal combinations of monomers and initiators. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 65, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glassner, M.; Vergaelen, M.; Hoogenboom, R. Poly(2-oxazoline)s: A comprehensive overview of polymer structures and their physical properties. Polym. Int. 2018, 67, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, Y.; Schlaad, H.; Yuan, J. Cationic poly(ionic liquid) with tunable lower critical solution temperature-type phase transition. ACS Macro Lett. 2013, 2, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacogne, C.D.; Schopferer, M.; Schlaad, H. Physical gelation of α-helical copolypeptides. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 2384–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bogomolova, A.; Secker, C.; Koetz, J.; Schlaad, H. Thermo-induced multistep assembly of double-hydrophilic block copolypeptoids in water. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2017, 295, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleszko-Torbus, N.; Wałach, W.; Utrata-Wesołek, A.; Dworak, A. Control of the crystalline properties of 2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline copolymers in condensed state and in solution depending on the composition. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 7636–7645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grube, M.; Leiske, M.N.; Schubert, U.S.; Nischang, I. POx as an alternative to PEG? A hydrodynamic and light scattering study. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 19051916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukyanenko, N.G.; Pastushok, V.N.; Bordunov, A.V.; Vetrogon, V.I.; Vetrogon, N.I.; Bradshaw, J.S. New phenol-containing bis(azacrown ether)s: Synthesis and complexing properties. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1994, 11, 1489–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simion, C.; Gherase, D.; Sima, S.; Simion, A.M. Serendipitous synthesis of a cyclic formamidine. Application to the synthesis of polyazamacrocycles. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2015, 18, 611–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhimova, E.B.; Ismagilov, R.A.; Ibragimov, A.G. Synthesis and fungicidal activity of bis-1,5,3-dithiazepanes and crown-like macroheterocycles. Russ. J. Gener. Chem. 2019, 89, 1591–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusentzeva, O.I.; Kharitonov, Y.V.; Fadeev, D.S.; Shults, E.E. Synthesis and spectroscopic studies of furan-bridged polyazamacrocycles through 15,16-bis((prop-2-ynylamino)methyl)labdatriene transformations. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2020, 96, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgese, G.; Verbraeken, B.; Ramakrishna, N.R.; Gombert, Y.; Cavalli, E.; Rosenboom, J.G.; Zenobi-Wong, M.; Spencer, N.D.; Hoogenboom, R. Chemical design of non-ionic polymer brushes as biointerfaces: Poly(2-oxazine)s outperform both poly(2-oxazoline)s and PEG. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 11667–11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bloksma, M.M.; Schubert, U.S.; Hoogenboom, R. Poly(cyclic imino ether)s beyond 2-substituted-2-oxazolines. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2011, 32, 1419–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinnwell, S.; Ritter, H. Microwave accelerated polymerization of 2-phenyl-5,6-dihydro-4H-1,3-oxazine: Kinetics and influence of end-groups on glass transition temperature. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2006, 27, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lübtow, M.M.; Hahn, L.; Haider, M.S.; Luxenhofer, R. Drug specificity, synergy and antagonism in ultrahigh capacity poly(2-oxazoline)/poly(2-oxazine) based formulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 10980–10983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloksma, M.M.; Paulus, R.M.; van Kuringen, H.P.; van der Woerdt, F.; Lambermont-Thijs, H.M.; Schubert, U.S.; Hoogenboom, R. Thermoresponsive poly(2-oxazine)s. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2012, 33, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, M.S.; Lübtow, M.M.; Endres, S.; Forster, S.; Flegler, V.J.; Böttcher, B.; Aseyev, V.; Pöppler, A.-C.; Luxenhofer, R. Think beyond the core: Impact of the hydrophilic corona on drug solubilization using polymer micelles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 24531–24543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaad, H.; Diehl, C.; Gress, A.; Meyer, M.; Demirel, A.L.; Nur, Y.; Bertin, A. Poly(2-oxazoline)s as smart bioinspired polymers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, D.; Brooks, W.L.A.; Sumerlin, B.S. New directions in thermoresponsive polymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7214–7243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luef, K.P.; Petit, C.; Ottersbock, B.; Oreski, G.; Ehrenfeld, F.; Grassl, B.; Reynaud, S.; Wiesbrock, F. UV-mediated thiol-ene click reactions for the synthesis of drug-loadable and degradable gels based on copoly(2-oxazoline)s. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 88, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenk, V.; Rossegger, E.; Ebner, C.; Bangerl, F.; Reichmann, K.; Hoffmann, B.; Höpfner, M.; Wiesbrock, F. RGD-functionalization of poly(2-oxazoline)-based networks for enhanced adhesion to cancer cells. Polymers 2014, 6, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kempe, K.; Vollrath, A.; Schaefer, H.W.; Poehlmann, T.G.; Biskup, C.; Hoogenboom, R.; Hornig, S.; Schubert, U.S. Multifunctional poly(2-oxazoline) nanoparticles for biological applications. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 1869–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargaville, T.R.; Forster, R.; Farrugia, B.L.; Kempe, K.; Voorhaar, L.; Schubert, U.S.; Hoogenboom, R. Poly(2-oxazoline) hydrogel monoliths via thiol-ene coupling. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2012, 33, 1695–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zardad, A.-Z.; Essop, C.Y.; Du Toit, L.C.; Kumar, P.; Mabrouk, M.; Kondiah, P.P.D.; Pillay, V. A review of thermo-and ultrasound-responsive polymeric systems for delivery of chemotherapeutic agents. Polymers 2016, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuckling, D.; Wycisk, A. Stimuli-responsive star polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2013, 51, 2980–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Choi, I.; Plamper, F.A.; Synatschke, C.V.; Müller, A.H.E.; Melnichenko, Y.B.; Tsukruk, V.V. Thermo-induced limited aggregation of responsive star polyelectrolytes. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 2112–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczuk, A.; Kronek, J.; Bosowska, K.; Trzebicka, B.; Dworak, A. Star poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)s—synthesis and thermosensitivity. Polym. Int. 2011, 60, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirova, A.; Golub, O.; Kirila, T.; Razina, A.; Tenkovtsev, A.; Filippov, A. Influence of arm length on aqueous solution behavior of thermosensitive poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline) stars. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2017, 295, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirova, A.; Rodchenko, S.; Milenin, S.; Tatarinova, E.; Kurlykin, M.; Tenkovtsev, A.; Filippov, A. Influence of a hydrophobic core on thermoresponsive behavior of dendrimer-based star-shaped poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline) in aqueous solutions. J. Polym. Res. 2017, 24, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirila, T.Y.; Kurlykin, M.P.; Tenkovtsev, A.V.; Filippov, A.P. Behavior of aqueous solutions of thermosensitive starlike polyalkyloxazolines with different arm structures. Polym. Sci. A 2017, 59, 826–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezonenko, T.; Qiu, X.-P.; Winnik, F.M.; Sato, T. Dehydration, micellization, and phase separation of thermosensitive polyoxazoline star block copolymers in aqueous solution. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirila, T.U.; Smirnova, A.V.; Filippov, A.S.; Razina, A.B.; Tenkovtsev, A.V.; Filippov, A.P. Thermosensitive star-shaped poly-2-ethyl-2-oxazine. Synthesis, structure characterization, conformation, and self-organization in aqueous solutions. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 120, 109–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirila, T.; Smirnova, A.; Razina, A.; Tenkovtsev, A.; Filippov, A. Synthesis and conformational characteristics of thermosensitive star-shaped six-arm polypeptoids. Polymers 2020, 12, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smirnova, A.V.; Kirila, T.Y.; Dudkina, M.M.; Tenkovtsev, A.V.; Filippov, A.P. Influence molecular architecture on behavior of thermoresponsive poly-2-ethyl-2-oxazine in saline media. Mendeleev Commun. 2020, 30, 802–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, T.X.; Bentley, M.D.; Harris, J.M.; Fang, Z.; Yoon, K.; Dizman, B.; Weimer, R.; Mero, A.; Pasut, G.; Veronese, F.M. Polyoxazoline: Chemistry, properties, and applications in drug delivery. Bioconjug. Chem. 2011, 22, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Qian, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Xie, C.; Wu, W.; Jiang, X. Supramolecular amphiphilic polymer-based micelles with seven-armed polyoxazoline coating for drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 5768–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhou, S.; Ge, L.; Wu, W.; Jiang, X. Translatable high drug loading drug delivery systems based on biocompatible polymer nanocarriers. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 1732–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, K.; Kanada, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Ding, N.; Kanazaki, K.; Mukai, T.; Ono, M.; Saji, H. Enhanced delivery of radiolabeled polyoxazoline into tumors via self-aggregation under hyperthermic conditions. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 3997–4003. [Google Scholar]
