Sensorized Robotic Skin Based on Piezoresistive Sensor Fiber Composites Produced with Injection Molding of Liquid Silicone
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fiber Sensor Preparation
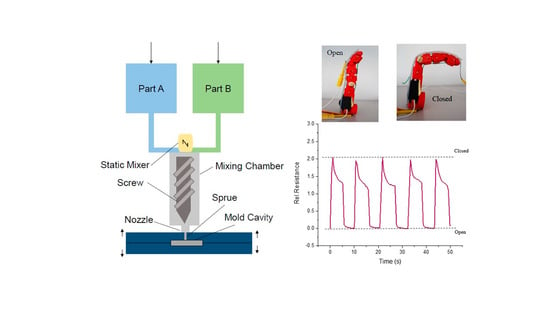
2.2. Sensor Fiber Composite Preparation by Liquid Injection Molding of Silicone Rubber
2.3. Tensile Testing
2.4. Modeling of the Stresses Exerted on the Fiber Inside the Composite
2.5. Robotic Finger with Sensorized Robotic Skin
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Tensile Tests up to Point of Fracture
3.2. Dynamic Tensile Tests
3.3. Modeling of the Stress-Strain Behavior of the Sensor Fiber Embedded in the Matrix
3.4. Effect of Relaxation
3.5. Application: Sensorized Robotic Skin for Robotic Finger
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rezayat, M.; Stafford, R. A Thermoviscoelastic Model for Residual-Stress in Injection Molded Thermoplastics. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1991, 31, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carella, A.R.; Alonso, C.; Merino, J.C.; Pastor, J.M. Sequential Injection Molding of Thermoplastic Polymers. Analysis of Processing Parameters for Optimal Bonding Conditions. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2002, 42, 2172–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachopoulos, J.; Strutt, D. Polymer Processing. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2003, 19, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menges, G.; Barth, P. Automation in Injection-Molding of Elastomers. Kautsch. Gummi Kunstst. 1986, 39, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Birkar, S.; Mead, J.; Barry, C. Injection Molding of Thermoplastic Elastomers for Microstructured Substrates. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2014, 87, 629–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Verma, A. A Brief Review on Injection Moulding Manufacturing Process. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azenha, J.; Gomes, M.; Silva, P.; Pontes, A.J. High Strength Injection Molded Thermoplastic Composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2018, 58, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Sun, L.; Dai, Z.; Xiong, Z.; Huang, B.; Zhang, Y. Experimental Investigation on Mechanical Properties and Failure Mechanisms of Polymer Composite-Metal Hybrid Materials Processed by Direct Injection-Molding Adhesion Method. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 263, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Chaitanya, S. Injection Molding of Natural Fiber Reinforced Composites; Thakur, V.K., Kessler, M.R., Eds.; Crc Press-Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 273–288. ISBN 978-1-4822-5267-5. [Google Scholar]
- Altaf, K.; Qayyum, J.A.; Rani, A.M.A.; Ahmad, F.; Megat-Yusoff, P.S.M.; Baharom, M.; Aziz, A.R.A.; Jahanzaib, M.; German, R.M. Performance Analysis of Enhanced 3D Printed Polymer Molds for Metal Injection Molding Process. Metals 2018, 8, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, H.; Liu, X.Y.; Hong, H. Fabrication of Metal Matrix Composites by Metal Injection Molding—A Review. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 200, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamidi, M.F.F.A.; Harun, W.S.W.; Samykano, M.; Ghani, S.A.C.; Ghazalli, Z.; Ahmad, F.; Sulong, A.B. A Review of Biocompatible Metal Injection Moulding Process Parameters for Biomedical Applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 78, 1263–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medvedovski, E.; Peltsman, M. Low Pressure Injection Moulding Mass Production Technology of Complex Shape Advanced Ceramic Components. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2012, 111, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshalkin, V.P.; Belyakov, A. Methods Used for the Compaction and Molding of Ceramic Matrix Composites Reinforced with Carbon Nanotubes. Processes 2020, 8, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhiwei, J. 7—Injection moulding of polymers. In Advances in Polymer Processing; Thomas, S., Weimin, Y., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2009; pp. 175–203. [Google Scholar]
- Mitschang, P.; Hildebrandt, K. 8—Polymer and composite moulding technologies for automotive applications. In Advanced Materials in Automotive Engineering; Rowe, J., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2012; pp. 210–229. ISBN 978-1-84569-561-3. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Mulvaney-Johnson, L.; Chen, N.; Wang, Q.; Coates, P.D. Small Scale Injection Moulding of Modified Poly(Vinyl Alcohol). Plast. Rubber Compos. 2010, 39, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, M.; Romero, A.; Cordobes, F.; Guerrero, A. Development of Crayfish Bio-Based Plastic Materials Processed by Small-Scale Injection Moulding. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, W.M.; Yan, L.; Xiang, W.; Cheok, B.T. A 3D CAD Knowledge-Based Assisted Injection Mould Design System. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2003, 22, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizon, J.R.C.; Valino, A.D.; Souza, L.R.; Espera, A.H.; Chen, Q.; Advincula, R.C. Three-Dimensional-Printed Molds and Materials for Injection Molding and Rapid Tooling Applications. MRS Commun. 2019, 9, 1267–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biles, W.E.; Gornet, T.J.; Davis, K.; Yi, A. Computer-Aided Design and Rapid Tool Development in Injection Molding Processes. Comput. Ind. Eng. 1995, 29, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.; Hague, R. Impact of Rapid Manufacturing on Design for Manufacture for Injection Moulding. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2003, 217, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, C.-C.; Lin, J.-X. Development of an Injection Mold for Liquid Silicone Rubber Using Rapid Tooling Technology. Smart Sci. 2019, 7, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkt, L. Injection-Molding of Silicone-Rubber. Kunstst. Ger. Plast. 1991, 81, 579–582. [Google Scholar]
- Heiner, J.; Stenberg, B.; Persson, M. Crosslinking of Siloxane Elastomers. Polym. Test 2003, 22, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohmer, K. High temperature addition curable silicone rubbers innovations and new developments. Kautsch. Gummi Kunstst. 2001, 54, 368–371. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, H.; Sahli, M.; Barriere, T.; Gelin, J.C. Multiphysics Modelling and Experimental Investigations of the Filling and Curing Phases of Bi-Injection Moulding of Thermoplastic Polymer/Liquid Silicone Rubbers. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 92, 3871–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Ortiz, J.P.; Osswald, T.A. Modeling Processing of Silicone Rubber: Liquid versus Hard Silicone Rubbers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 119, 1864–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alajoki, T.; Koponen, M.; Juntunen, E.; Petaja, J.; Heikkinen, M.; Ollila, J.; Sitomaniemi, A.; Kosonen, T.; Aikio, J.; Makinen, J.-T. In-mould Integration of Electronics into Mechanics and Reliability of Overmoulded Electronic and Optoelectronic Components. In 2009 European Microelectronics and Packaging Conference (EMPC 2009), Vols 1 and 2; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 1–6. ISBN 978-1-4244-4722-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kololuoma, T.; Keränen, M.; Kurkela, T.; Happonen, T.; Korkalainen, M.; Kehusmaa, M.; Gomes, L.; Branco, A.; Ihme, S.; Pinheiro, C.; et al. Adopting Hybrid Integrated Flexible Electronics in Products: Case—Personal Activity Meter. IEEE J. Electron Devices Soc. 2019, 7, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, H.; Boukallel, M.; Althoefer, K. Tactile Sensing for Dexterous In-Hand Manipulation in Robotics-A Review. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2011, 167, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Zhu, H.; Liu, H.; Liu, N.; Chen, T.; Yang, Z.; Sun, L. The Design and Characterization of a Flexible Tactile Sensing Array for Robot Skin. Sensors 2016, 16, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovač, M. The Bioinspiration Design Paradigm: A Perspective for Soft Robotics. Soft Robot. 2013, 1, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiya, R.S.; Metta, G.; Valle, M.; Sandini, G. Tactile Sensing-From Humans to Humanoids. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2010, 26, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, B.; Shah, D.; Li, J.; Thuruthel, T.G.; Park, Y.-L.; Iida, F.; Bao, Z.; Kramer-Bottiglio, R.; Tolley, M.T. Electronic Skins and Machine Learning for Intelligent Soft Robots. Sci. Robot. 2020, 5, eaaz9239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolozzi, C.; Natale, L.; Nori, F.; Metta, G. Robots with a Sense of Touch. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvera-Tawil, D.; Rye, D.; Velonaki, M. Artificial Skin and Tactile Sensing for Socially Interactive Robots: A Review. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2015, 63, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbay Yildiz, S.; Mutlu, R.; Alici, G. Fabrication and Characterisation of Highly Stretchable Elastomeric Strain Sensors for Prosthetic Hand Applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 247, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerratt, A.P.; Michaud, H.O.; Lacour, S.P. Elastomeric Electronic Skin for Prosthetic Tactile Sensation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 2287–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Man, Q.; Hu, C.; Asghar, W.; Li, F.; Yu, Z.; Shang, J.; Liu, G.; et al. A Skin-Inspired Tactile Sensor for Smart Prosthetics. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgopoulou, A.; Kummerlöwe, C.; Clemens, F. Effect of the Elastomer Matrix on Thermoplastic Elastomer-Based Strain Sensor Fiber Composites. Sensors 2020, 20, 2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Georgopoulou, A.; Michel, S.; Vanderborght, B.; Clemens, F. Piezoresistive Sensor Fiber Composites Based on Silicone Elastomers for the Monitoring of the Position of a Robot Arm. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 112433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgopoulou, A.; Sebastian, T.; Clemens, F.J. Thermoplastic Elastomer Composite Filaments for Strain Sensing Applications Extruded with an FDM 3D Printer. Flex. Print. Electron. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnykowycz, M.; Koll, B.; Scharf, D.; Clemens, F. Comparison of Piezoresistive Monofilament Polymer Sensors. Sensors 2014, 14, 1278–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgopoulou, A.; Vanderborght, B.; Clemens, F. Multi-Material 3D Printing of Thermoplastic Elastomers for Development of Soft Robotic Structures with Integrated Sensor Elements. In Industrializing Additive Manufacturing; Meboldt, M., Klahn, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 67–81. [Google Scholar]
- Kulik, V.M.; Boiko, A.V.; Bardakhanov, S.P.; Park, H.; Chun, H.H.; Lee, I. Viscoelastic Properties of Silicone Rubber with Admixture of SiO2 Nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 5729–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, A.; Wapler, M.C.; Wallrabe, U. A Quick and Accurate Method to Determine the Poisson’s Ratio and the Coefficient of Thermal Expansion of PDMS. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seghir, R.; Arscott, S. Extended PDMS Stiffness Range for Flexible Systems. Sens. Actuator A-Phys. 2015, 230, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holownia, B.P. Effect of Carbon Black on Poisson’s Ratio of Elastomers. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1975, 48, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Asaro, M.E.; Otten, M.S.; Chen, S.; Lang, J.H. Multidimensional Characterization of Piezoresistive Carbon Black Silicone Rubber Composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thingiverse.com Robotic Finger by Tonzo. Available online: https://www.thingiverse.com/thing:686474 (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Georgopoulou, A.; Clemens, F. Piezoresistive Elastomer-Based Composite Strain Sensors and Their Applications. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Thomas, A.G.; Busfield, J.J.C. Stress Relaxation, Creep and Set Recovery of Elastomers. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2015, 68, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Composite | R0 (kΩ) | GF (ε = 20–100%) | GF (ε = 100–150%) | GF (ε = 150–200%) | GF (ε = 200–270%) | GF (ε > 270%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ShA50 25A | 5.6 ± 0.6 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 6 |
| ShA50 40A | 4.6 ± 0.3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| ShA50 60A | 2.7 ± 0.5 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | - |
| ShA70 25A | 6.5 ± 0.3 | 4 | 4 | 11 | 24 | - |
| ShA70 40A | 4.0 ± 0.8 | 5 | 5 | 14 | 24 | - |
| ShA70 60A | 2.7 ± 0.2 | 4 | 3 | - | - | - |
| Composite | Drift at 50% Strain (%) | Drift at 100% Strain (%) | Strain Where Buckling Appears (%) | Strain Where the Uncertainty of the Sensor Signal Appears (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ShA50 25A | 23 | 1 | 17 | 49 |
| ShA50 40A | 11 | 1 | 20 | 47 |
| ShA50 60A | 13 | 5 | 32 | 36 |
| ShA70 25A | 23 | 3 | 27 | 47 |
| ShA70 40A | 14 | 1 | 28 | 21 |
| ShA70 60A | 8 | 5 | 32 | 35 |
| Shore Hardness of the Matrix | 50% Strain | 100% Strain |
|---|---|---|
| 25A | 4% | 3% |
| 40A | 4% | 2% |
| 60A | 13% | 3% |
| Shore Hardness of the Matrix | 50% Strain | 100% Strain |
|---|---|---|
| 25A | 114% | 13% |
| 40A | 9% | 9% |
| 60A | 14% | 8% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Georgopoulou, A.; Michel, S.; Clemens, F. Sensorized Robotic Skin Based on Piezoresistive Sensor Fiber Composites Produced with Injection Molding of Liquid Silicone. Polymers 2021, 13, 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13081226
Georgopoulou A, Michel S, Clemens F. Sensorized Robotic Skin Based on Piezoresistive Sensor Fiber Composites Produced with Injection Molding of Liquid Silicone. Polymers. 2021; 13(8):1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13081226
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeorgopoulou, Antonia, Silvain Michel, and Frank Clemens. 2021. "Sensorized Robotic Skin Based on Piezoresistive Sensor Fiber Composites Produced with Injection Molding of Liquid Silicone" Polymers 13, no. 8: 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13081226
APA StyleGeorgopoulou, A., Michel, S., & Clemens, F. (2021). Sensorized Robotic Skin Based on Piezoresistive Sensor Fiber Composites Produced with Injection Molding of Liquid Silicone. Polymers, 13(8), 1226. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13081226