- Aseyev, V.; Tenhu, H.; Winnik, F.M. Self Organized Nanostructures of Amphiphilic Block Copolymers II; Muller, A.H.E., Borisov, O., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 29–89. [Google Scholar]
- Heyda, J.; Dzubiella, J. Thermodynamic description of hofmeister effects on the LCST of thermosensitive polymers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 10979–10988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eeckman, F.; Amighi, K.; Moes, A.J. Effect of some physiological and non-physiological compounds on the phase transition temperature of thermoresponsive polymers intended for oral controlled-drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 222, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cremer, P.S. Chemistry of hofmeister anions and osmolytes. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2010, 61, 63–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amirova, A.I.; Blokhin, A.N.; Razina, A.B.; Tenkovtsev, A.V.; Filippov, A.P. The behavior of thermoresponsive star-shaped poly-2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline in saline media. Mendeleev Commun. 2019, 29, 472–474. [Google Scholar]
- Amirova, A.I.; Kirila, T.U.; Blokhin, A.N.; Razina, A.B.; Bursian, A.E.; Tenkovtsev, A.V.; Filippov, A.P. Influence of hydrophilic and hydrophobic low-molecular-weight compounds on the thermoresponsiveness of star-shaped poly-2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline in solutions. Mendeleev Commun. 2020, 30, 502–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H. Are ionic liquids kosmotropic or chaotropic? An evaluation of available thermodynamic parameters for quantifying the ion kosmotropicity of ionic liquids. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2006, 81, 877–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Olubajo, O.; Song, Z.; Sims, A.L.; Person, T.E.; Lawal, R.A.; Holley, L.D.A. Effect of kosmotropicity of ionic liquids on the enzyme stability in aqueous solutions. Bioorg. Chem. 2006, 34, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, S.Z.; Thormann, E. The Hofmeister series: Specific ion effects in aqueous polymer solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 555, 615–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abezgauz, L.; Kuperkar, K.; Hassan, P.A.; Ramon, O.; Bahadur, P.; Danino, D. Effect of Hofmeister anions on micellization and micellar growth of the surfactant cetylpyridinium chloride. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 342, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossegger, E.; Schenk, V.; Wiesbrock, F. Design strategies for functionalized poly(2-oxazoline)s and derived materials. Polymers 2013, 5, 956–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weber, C.; Hoogenboom, R.; Schubert, U.S. Temperature responsive bio-compatible polymers based on poly(ethylene oxide) and poly(2-oxazoline)s. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 686–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, L.T.T.; Lambermont-Thijs, H.M.L.; Schubert, U.S.; Hoogenboom, R.; Kjøniksen, A.L. Thermoresponsive poly(2-oxazoline) block copolymers exhibiting two cloud points: Complex multistep assembly behavior. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 4337–4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinschulte, A.A.; Schulte, B.; Rütten, S.; Eckert, T.; Okuda, J.; Möller, M.; Schneider, S.; Borisov, O.V.; Plamper, F.A. Effects of architecture on the stability of thermosensitive unimolecular micelles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 4917–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirila, T.; Smirnova, A.; Kurlykin, M.; Tenkovtsev, A.; Filippov, A. Self-organization in aqueous solutions of thermosensitive star-shaped and linear gradient copolymers of 2-ethyl-2-oxazoline and 2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline. Colloid. Polym. Sci. 2020, 298, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirile, T.Y.; Tobolina, A.I.; Elkina, A.A.; Kurlykin, M.P.; Tenkovtsev, A.V.; Filippov, A.P. Self-assembly processes in aqueous solutions of eat-sensitive star-shaped poly-2-ethyl-2-oxazoline. Fiber Chem. 2018, 50, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, A.V.; Kirila, T.U.; Kurlykin, M.P.; Tenkovtsev, A.V.; Filippov, A.P. Behavior of aqueous solutions of polymer star with block copolymer poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) and poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline) arms. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2017, 22, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirova, A.; Rodchenko, S.; Filippov, A. Time dependence of the aggregation of star-shaped poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazolines) in aqueous solutions. J. Polym. Res. 2016, 23, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Clash, C.; Pearce, E.M.; Kwei, T.K.; Aponte, M.A. Solubility and miscibility of poly(ethyl-oxazoline). J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1988, 26, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyama, H.; Kobayashi, S. A novel thermo-sensitive polymer. Poly(2-iso-propyl-2-oxazoline). Chem. Lett. 1992, 21, 1643–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, C.; Akiyama, Y.; Kataoka, K.; Winnik, F.M. Microcalorimetric study of the temperature-induced phase separation in aqueous solutions of poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazolines). Macromolecules 2004, 37, 2556–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloksma, M.M.; Bakker, D.J.; Weber, C.; Hoogenboom, R.; Schubert, U.S. The effect of Hofmeister salts on the LCST transition of poly(2-oxazoline)s with varying hydrophilicity. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroffenegger, M.; Zirbs, R.; Kurzhals, S.; Reimhult, E. The role of chain molecular weight and Hofmeister series ions in thermal aggregation of poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline) grafted nanoparticles. Polymers 2018, 10, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magnusson, J.P.; Khan, A.; Pasparakis, G.; Saeed, A.O.; Wang, W.; Alexander, C. Ion-sensitive “Isothermal” responsive polymers prepared in water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10852–10853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Cremer, P.S. Interactions between macromolecules and ions: The Hofmeister series. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2006, 10, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Furyk, S.; Bergbreiter, D.E.; Cremer, P.S. Specific ion effects on the water solubility of macromolecules: PNIPAM and the Hofmeister series. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 14505–14510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varanaraja, Z.; Kim, J.; Becer, C.R. Poly(2-oxazine)s: A comprehensive overview of the polymer structures, physical properties and applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 147, 110–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.A.; Gayathri, C.; Gil, R.R.; Kowalewski, T.; Matyjaszewski, K. Comparison of the thermoresponsive deswelling kinetics of poly(2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethyl methacrylate) hydrogels prepared by ATRP and FRP. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 4791–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Akiyama, Y.; Winnik, F.M.; Kataoka, K. Versatile synthesis of end-functionalized thermosensitive poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazolines). Macromolecules 2004, 37, 6786–6792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christova, D.; Velichkova, R.; Loos, W.; Goethals, E.J.; Prez, F.D. New thermo-responsive polymer materials based on poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) segments. Polymer 2003, 44, 2255–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Polymer | teq(max), s | |
|---|---|---|
| NaCl | N-PTS | |
| CPh6-PEtOz | 4500 | 3800 |
| CPh6-PiPrOz | 8800 | 8000 |
| CPh6-PEtOx | 3600 | 4200 |
| CPh6-PiPrOx | 7500 | 8500 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kirila, T.; Smirnova, A.; Razina, A.; Tenkovtsev, A.; Filippov, A. Influence of Salt on the Self-Organization in Solutions of Star-Shaped Poly-2-alkyl-2-oxazoline and Poly-2-alkyl-2-oxazine on Heating. Polymers 2021, 13, 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071152
Kirila T, Smirnova A, Razina A, Tenkovtsev A, Filippov A. Influence of Salt on the Self-Organization in Solutions of Star-Shaped Poly-2-alkyl-2-oxazoline and Poly-2-alkyl-2-oxazine on Heating. Polymers. 2021; 13(7):1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071152
Chicago/Turabian StyleKirila, Tatyana, Anna Smirnova, Alla Razina, Andrey Tenkovtsev, and Alexander Filippov. 2021. "Influence of Salt on the Self-Organization in Solutions of Star-Shaped Poly-2-alkyl-2-oxazoline and Poly-2-alkyl-2-oxazine on Heating" Polymers 13, no. 7: 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071152
APA StyleKirila, T., Smirnova, A., Razina, A., Tenkovtsev, A., & Filippov, A. (2021). Influence of Salt on the Self-Organization in Solutions of Star-Shaped Poly-2-alkyl-2-oxazoline and Poly-2-alkyl-2-oxazine on Heating. Polymers, 13(7), 1152. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071152